Decimal numbers are used to represent parts of a whole.
A decimal point ( . ) separates the whole number part from the fractional part.
For example, in the number 325.678:
- 325 is the whole number part
- 678 is the fractional part
Each digit in a decimal has a place value:
| Place | Example_Digit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Hundreds | 3 | 300 |
| Tens | 2 | 20 |
| Units | 5 | 5 |
| Tenths | 6 | 0.6 |
| Hundredths | 7 | 0.07 |
| Thousandths | 8 | 0.008 |
Therefore:
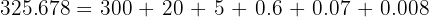

Terminating Decimal Numbers
A terminating decimal is a number that has a finite number of digits after the decimal point.
It comes to an end — it doesn’t go on forever.
Examples:
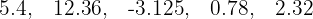
All of these stop after a certain number of digits.
Worked Example
Convert the fraction seven-eighths into a decimal.
We divide 7 by 8:
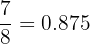
The decimal ends after three places, so it is terminating.
Non-Terminating Decimal Numbers
A non-terminating decimal goes on forever — it has an infinite number of digits after the decimal point.
These are of two types:
- Recurring (Repeating)
- Non-Recurring (Non-Repeating)
a) Recurring Decimal Numbers
A recurring decimal has a set of digits that repeat indefinitely in a fixed pattern.
Examples:
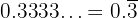

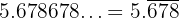
The bar (overline) indicates the repeating digits.
Worked Example 1 — Pure Recurring Decimal
Convert 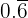 into a fraction.
into a fraction.
Let:
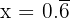
Multiply both sides by 10:
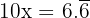
Subtract the first equation from this:
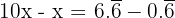
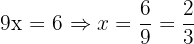
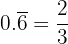
Worked Example 2 — Mixed Recurring Decimal
Convert 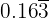 into a fraction.
into a fraction.
Let:

Multiply by 1000 (to move the decimal just before the repeating part):

Multiply by 10 (for one repeat shift):
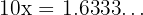
Subtract:
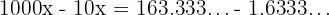
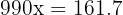

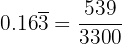
b) Non-Recurring Decimal Numbers
These are non-terminating decimals that do not repeat.
The digits after the decimal point go on forever without any pattern.
Such numbers are called irrational numbers.
Examples:
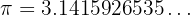
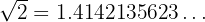
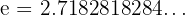
They neither stop nor repeat.
Worked Example
Show that 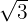 is a non-terminating, non-recurring decimal.
is a non-terminating, non-recurring decimal.
Using a calculator:
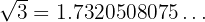
The digits go on infinitely and show no repeating pattern.
Therefore, 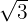 is non-terminating and non-recurring, and hence irrational.
is non-terminating and non-recurring, and hence irrational.
Rounding Decimal Numbers
Sometimes, we need to round decimals to a specific place value (e.g., 1 decimal place, 2 decimal places).
Rule:
- Identify the digit in the place value you’re rounding to.
- Look at the next digit (to the right): If it’s 5 or more, round up; if it’s less than 5, leave it.
Worked Example
Round 567.81456 to 3 decimal places:
The value in the 3rd decimal place position is 4. The next digit is 5, so we round up, taking the previous digit from 4 → 5.
Final answer: 567.815
Summary
Decimal numbers express whole and fractional parts using a decimal point. They can be terminating, recurring, or non-recurring. Terminating and recurring decimals are rational, while non-recurring decimals are irrational. Recognising these types helps in understanding number patterns, rounding, and fraction conversions.
Summarise with AI:












what will be the answer when 12.345 is subtracted from 234.00 multiplied by 778.90 and divided by67.23
If we follow the order of operations (multiply and divide first, then subtract):
1. (234.00 \times 778.90 = 182,262.6)
2. (182,262.6 \div 67.23 \approx 2711.03)
3. (2711.03 – 12.345 \approx 2698.69)
**Final answer: ≈ 2,698.69**
If it is (0.0072÷6)
find the square root in decimal form of 6.7081
find the square root in decimal form of 6.7081
find the square root in decimal form of 6.7081
find the square root in decimal form of 6.7081
find the square root in decimal form of 6.7081
find the square root in decimal form of 6.7081
find the square root in decimal form of 6.7081
find the square root in decimal form of 6.7081
find the square root in decimal form of 6.7081
find the square root in decimal form of 6.7081
find the square root in decimal form of 6.7081
find the square root in decimal form of 6.7081
find the square root in decimal form of 6.7081
find the square root in decimal form of 6.7081
find the square root in decimal form of 6.7081
find the square root in decimal form of 6.7081
find the square root in decimal form of 6.7081
find the square root in decimal form of 6.7081
find the square root in decimal form of 6.7081
find the square root in decimal form of 6.7081
find the square root in decimal form of 6.7081
find the square root in decimal form of 6.7081
find the square root in decimal form of 6.7081