Chapters

Solving Simultaneous Equations Using Substitution (Class 10 Guide)
Simultaneous equations are pairs (or sometimes sets) of equations that must be true at the same time. In GCSE Maths, you’ll often meet them in the form of two equations with two unknowns (usually x and y). For example:
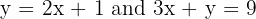
The substitution method is one of the main ways to solve these equations. It works by replacing one variable with an equivalent expression from the other equation — so you reduce the problem to a single equation with just one unknown.
Step-by-step method
1. Make one variable the subject
Looking back at the equations above, pick one that is already written (or can easily be rearranged) to express x or y in terms of the other. For example:
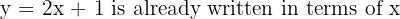
2. Substitute into the other equation
Replace the y in the second equation with the expression 2x+1. So:
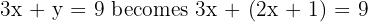
3. Simplify and solve
Now you only have one variable:
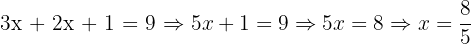
4. Substitute back
Put this value of x into the expression for y:
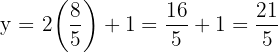
5. Write the solution as a pair
The solution to the simultaneous equations is:

Practice Questions & Solutions
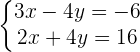
Step 1:

Step 2:
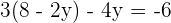
Step 3:
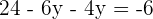

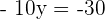

Step 4:
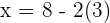


Step 5:

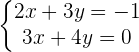
Step 1:

Step 2:
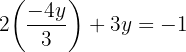
Step 3:
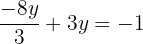
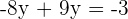

Step 4:
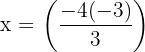

Step 5:

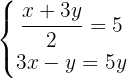
Step1:
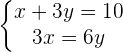

Step 2:
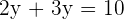
Step 3:


Step 4:


Step 5:


Step 1:
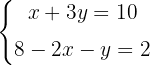
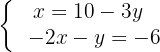
Step 2:
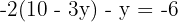
Step 3:
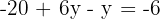
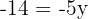
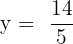
Step 4:
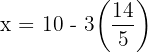
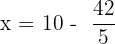
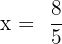
Step 5:
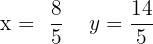
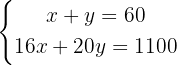
Step 1:
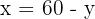
Step 2:

Step 3:
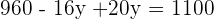
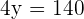

Step 4:


Step 5:

Summarise with AI:












Hi , I m Abhishek Mittal , a passionate maths assistant professor, having experience more than 10 years with almost all top brands (Cuemath, Byjus, FIITJEE, Allen) online and offline and in-person .
Want to join Superprof , Kindly guide me.
Hi Abhishek, thanks so much for reaching out! With your experience, you’d be a fantastic fit for Superprof.
Joining is simple:
1. Visit the Superprof website and click “Become a tutor”.
2. Create your profile, add your teaching experience, qualifications and subjects.
3. Upload a clear photo and write a friendly, detailed description of your teaching style — this really helps students choose you.
4. Set your rates and availability, and once your profile is validated, students can start contacting you directly.
If you need help setting up or optimising your profile, feel free to write to our customer services team at hello@superprof.com — they’ll be happy to guide you!
nice work
Thank you! 😊 We’re glad you found the worksheet helpful. Keep up the great work with your studies!