Chapters
In this article, we will discuss the three main types of enzymes that break down the three essential biological molecules: carbohydrates, proteins and fats. But before discussing these enzymes, first, let us recall what are enzymes and what role do they play in our body.

What are Enzymes?
We know that enzymes act as biological catalysts, i.e. they speed up the reaction. After the reaction, the nature of the enzymes remains unchanged which means that they do not get used up during the reaction. They are referred to as "biological catalysts" because they are made up of living cells.
Enzymes are essential to carry out certain processes in living organisms that are critical for their survival. For instance, digestive enzymes present in the human body enable us to digest food within hours. If these enzymes would not be there, then it would take us weeks to digest even a single meal.
Many factors affect the activity of enzymes, but the three main factors are:
- Temperature
- pH
- Substrate and enzyme concentration
Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids are three biological molecules that are present in our diet. These molecules provide us with energy. The enzymes present in our digestive system break down these molecules into simpler units.
Three Main Types of Digestive Enzymes
Digestion is the process in which our body breaks down large, insoluble food molecules into smaller, water-soluble molecules. Large insoluble molecules like proteins and starch are made up of chains of smaller molecules. These chains are held together through chemical bonds which need to be broken. This breakdown occurs with the help of mechanical and chemical processes. Mechanical digestion occurs through:
- chewing of food in the mouth with the help of teeth
- churning in the stomach
For chemical digestion, we need enzymes. The three main types of digestive enzymes are:
- Carbohydrase
- Proteases
- Lipase
1. Carbohydrase
Carbohydrase are digestive enzymes that break down carbohydrates into simple sugar. These enzymes are secreted by our mouth, pancreas and small intestine.
Enzymes that breakdown different types of carbohydrates
Different types of carbohydrates are broken down by different types of carbohydrase enzymes. Some of these are listed and explained below:
- Amylase: Starch is a kind of carbohydrate that is broken down by a carbohydrase enzyme known as amylase. Amylase is secreted by our mouth and is present in saliva. It begins working as soon as start chewing our food. Long, complex starch molecules known as polysaccharides are broken down by the amylase enzyme into smaller and simpler disaccharide molecules known as maltose. The word equation of this reaction is given below:
Starch 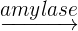 maltose
maltose
- Maltase: Maltose is a disaccharide molecule that needs to be digested further before absorption. The enzyme known as maltase breaks down maltose into glucose. The word equation of this reaction is given below:
Maltose 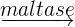 glucose
glucose
- Sucrase: The sucrase enzyme is responsible for breaking down the dietary sugar sucrose into glucose and fructose. Sucrose is also a disaccharide molecule. The word equation for this reaction is given below:
Sucrose 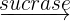 glucose + fructose
glucose + fructose
- Lactase: Lactose is another dietary sugar that is a disaccharide molecule. The enzyme lactase breaks down lactose into glucose and galactose. The word equation of this reaction is given below:
Lactose 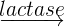 glucose + galactose
glucose + galactose
2. Protease
The enzymes that digest proteins in our food are known as protease. These enzymes are secreted by our stomach, pancreas and small intestine. Our stomach secretes a protease enzyme known as pepsin. Proteins are made of long chains of amino acids. The protease enzymes break down these long chains into peptides and individual amino acids. Peptides are smaller chains of amino acids and individual amino acids are small and can be absorbed easily in the small intestine. The word equation of this reaction is given below:
Proteins 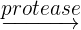 amino acids
amino acids
3. Lactase
The enzymes that break down complex lipid or fat molecules present in our diet into simpler, soluble fatty acid and glycerol molecules are referred to as lipase. These enzymes are secreted by our pancreas and walls of the small intestine. The word equation of fat
Lipase is secreted by the pancreas and the walls of the small intestine. It digests complex fat (or lipid) molecules into simple, soluble fatty acid and glycerol molecules. The word equation for this reaction is:
Lipids 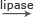
Summarise with AI:













i like the article
Hi Sam! Thank you! Great to hear that you found this resource useful.
welcome
Hi Suunu! Thanks for reaching out. Hope you’ve found this resource useful 😊!
i have learnt a lot which i did not know
am senior three student but this is cool
Am impressed
Am impressed
learning is the best