Chapters
- Aerobic Respiration
- Aerobic Respiration Chemical Equation
- Anaerobic Respiration
- How anaerobic respiration occurs in muscles?
- Anaerobic Respiration in Yeast and Plants
- Differences Between Aerobic Respiration and Anaerobic Respiration
- Investigating End products of Respiration
- Investigating the Production of Carbon dioxide
- Investigating Heat Generation
In this article, we will discuss aerobic and anaerobic respiration in detail. We will specifically discuss their chemical and word equations, and the differences between them. In the end, we will investigate the end products of respirations by conducting simple experiments. So, let us get started with an introduction first.
Introduction
All living organisms require energy released as a result of respiration for their important life processes. There are two types of respiration:
- Aerobic respiration: It needs oxygen
- Anaerobic respiration: It does not need oxygen
In the next section, we will discuss aerobic respiration in detail.

Aerobic Respiration
Birds and mammals need to maintain a consistent body temperature. To do so, they need energy. Besides maintaining body temperature, energy is also needed for other life processes such as cell division, muscle contraction, growth, active transport, nerve impulses, and protein synthesis.
Chemical reactions included in respiration break down nutrient molecules in living cells of the organisms to release energy.
Oxygen is needed in aerobic respiration and it involves the release of the comparatively large amount of energy present in the cells by the breakdown of food substances.
Aerobic Respiration Chemical Equation
The chemical equation of aerobic respiration is given below:
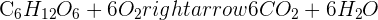
The word equation of this type of respiration is given below:
Glucose + Oxygen 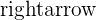 Carbon dioxide + Water
Carbon dioxide + Water
Aerobic respiration occurs all the time in plants and animals. Remember that respiration and breathing are different from each other. Breathing is similar to ventilation that involves taking the air in and out of the body. The majority of the reactions in aerobic respiration occur inside the mitochondria in the cells. Mitochondria refer to the small organelles present in the cytoplasm of the cell.
In the next section of the article, we will discuss anaerobic respiration in detail.
Anaerobic Respiration
Anaerobic respiration occurs in the absence of oxygen. It means that this type of respiration does not need oxygen. It involves the release of the comparatively small amount of energy present in the cells through a breakdown of food substances in the absence of oxygen.
How anaerobic respiration occurs in muscles?
During strenuous exercise, anaerobic respiration occurs in muscles. It breaks down glucose into lactic acid. The chemical equation of this process is given below:
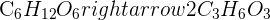
The word equation of this chemical reaction is:
Glucose 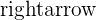 Lactic acid
Lactic acid
This type of respiration does not break down glucose completely, so relatively little energy is released in this process as compared to aerobic respiration. When we exercise vigorously, the lactic acid builds up in the muscles. There is a need to oxidize this lactic acid into carbon dioxide and water later. It results in oxygen debt which is also referred to as excess post-exercise consumption (EPOC). It should be recompensed once we stop exercising. Due to this, we breathe deeply for some minutes after finishing the exercise.
In the next section of the article, we will discuss how anaerobic respiration occurs in yeast and plants.
Anaerobic Respiration in Yeast and Plants
Plant cells and a few microorganisms also undergo anaerobic respiration. In yeast, anaerobic respiration is employed while bread making. The chemical equation of anaerobic respiration in yeast and plants is given below:
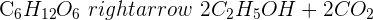
The word equation is:
Glucose  Ethanol + Carbon dioxide
Ethanol + Carbon dioxide
In bread making, carbon dioxide bubbles not only expand the dough but also assist to raise the bread.

In the next section of the article, we will discuss the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Differences Between Aerobic Respiration and Anaerobic Respiration
- Aerobic respiration: It needs oxygen and involves the complete breakdown of glucose. The end products of this type of respiration are water and carbon dioxide. A relatively large amount of energy is released as a result of aerobic respiration.
- Anaerobic respiration: Anaerobic respiration does not require oxygen and it involves incomplete glucose breakdown. The end products of this kind of respiration are different in different organisms. In animal cells, the end product of anaerobic respiration is lactic acid, whereas, in yeast and plant cells, the end products are ethanol and carbon dioxide. A relatively small amount of energy is released as a result of anaerobic respiration.
Important fact: 19 times more energy is released in aerobic respiration as compared to anaerobic respiration, considering that the same amount of glucose is utilized.
In the next sections of the article, we will investigate the end products of respiration through simple experiments.
Investigating End products of Respiration
In living organisms, we can investigate respiration by conducting experiments to demonstrate the generation of carbon dioxide and heat energy.
Investigating the Production of Carbon dioxide
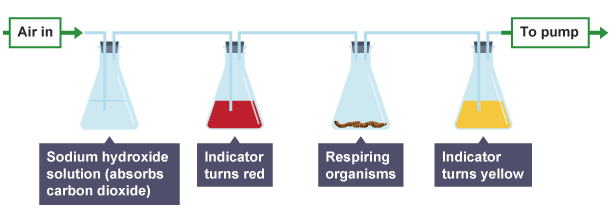
In the presence of carbon dioxide gas, limewater turns milky. We can use this attribute of limewater to demonstrate that the air we exhale has more carbon dioxide than the air we inhale.
A weakly acidic solution is created when carbon dioxide is dissolved in water. The presence of carbon dioxide in the solution can be demonstrated using a hydrogen carbonate indicator.
- When no carbon dioxide is present (neutral pH), the indicator turns red
- In the presence of carbon dioxide (low pH), the indicator turns yellow
In this particular experiment, a sodium hydroxide solution in the left-hand flask absorbs carbon dioxide. Therefore, this indicates that the respiring organism must have generated carbon dioxide which is identified in the right-hand flask.
Investigating Heat Generation
The heat released can be shown by conducting an experiment using germinating seeds. Two types of vacuum flasks are employed in this experiment:
- One that contains living plant material
- One that contains dead plant material (the control)
Both the flasks have the following outcomes:
- If the initial temperature of the living plant material is
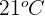 , then its end temperature will be
, then its end temperature will be 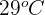 . The temperature variation would be
. The temperature variation would be 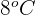 .
. - If the initial temperature of the dead plant material is
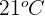 , then the end temperature will also be
, then the end temperature will also be 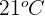 .
.
From this experiment, we can conclude that since the dead plant was not respiring, therefore the temperature change is 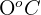 . The temperature of the vacuum flask containing living plant material was raised because the plant was respiring, and heat energy was released as a result of this process.
. The temperature of the vacuum flask containing living plant material was raised because the plant was respiring, and heat energy was released as a result of this process.
Summarise with AI:













i like the article
Hi Sam! Thank you! Great to hear that you found this resource useful.
welcome
Hi Suunu! Thanks for reaching out. Hope you’ve found this resource useful 😊!
i have learnt a lot which i did not know
am senior three student but this is cool
Am impressed
Am impressed
learning is the best