The GCSE Maths syllabus for 2026 encompasses a comprehensive range of topics designed to equip students with essential mathematical skills. This guide provides an in-depth look at the syllabus components, recent updates, and effective strategies for excelling in exams.
Key Changes in the 2025/2026 GCSE Maths Syllabus
- 📘 Core syllabus topics remain unchanged
The GCSE maths syllabus continues to follow the national curriculum set by the Department for Education.¹ Students are still assessed across Number, Algebra, Ratio and Proportion, Geometry and Measures, Probability, and Statistics. - 🧠 Greater emphasis on problem-solving and reasoning
Exams continue to focus heavily on applying mathematical knowledge to unfamiliar and real-world situations, rather than simply recalling methods or formulas. - 📄 Formula sheets remain available (2025–2027 exams)
Students will receive formula sheets during exams, meaning success depends more on understanding how and when to apply formulas rather than memorising them. - 🧮 Continued use of calculator and non-calculator papers
The GCSE maths exam structure still includes one non-calculator paper and two calculator papers, testing both procedural fluency and analytical thinking. - 📊 Assessment continues to reward method and working out
Marks are awarded for logical mathematical processes and reasoning, meaning students can gain credit even if their final answer is incorrect. - 🎓 Stronger focus on real-world mathematical application
Topics such as compound measures, growth and decay, and statistical interpretation continue to reflect practical problem-solving skills used in further education and employment.

Key Changes in the 2025/2026 GCSE Maths Syllabus
AQA is one of the principal exam boards for GCSE Maths in Britain and is taken by thousands of students across the United Kingdom.
The GCSE Maths course is designed to help fourteen- to sixteen-year-olds (though older students can take the course as well) pass the national GCSE exam using the most up-to-date curriculum. This article walks you through the key components of the 2025/2026 GCSE Maths syllabus, highlighting clarifications and assessment updates rather than major curriculum changes. After you put this article down, you’ll find yourself with a sense of direction on how to get the grade you deserve in the subject!
Since the GCSE curriculum and exam structure are always evolving, so too should your approach to learning. The GCSE Maths syllabus for 2025/2026 continues to follow the national subject content set by the Department for Education, with assessment adjustments and formula sheet provisions remaining in place.³ One notable change is the emphasis on problem-solving and thinking skills. Students will continue to face questions that require the application of knowledge in real-world scenarios, alongside structured procedural skills. Importantly, formula sheets remain available for examinations through the 2025–2027 assessment period.² You can expect more questions to provide you with real-life scenarios that encourage you to take the material you have covered in the maths class over the years and apply it practically.

While the core subject content remains consistent across exam boards, students should ensure they are confident across all assessed topics, as emphasis may vary between Foundation and Higher-tier papers.⁴
- Find the equation of a line through two points or through one point with a given gradient
- Recognise and use sequences of triangular, square and cube numbers, Fibonacci-type sequences, quadratic sequences and geometric sequences
- Calculate compound measures, including pressure in numerical and algebraic contexts
- Express a multiplicative relationship between two quantities as a ratio or a fraction.
- Write a ratio as a linear function
- Set up, solve and interpret growth and decay problems
- Use inequality notation to specify simple error intervals due to truncation or rounding.
- Understand the≠ s symbol
- Use the standard convention for labelling sides and angles of polygons.
- Derive the sum of angles in a triangle
- Work with percentages greater than 100%
- Know the exact values of sin and cos for θ = 0°, 30°, 45°, 60° and 90°; know the exact value of tan for θ = 0°, 30°, 45° and 60°.
- Consider outliers when calculating the range of distribution.
- Know that correlation does not imply causation.
- Use Venn diagrams.
Being prepared to answer these questions will help you to achieve your potential in the subject, no matter what level you decide to sit. Each student must either take the higher or the foundation tier. They differ in content and grading. For the higher-tier paper, your grade will be in the range of 4 to 9. Algebraic fractions and surds continue to be assessed, particularly at Higher tier, requiring students to simplify and manipulate expressions accurately.
Students will be required to demonstrate understanding of these topics, particularly in simplifying and manipulating fractions effectively. The syllabus includes geometry topics such as proving properties of shapes and solving problems related to circle theorems, which remain key Higher-tier areas. By preparing some of the more commonly asked questions on this topic, you can give yourself an advantage over other students sitting the GCSE exam across the UK.
The number of students expected to sit the GCSE maths exam in 2025.
The GCSE Maths course is designed to equip students with skills valued in further education, employment, and everyday life, with a continued emphasis on reasoning and problem-solving.⁸ The GCSE Maths assessment framework continues to emphasise reasoning, interpretation, and the effective use of calculators where permitted under exam conditions.
These amendments will help students realise the practical application of maths and better prepare them for modern university courses and an evolving workplace. You may also wish to speak to an online maths tutor who can offer you instructional advice on what they think is right for you in relation to how you learn and what they deem is a realistic outcome for you. Here is a quick reminder of the grades you can achieve from one tier to the next.
| Foundation | Higher |
|---|---|
| Grades 1-5 | Grades 3-9 |
Check for Maths tutor York here on Superprof.
Detailed Breakdown of the GCSE Maths Syllabus
Now that you have a sense of what to expect in the 2025/2026 GCSE maths syllabus, let's take a closer look at the topics that you will cover as you navigate the course throughout your years of schooling. The GCSE Maths exam focuses on the practical side of mathematics. It tests a candidate's ability to apply core mathematical concepts to solve everyday problems.
Number
The Number topic in the GCSE Maths Syllabus covers a wide range of essential concepts and skills that form the foundation of mathematical understanding. This means it is likely to appear in some way in your exam, whether it’s specifically asked for or not. Let's explore the key areas within this section so that you can begin jumping up a few grades in the subject:
Structure and Calculation
You'll explore maths functions like adding, subtracting, multiplying and dividing using them with numbers, decimals and fractions (both proper and improper, including mixed numbers). One key learning that emerges throughout this topic is how different processes relate to one another, such as inverse operations, which make calculations and expressions much easier.
A private maths educator can be the answer to reaching your potential in your GCSEs and further education.

Fractions, Decimals and Percentages
Fractions ➗
A fraction represents a part of a whole
Example:
3/4 means three out of four equal parts.
Decimals ️⃣
A decimal is another way to represent fractions and parts of a whole.
Example:
0.75 is the decimal equivalent of 3/4.
Percentages %
A percentage is a fraction of 100. It is used to describe proportions and compare quantities.
Example:
75% means 75 out of 100, and it is equivalent to 75/100 or 0.75
This subsection focuses on the interrelationships among fractions, decimals, and percentages, which represent different ways of expressing proportions. You could be asked a question that appears to examine an entirely different topic, but being able to manipulate your answer into the required form is generally where students can move from achieving a high partial to full credit. Now, you should be beginning to see the importance of having a strong grasp of this section of the syllabus.
Measures and Accuracy
In this section, you'll learn about the units of measurement for weight, distance, time, currency, and other metrics, as well as combined measurements. This section is important not only if your goal is to maximise your grade in the GCSE exams, but also if you are relied upon throughout the A-level maths course and even at university!
This is because these measurements are frequently used when dealing with the rate of change under the topic of Calculus, so make sure to pay extra close attention to this topic when you cover it in your maths class. Regardless of where you are in the UK, a search for a Maths tutor in Manchester on the Superprof homepage will help you grasp these concepts.
Algebra
While Algebra is often a topic that is entirely new to students studying GCSE maths, there is certainly no getting around it, given how often it appears throughout the exam papers each year. Once you get your head around the mix of numbers and letters, it’s not all that bad!
You will learn to use and interpret algebraic notation, including understanding the meaning behind expressions like ab (representing a × b), 3y (representing y + y + y or 3 × y), and a^2 (representing a × a).
If algebra is something that you struggle with, then the above video provides great instructions on how to tackle basic algebraic equations. Throughout your classes at school, you will become familiar with coefficients written as fractions rather than decimals and the proper use of brackets.
You'll also learn to expand products of two or more binomials and factorise quadratic expressions of the form x^2 + bx + c, including the difference of two squares and expressions of the form ax^2 + bx + c. Setting up and solving simple equations, such as two simultaneous equations to find an unknown variable, is also a crucial skill to learn.
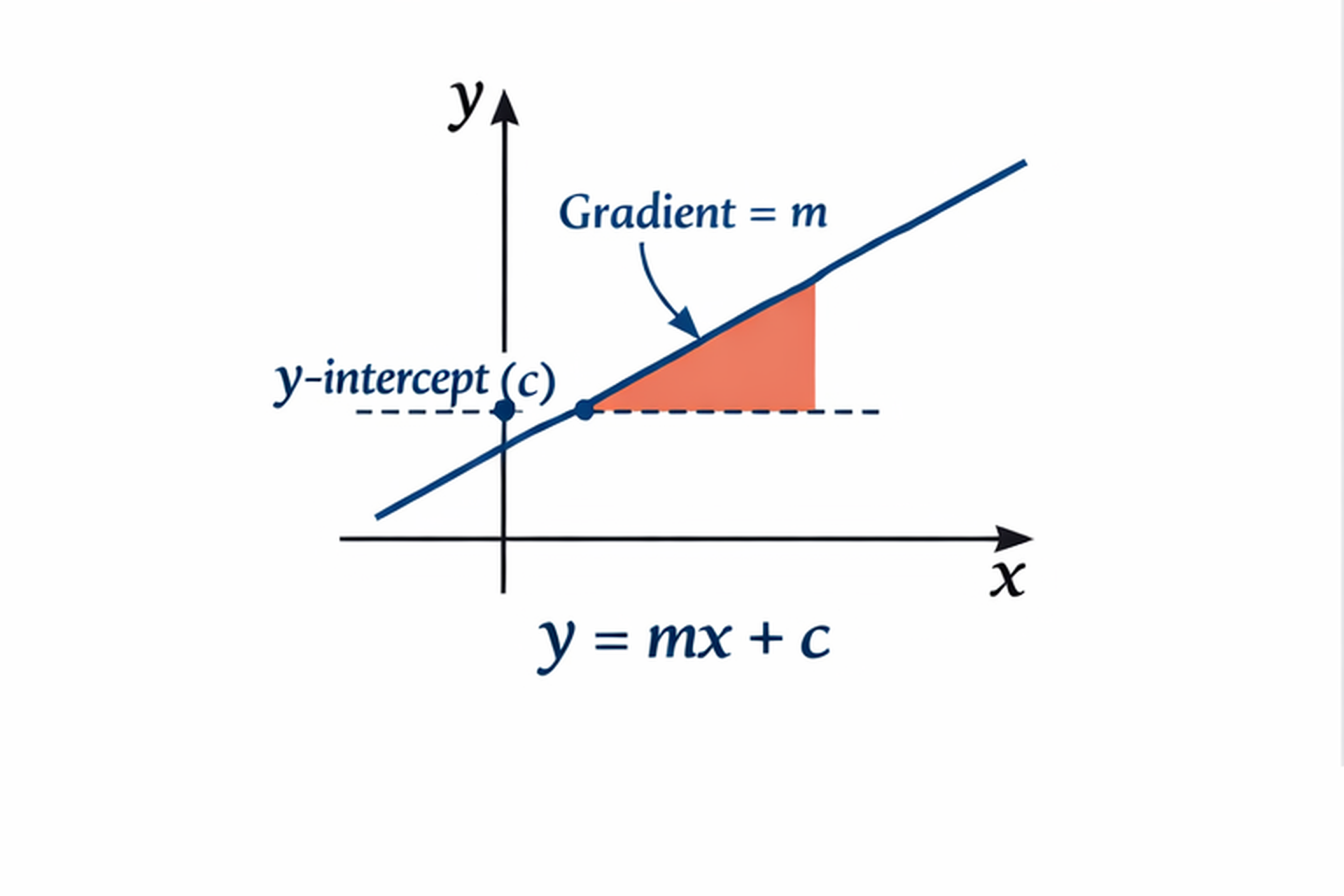
Once you have this nailed down, you will want to start familiarising yourself with plotting graphs of equations and identifying parallel and perpendicular lines using the equation y = mx + c.
Ratio, Proportion and Rates of Change
Ratio ⚖️
A comparison of two quantities by division
Example: The ratio of 2 to 3 can be written as 2:3
Proportion 🔢
An equation stating that two ratios are equal
Example: If 4/8 = 1/2, then 4:8 is proportional to 1:2
Rates of Change ⏱️
The speed at which a variable changes over a specific period of time.
Example: Velocity is the rate of change of position with respect to time
In the section of GCSE Maths Syllabus that covers Ratio, Proportion and Rates of Change, you'll delve into a range of concepts and methods related to connections and changes in speed. As we were saying earlier, you’ll see how measurements from the number topic also feature in this section of the syllabus. If you ask any maths teacher, they will likely tell you how this topic is a step up from some of the other examinable material across the course.
This doesn’t mean that you are at a disadvantage; in fact, the GCSE marking schemes often award more marks to students who make logical attempts to answer the exam questions. So make sure to include rough work and try to break down the questions into manageable steps! You can expect to work with combined units such as speed, wage rates, and unit pricing, while also comparing lengths, areas, and volumes using ratio notation and scale factors. Don’t worry; once you start working through the topic, it will make much more sense.
Geometry and Measures
Most GCSE students tend to take to the geometry portion of the syllabus more easily because it is easier to visualise. The topics also make for more engaging questions, since the exam questions include interesting practical applications. In the Geometry and Measurement section of the GCSE Math Syllabus, students will explore a variety of topics concerning shapes, sizes, and spatial properties. Key topics covered in this section encompass understanding the characteristics of shapes, calculating area, volume, and surface area, and honing skills in precise measurement and unit conversion.
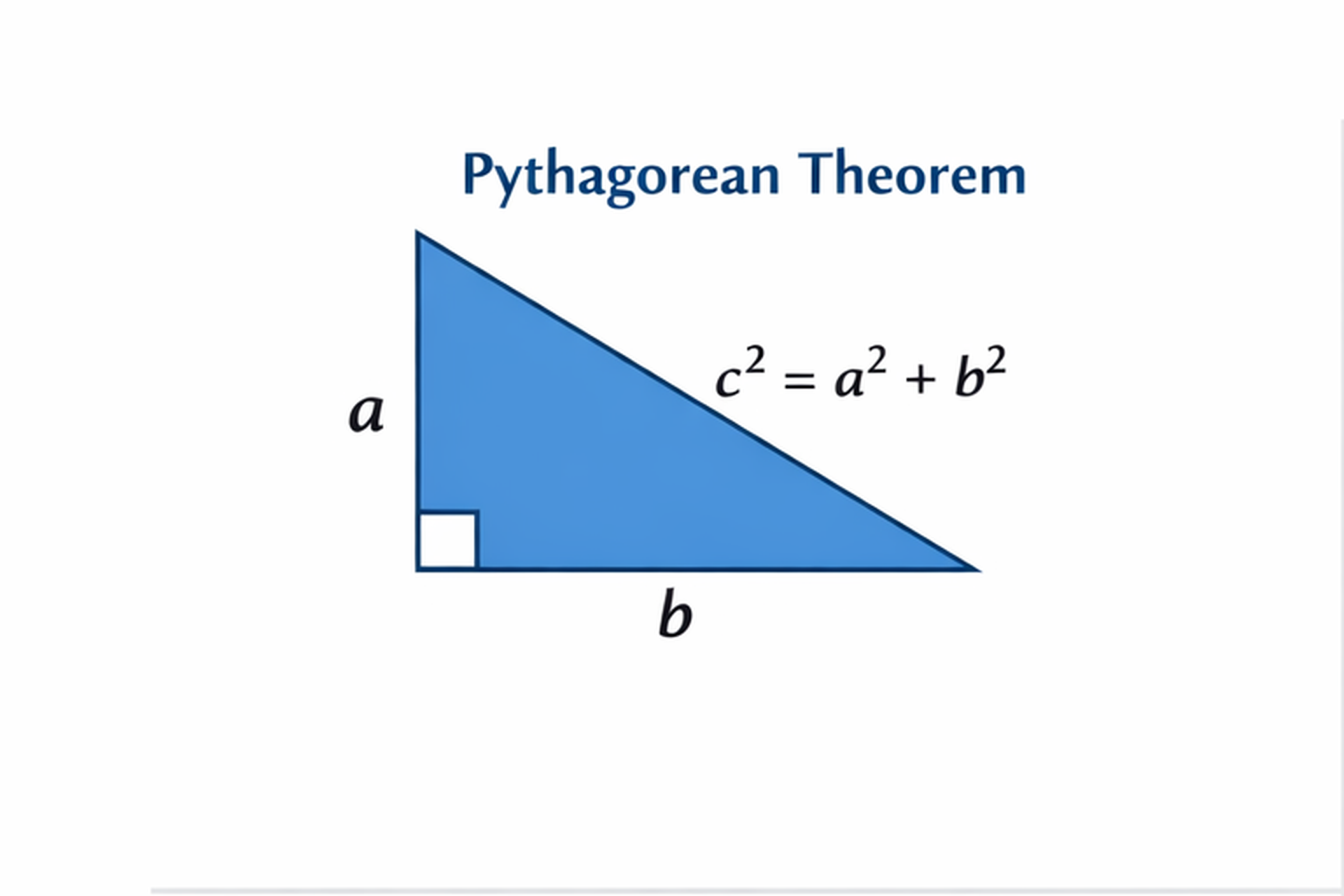
The famous Pythagorean theorem, both in 2-D and 3-D, is included as well. Planes, diagonals of a cuboid, trigonometric ratios of sine, cosine, and theta to find the angles between lines and a plane, angles of elevation, angles of depression and solving 2D and 3D problems are all very important parts of geometry. One of the more challenging problems you might want to brush up on is finding the perpendicular distance from a point to a line, and applying knowledge of angles at a point on a line and of vertically opposite angles.
Probability
Probability is another favourite topic among students and teachers alike, as it offers some interesting real-world applications to help visualise and solve problems. If you flick through your school textbook, you’ll likely find a range of questions asking you to analyse the value of popular casino games or a series of coin tosses.
Learning the vocabulary of probability sets the basis for other key concepts in the subject. Students should learn to distinguish between unlikely, equally likely, even chance and impossible events and should be able to mark probabilities as well as events on a probability scale of either 0 or 1.
The key skills to learn probability is:
- Using estimates, measures of probability, relative frequency, theoretical models
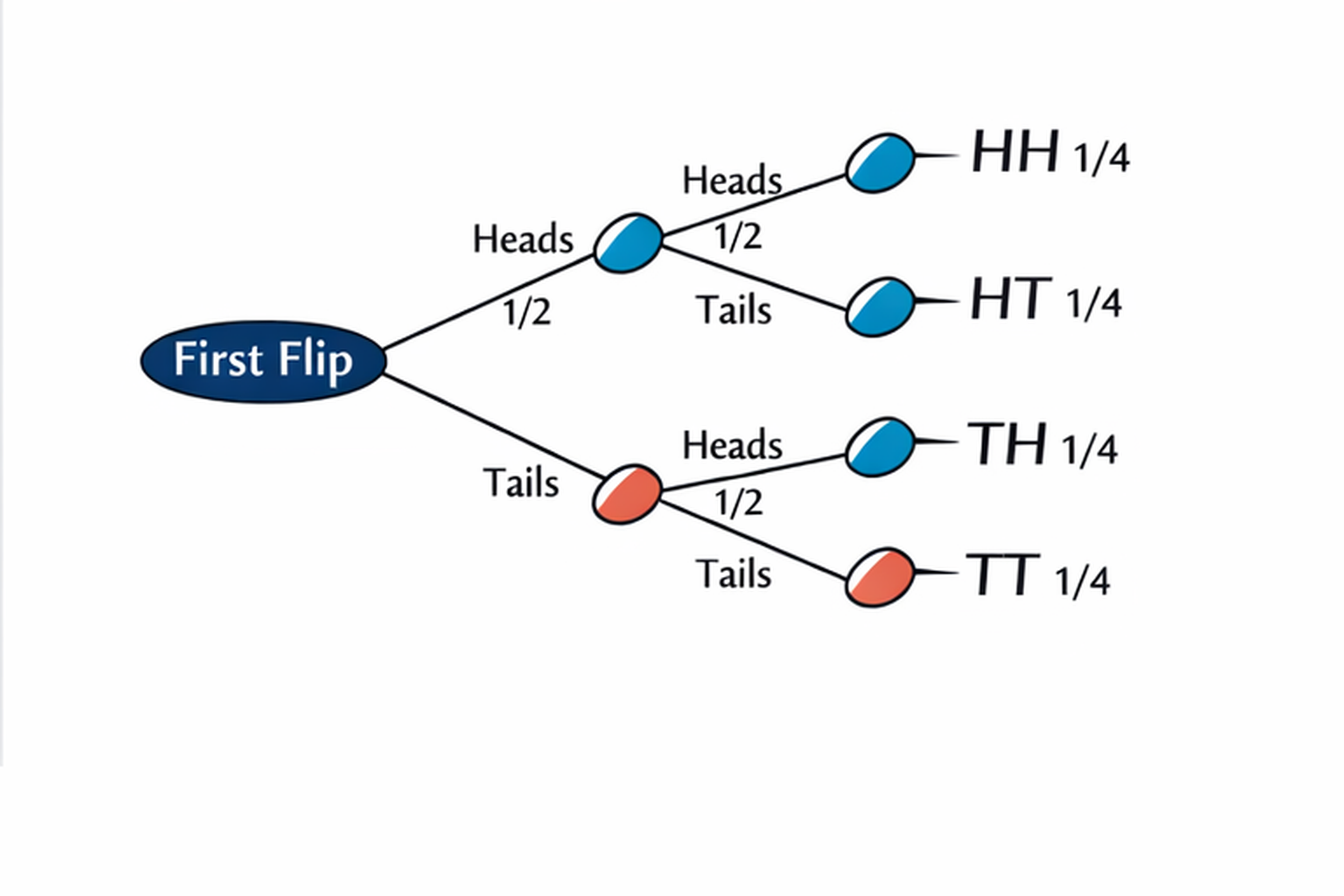
- Finding the probability of successive events, for example, the toss of a coin or several throws of a dice.
The GCSE Maths course mentioned above is for both the foundation and higher tier, but the higher tier includes slightly advanced topics in addition to the ones mentioned above.
Statistics
As you progress through the later stages of the GCSE syllabus, you'll gain insights into statistics, such as presenting data and interpreting graphs. Along with creating representations, you'll also learn to analyse and evaluate existing ones. Statistics is used to solve problems through statistical analysis and the collection of data from multiple sources.
The discussion above details the key terms you will need to know before you sit your GCSE maths paper. Students also need to learn the following in order to master the statistics portion of GCSE Maths:
- Identifying the sources of bias and understanding how data relates to a certain problem and how the size of samples affects the conclusions
- They should be able to design a survey or an experiment and identify the type of data that needs to be collected and the format of the data. Their concepts of population and sample should be crystal clear, and they should also consider fairness and be able to either design or criticise a questionnaire
- Their understanding should include the know-how of designing data-collection sheets, which enable them to distinguish between different kinds of data
- Extracting data from lists and tables, using and designing two-way tables for both grouped data and discrete data, producing charts, diagrams, histograms, graphs, etc., for all kinds of data types and learning to find mean, median, mode, range, and modal class are all part of very crucial topics in statistics.
Improve your maths grades with an A-level Maths tutor here on Superprof.

Assessment Objectives and Exam Structure
The GCSE Maths qualification is split across three written exams.⁶ All exam boards follow a structure. However, question style and layout may differ, so always check your exam board's syllabus before studying.
| Paper | Calculator Allowed | Duration | Content Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paper 1 | No | 1 hour 30 minutes | Any syllabus topic |
| Paper 2 | Yes | 1 hour 30 minutes | Any syllabus topic |
| Paper 3 | Yes | 1 hour 30 minutes | Any syllabus topic |
Foundation Tier vs Higher Tier
Students are entered for either the Foundation or Higher Tier.⁷ This is based on their ability. It also affects their target grade range.
| Tier | Grade Range Available |
|---|---|
| Foundation Tier | Grades 1–5 |
| Higher Tier | Grades 4–9 |
AO1: Use and Apply Standard Technique
AO1 focuses heavily on core mathematical skills such as arithmetic, algebraic manipulation, and working with formulae.⁵ Students must demonstrate accuracy and confidence when applying these standard techniques.
AO2: Reason, Interpret and Communicate Mathematically
This objective often appears in multi-step problems where students must demonstrate understanding rather than simply applying a formula. Questions may require written explanations or interpretation of mathematical results.
AO3: Solve Problems Within Mathematics and Real-Life Contexts
AO3 focuses on problem-solving skills and real-world application. Students may be required to:
These questions are often the most challenging but also carry significant marks. They are designed to test how well students can apply mathematical thinking in unfamiliar or practical scenarios.
Formula Sheets and Exam Expectations
Formula sheets are provided during GCSE Maths examinations. These are expected to remain available through the 2025-2027 exam series. These sheets include commonly used equations, such as area, volume, and trigonometric formulae. While these are provided, remember that you still have to understand when and how these formulas are applied. Exams still place strong emphasis on reasoning, interpretation, and multi-step problem solving.
How GCSE Maths Is Marked
Examiners award marks not just for correct answers but also for method and reasoning (showing your working). Showing working is important, as you can still gain marks if your final answer is incorrect. It's worthwhile to attempt every question if you have time during an exam.
Effective Study Strategies for GCSE Maths
Exam Strategy 📝
Distinguish between learning the syllabus and mastering exam techniques using past papers
Time Management ⏰
Allocate time effectively during exams by breaking down time per question based on the marks available
Revision Resources 🧐
Use various learning resources and practice under exam conditions to maximise performance and confidence
One thing that you will want to learn sooner rather than later is that covering the GCSE syllabus in its entirety and maximising your performance in the exams are often two separate things. While covering all of the topics that are featured in your school textbook will give you a good understanding of the concepts that you will be examined on, a few of the complexities of exam questions tend to appear in the papers.
Your maths textbook is perhaps the best resource for introducing a new topic and progressively increasing the difficulty of the questions as you work through the chapters. But this means there are limited questions on each topic, which will help you become familiar with exam-level questions. It's also important to diversify your GCSE maths learning resources so that you can be sure that no stone is left unturned!
If you want to maximise the grade you receive in the subject when you get around to opening up your results envelope after the summer, then you will want to mix exam preparations into your preparation. The best way to do this is by working through past papers to get familiar with how the questions are likely to be asked, so that there's nothing that can throw you off on the day.
Would you believe it if we told you that time management is actually one of the main things that hold students back from achieving their potential in the GCSE maths exam? You can have a strong grasp of all the topics across the maths GCSE syllabus, but if you fail to complete the paper in time, you'll miss out on a portion of the marks and cap the grade that you can achieve in the subject.
Make sure to manage your time across all three examination papers (one non-calculator and two calculator papers), allocating time proportionately based on mark weighting. You will want to do this by breaking down the number of marks available for each question and giving yourself a proportionate amount of time to work through it.
You don't want to spend too much time trying to figure out a question that is only worth 5 marks when you could be working through a question that will have a greater impact on your grade. By timing yourself while working through past exam papers, you will become familiar with the exam setting and navigate the paper under the same conditions that you will be under when the date approaches.
Adopting an exam-focused approach while you work through the GCSE syllabus is the best way to ensure you get a good grade, if not a prestigious 9! Don't wait any longer, get stuck into maths right now! Find a maths tutor for A-level maths and GCSE Maths revision, and see how your confidence grows by leaps and bounds.
References
- AQA. GCSE Mathematics (8300) Specification at a Glance. AQA, https://www.aqa.org.uk/subjects/mathematics/gcse/mathematics-8300/specification/specification-at-a-glance. Accessed 12 Feb. 2026.
- AQA. GCSE Maths and GCSE Sciences: Formulae and Equation Sheets for 2025–2027. AQA, https://www.aqa.org.uk/news/gcse-maths-and-gcse-sciences-formulae-and-equation-sheets-for-2025-2027. Accessed 12 Feb. 2026.
- Department for Education. Mathematics Programmes of Study: Key Stage 4. GOV.UK, https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/national-curriculum-in-england-mathematics-programmes-of-study. Accessed 12 Feb. 2026.
- Ofqual. Proposed Changes to the Assessment of Mathematics GCSEs in 2025, 2026 and 2027. GOV.UK, https://www.gov.uk/government/consultations/proposed-changes-to-the-assessment-of-mathematics-physics-and-combined-science-gcses-in-2025-2026-and-2027. Accessed 12 Feb. 2026.
- OCR. GCSE (9–1) Mathematics Subject Content Clarification. OCR, https://www.ocr.org.uk/administration/support-and-tools/subject-updates/gcse-maths-clarification-742180/. Accessed 12 Feb. 2026.
- Pearson Edexcel. GCSE (9–1) Mathematics Specification. Pearson, https://qualifications.pearson.com/en/qualifications/edexcel-gcses/mathematics-2015.html. Accessed 12 Feb. 2026.
- Pearson Edexcel. January 2026 Mathematics and Statistics Update. Pearson, https://qualifications.pearson.com/en/news-policy/subject-updates/mathematics/january-2026-maths-and-statistics-update.html. Accessed 12 Feb. 2026.
- Third Space Learning. GCSE Exam Dates 2026 and Exam Structure Guide. Third Space Learning, https://thirdspacelearning.com/blog/gcse-dates-2026/. Accessed 12 Feb. 2026.
Summarise with AI:
















Thank you very much.
This guide has helped me a lot
Thank you very much
Thank you very much
now that called communication with simplicity. thanks an million its a relief to read this in simple language
Hi does this guide cover all the topics that will definitely be in the test?
Hi,
Thank you for your question! While this guide covers key topics commonly found on the test, it’s important to note that exams can vary and changes can be made to the curriculum. I recommend checking with your official examination board regularly to ensure you’re prepared for all possible topics.
Best of luck with your studies!
ok my examination board is AQA
Thank you for sharing that your examination board is AQA. The AQA GCSE Maths syllabus encompasses a range of topics, including number operations, algebra, ratio, proportion, rates of change, geometry, measures, statistics, and probability.