Chapters
In Euclidean space, a Euclidean vector is a geometric object that possesses both a magnitude and a direction. A vector can be pictured as an arrow. Its magnitude is its length, and its direction is the direction that the arrow points to. The magnitude of a vector n1 is denoted by ||n1||.
The dot product of two Euclidean vectors n1 and n2 is defined by
n1· n2 = ||n1|| ||n2|| cos α
where α is the angle between n1 and n2.
The angle between two planes is equal to the acute angle determined by the normal vectors of the planes.

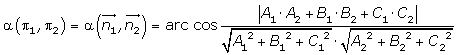
Two planes are perpendicular if their normal vectors are orthogonal.


The best Maths tutors available
Example
Determine the angle between the following planes:



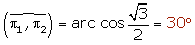
Summarise with AI:













I WANT TO CONTINUE WITH SOLVED PROBLEMS OF APPLICATION OF CROSS PRODUCTS OF VECTORS