There are over 500 million speakers across India and various parts of the globe.
So, you have decided to take the plunge and learn how to speak Hindi. For many, the decision of what language to learn often boils down to the practicality of acquiring the linguistic skills. Well, what better reason to learn Hindi than it being one of the most widely spoken languages in the world? On top of that, the language unlocks one of the world’s richest cultures, all while enhancing your prospects for work and travel in the process.
To effectively learn the Hindi alphabet and its pronunciation, it's essential to understand the Devanagari script, which comprises 13 vowels and 33 consonants. Each letter has a distinct sound, and mastering these is crucial for accurate communication in Hindi. This guide provides detailed charts, audio examples, and practical tips to help you pronounce each letter correctly.

Overview of the Hindi Alphabet
Now, the bulk of the Hindi-speaking population resides on the other side of the globe, so let’s touch on some aspects of the language that you’d be forgiven for not already knowing. The Hindi alphabet is written in the Devanagari script. All language learners will rejoice when they hear that it’s a phonetic script, which basically means that it sounds as it is read. So, you shouldn’t run into too much difficulty in trying to grasp how the language sounds when you first start out. You also won’t have to worry as much about pronouncing something entirely wrong, which is definitely a welcome reassurance!
The cool thing is that each letter in Devanagari actually represents a specific sound. This should make the learning process feel a little more logical for you. You may even take to it faster than other languages you’ve tasked yourself with learning in the past. Just like you’ll be used to with English, the script is also written from left to right, only it features a distinctive horizontal line running along the top of each word. So, why is all this important? Well, understanding the script’s structure is actually going to be crucial when it comes to pronunciation. For starters, you’ll be able to rely on it when it comes to getting visual cues on how each syllable should sound. Once you’ve learned to recognize these patterns, reading and speaking Hindi will become significantly easier.
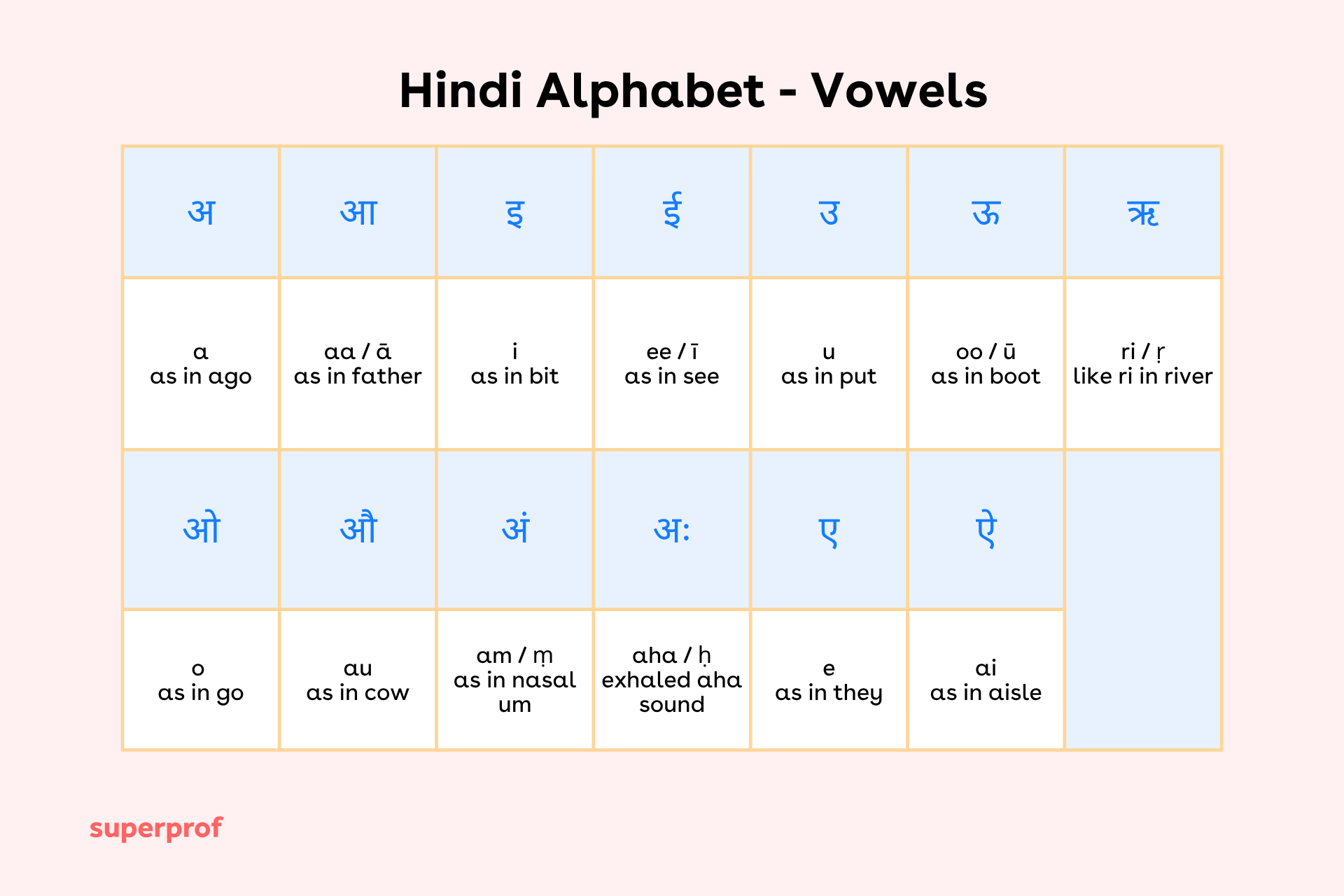
This script consists of 13 vowels (स्वर) and 33 consonants (व्यंजन), making up the building blocks of Hindi words.

Hindi Vowels (स्वर)
For some, the process of learning a language is something we haven't gone through since being an enfant. Most schools offer languages as part of the GCSE and A-level curriculum here in the UK, so hopefully you won't have to remember as far back, but when learning a language, you'll have started with the vowels and made your way from there.
Independent Vowels
| Devanagari | Transliteration | English Approximation |
|---|---|---|
| अ | a | ago |
| आ | aa | father |
| इ | i | bit |
| ई | ee | see |
| उ | u | push |
| ऊ | oo | boot |
| ऋ | ri | rishi (retroflex r) |
| ए | e | they |
| ऐ | ai | aisle |
| ओ | o | go |
| औ | au | house |
| अं | am | sung (nasalized) |
| अः | aha | echoed breath |
Hindi has 13 vowels, which is more than double what we are used to in English. They are known as “independent vowels” when they appear at the beginning of a syllable. They can make quite the difference in a word, so you’ll need to make sure to keep your eyes peeled for any vowels to ensure you nail that pronunciation. Find Hindi lessons London on Superprof.
Dependent Vowels (Matras)
| Independent Vowel | Matra | Example with क (ka) |
|---|---|---|
| आ (aa) | ा | का (kaa) |
| इ (i) | ि | कि (ki) |
| ई (ee) | ी | की (kee) |
| उ (u) | ु | कु (ku) |
| ऊ (oo) | ू | कू (koo) |
| ऋ (ri) | ृ | कृ (kri) |
| ए (e) | े | के (ke) |
| ऐ (ai) | ै | कै (kai) |
| ओ (o) | ो | को (ko) |
| औ (au) | ौ | कौ (kau) |
This next one is a little harder to grasp as it differs from many of the major languages spoken across the UK and Europe. In Hindi, vowels also appear as diacritical marks known as “matras” when they follow consonants.

However, the main thing you’ll want to note is that these marks are attached to the consonant and change its inherent ‘a’ sound to the intended vowel.
While familiarising yourself with matras might pose a slightly more difficult challenge, it’s crucial when it comes to forming accurate syllables and understanding word structure.

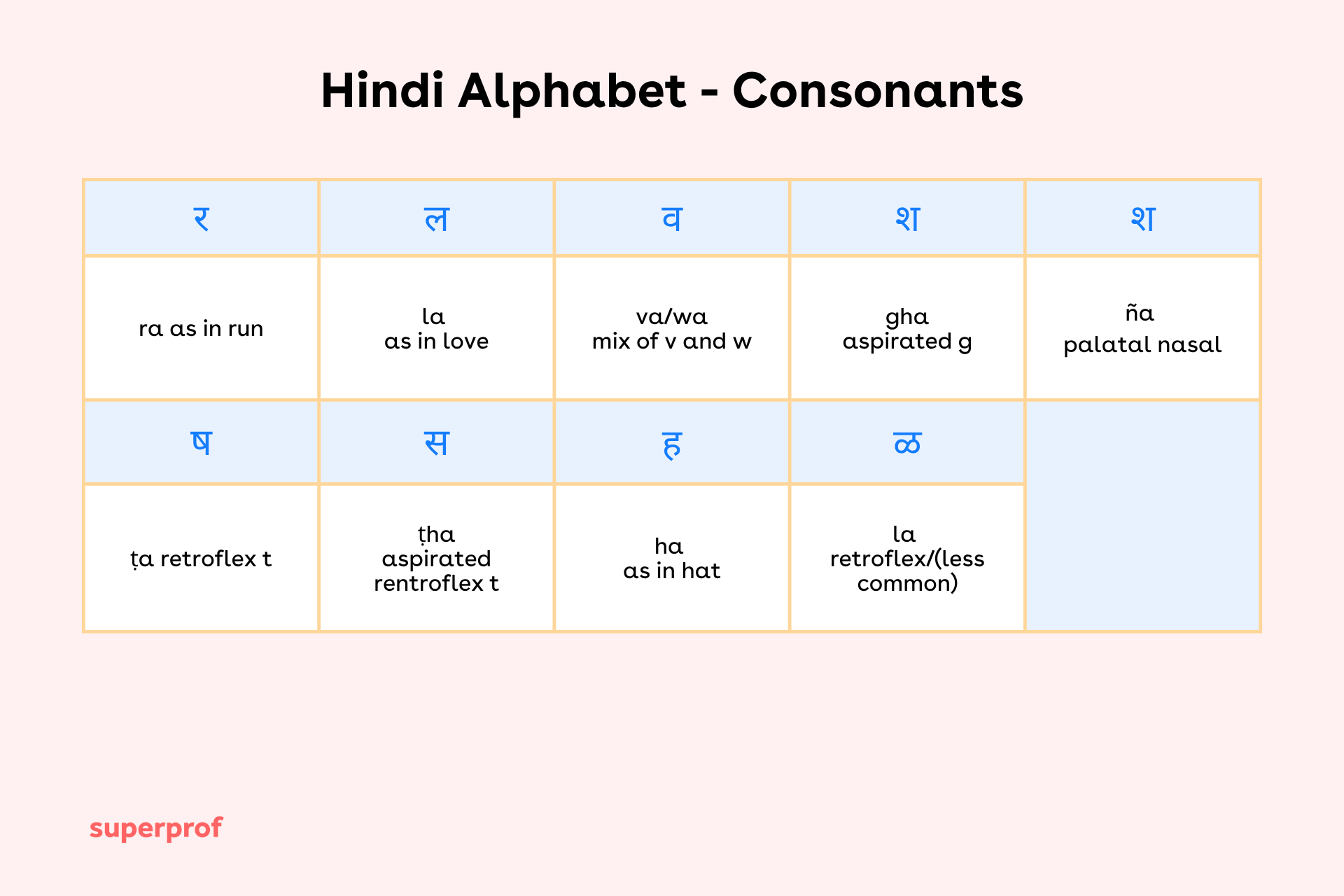
Hindi Consonants (व्यंजन)
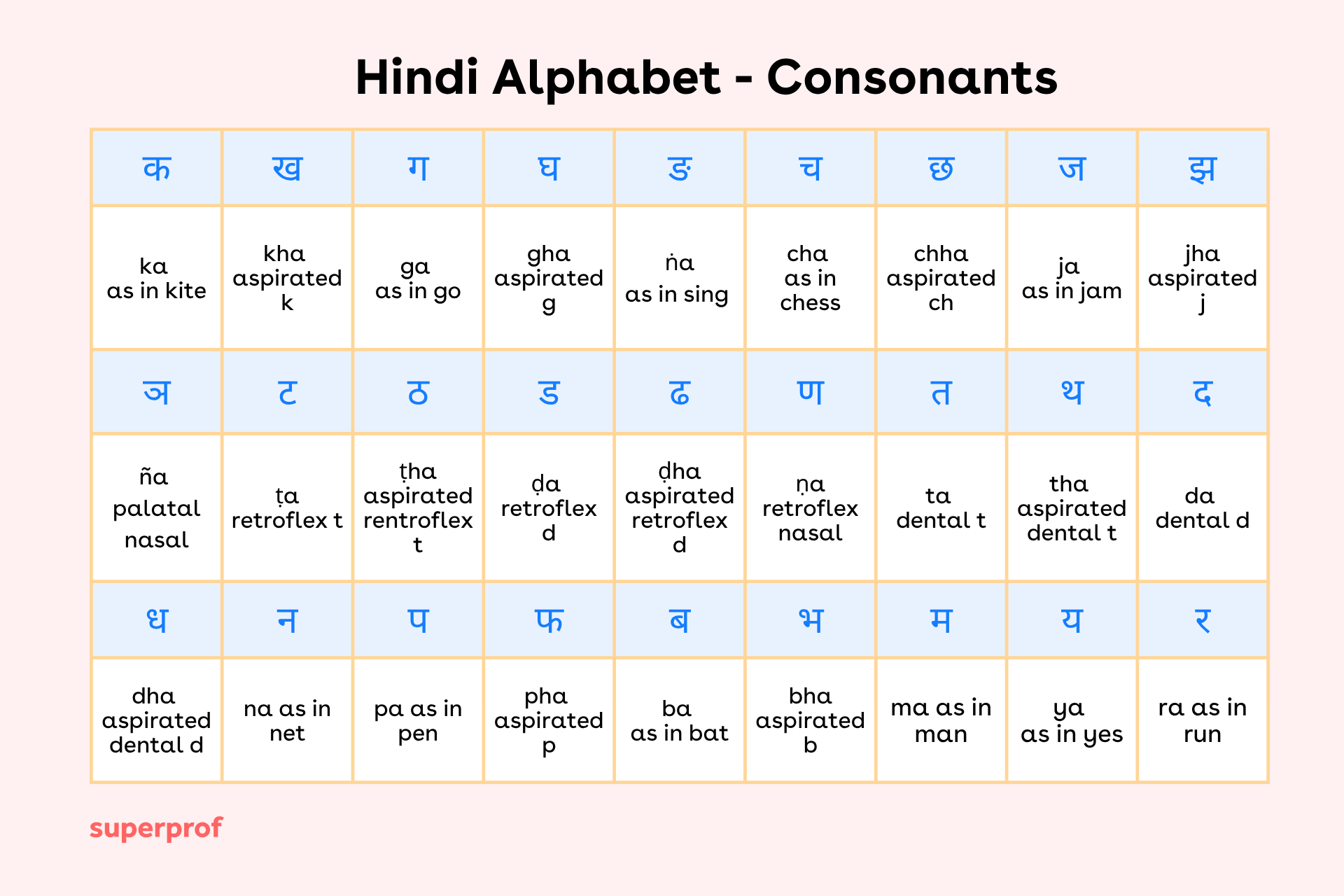
With vowels out of the way, you might have guessed that the next section that we’d be taking a look at for you to master your pronunciation would be Consonants. These 33 characters provide the structural framework of words and syllables in the language. Knowing how they are organised will also make the learning process a hell of a lot easier, seeing as you’ll be much more confident when it comes to pronunciation and spelling. You can even use Bollywood movies to learn Hindi and have fun at the same time!
Classification of Consonants
| Type | Letters | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Velar | क, ख, ग, घ, ङ | Back of the mouth |
| Palatal | च, छ, ज, झ, ञ | Middle of the mouth |
| Retroflex | ट, ठ, ड, ढ, ण | Tongue curled back to the palate |
| Dental | त, थ, द, ध, न | Tongue touches the teeth |
| Labial | प, फ, ब, भ, म | Using the lips |
| Semi-vowel | य, र, ल, व | Partly vowel-like |
| Sibilant | श, ष, स | Hissing sounds |
| Aspirate | ह | Breath-like sound |
What’s interesting about consonants in Hindi is they are grouped based on the area of the mouth involved in producing them. For instance, Velar consonants like ‘क’ and ‘ग’ are pronounced from the back of the mouth, palatal ones like ‘च’ and ‘ज’ come from the middle, while retroflex consonants such as ‘ट’ and ‘ड’ involve curling the tongue back.
Pronunciation Guide
Once you grow familiar with vowels and consonants, you’ll actually come to realise that Hindi consonants maintain a more consistent pronunciation compared to English. One of the major differences that will surface is between aspirated and unaspirated consonants.
For example, ‘क’ (ka) is unaspirated, whereas ‘ख’ (kha) includes more of a breathy puff of air.
Now that you’re aware of the pattern, you’ll come to notice that it applies across many pairs like ‘ग’ and ‘घ’, or ‘ब’ and ‘भ’.
If you’re a native English speaker, then you’re likely going to have a little trouble when it comes to sounds like ‘ट’ and ‘ड’, as they don’t exist in English.

So, just like you had done as a baby, you’ll likely need to sound it out a bunch of times before learning how to make these sounds correctly. This is going to take quite a bit of practice and attention to tongue placement before you know how Hindi is pronounced.
Special Characters and Ligatures
Okay, at this point, you can take a moment to pat yourself on the back, as you’re well on your way to learning all you need to know in order to pronounce Hindi like a native speaker. The next hurdle that stands in your way are the additional symbols that are used to convey sound combinations and nuances. These include conjunct consonants and diacritical marks that affect pronunciation. You’ll notice that by taking the time to learn these characters, you’ll experience a significant boost in your reading fluency.
Conjunct Consonants (संयुक्ताक्षर)
| Conjunct | Components | Pronunciation Example |
|---|---|---|
| क्ष | क् + ष | ksha |
| त्र | त् + र | tra |
| ज्ञ | ज् + ञ | gya |
| श्र | श् + र | shra |
Hindi features conjunct consonants, where two or more consonants combine without an intervening vowel. This is important for you to make a note of, as they often form new ligature symbols that differ in appearance from their base components. Let’s take ‘क्’ and ‘ष’ for example; these consonants actually combine to form ‘क्ष’ (kṣa), and ‘त्’ and ‘र’ also do the same to form ‘त्र’ (tra). These conjuncts are common in written Hindi and, while they definitely pose quite the challenge for those who might still be coming to terms with the nuances of the Hindi language, recognising frequent ones helps speed up reading fluency.
Nasalisation and Other Diacritics
| Symbol | Name | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| ं | Anusvara | Adds nasal tone | मां (maaṃ) |
| ँ | Chandrabindu | Lighter nasalization | हँसी (hansī) |
| ः | Visarga | Echoed breath after vowel | दुःख (duḥkh) |
Okay, now we’ve got the finish line in sight. The final boss of Hindi pronunciation that stands in your way is in Nasalisation and Diacritics. Diacritics like the anusvara (ं), chandrabindu (ँ), and visarga (ः) play vital roles in pronunciation. The anusvara adds a nasal tone to the vowel, as in ‘मां’ (maaṃ), while the chandrabindu creates a lighter nasal sound. The visarga adds a soft breath after the vowel, noticeable in words like ‘दुःख’ (duḥkh). While these symbols may seem small, you wouldn’t believe the impact they can have on the pronunciation and meaning of a sentence, so you’ll need to conquer them in order to conquer the language.
Mastering Hindi Pronunciation
Pronouncing Hindi correctly is key to being understood, and language learners like yourself often face several challenges when transitioning from English. Identifying these challenges and using the right tools can make a world of difference. In order to ensure that you have the right direction for your learning going forward, we’ve decided to leave you with some avenues in which you can progress your pronunciation after you put this article down.
Duolingo
A massive part of what determines if someone is successful with their learning or not is how they incorporate learning into their lifestyle. There are few ways of doing this as effective as taking your learning with you everywhere you go through an application on your phone. Through this app, you’ll be able to bust out some pronunciation practice wherever you find yourself with a few minutes to spare. You’ll have beginner-friendly Hindi courses that include alphabet drills, pronunciation practice, and gamified lessons that keep learners engaged. But of course, you can learn to speak Hindi - but you also need to learn to read and write it.
HindiPod101
Integrating your learning into your everyday life can be as simple as throwing on an educational podcast on in the background as you go about your chores at home. Taking your learning outside of the classroom and listening got a podcast or video from the likes of HindiPod101 can work wonders, as you’ll be able to hear exactly how the language sounds when spoken out loud. It provides structured audio and video lessons that focus on grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation.
Superprof
There is no resource as effective as private tuition when it comes to improving your pronunciation. No matter where you are situated, through Superprof’s online tutoring platform, you’ll be able to pair up with native speakers, whether you wish to learn in person or online.

The instant feedback and personal direction that you’ll receive will allow you to assess and subsequently strengthen any weaknesses you might have when it comes to your pronunciation.
It's the fastest avenue to fluency and perfect pronunciation that a language learner like yourself can take.
Find the best Hindi language course on Superprof!
Improving your Pronunciation of Hindi
Learning the Hindi alphabet might seem daunting at first, but with consistent effort and the right resources, it becomes an enjoyable and rewarding journey. While it might be quite different to any other language you've encountered, it makes the learning experience all the more stimulating and rewarding.
As long as you follow a structure, remain consistent and don't doubt yourself, you should grasp the pronunciation of the language sooner than you might have thought possible. Like any language, confidence comes with repetition and exposure! So, now that you have some clarity on what you need to know, and the resources you can use to get there, you have everything you need to begin taking steps towards fluency!
Summarise with AI:















India has more English speakers than Great Britain and most of them are polyglots and yet India is unable to provide equal education/information regardless the medium of instruction through transcription, transliteration and translation. Most world languages have modified their alphabets and use most modern alphabet in writings. Vedic Sanskrit alphabet have been modified to Devanagari and to simplest Gujanagari(Gujarati) script and yet Hindi is taught in a very printing ink wasting non cursive complex script to millions of children in India. Why not adopt a simple script at national level? Indian states can retain their languages, scripts and culture by teaching highly propagated Hindi/Sanskrit in regional scripts to impart technical education through a script converter or in India’s simplest Gujanagari script along with a Roman script to revive Brahmi script.
अ आ इ ई उ ऊ ऍ ए ऐ ऑ ओ औ अम् अन् अः………..Devanagari
અ આઇઈઉઊઍ એ ઐ ઑ ઓ ઔ અમ્ અન્ અઃ………Gujanagari(Gujarati)
a ā i ī u ū ă e ai ŏ o au am an aḥ……………Roman
a aa i ii u uu ae e ai aw o au an am ah
क ख ग घ च छ ज झ ट ठ ड ढ ण
ક ખ ગ ઘ ચ છ જ ઝ ટ ઠ ડ ઢ ણ
ka kha ga gha ca cha ja jha/za ṭa ṭha ḍa ḍha ṇa
त थ द ध न प फ ब भ म य र ल व
ત થ દ ધ ન પ ફ બ ભ મ ય ર લ વ
ta tha da dha na pa pha/fa ba bha ma ya ra la va
श स ष ह ळ क्ष ज्ञ
શ સ ષ હ ળ ક્ષ જ્ઞ
sha sa ṣa ha ḽa kṣa gya
अं आं इं ईं उं ऊं एं ऐं ओं औं अँ आँ इँ ईँ उँ ऊँ एँ ऐँ ओँ औं
ȧ ā̇ ï ī̇ u̇ ū̇ ė aï ȯ au̇ a̐ ā̐ i̐ ī̐ u̐ ū̐ e̐ ai̐ o̐ au̐……..Roman Diacritics
Yes, that is a problem! Thank you for your input.