Chapters
In this article, we will investigate the importance of light and distance in photosynthesis. But before proceeding to discuss that, first, let us recall what is photosynthesis and how this process occurs.

What is Photosynthesis?
We can define photosynthesis as:
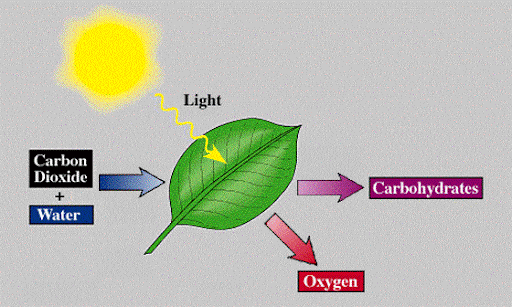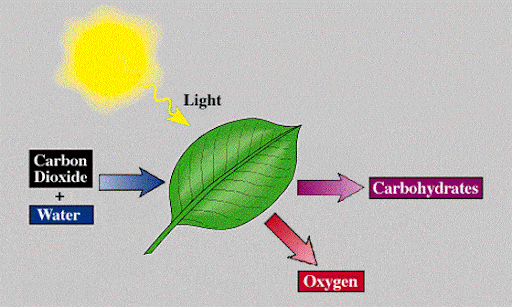
The process through which plants make their own food by using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to create glucose and oxygen is referred to as photosynthesis
The following things are essential for photosynthesis to occur:
- Chlorophyll
- Carbon dioxide from the air
- Water from soil
- Light energy
Plants release glucose and oxygen (as a by-product) as a result of this process.
Process of Photosynthesis
Now, let us see how this process occurs.
Photosynthesis is a chemical reaction that requires light energy. This process is referred to as an endothermic reaction because, during the process, the reactants involved in the process absorb heat to create products.
We already know that chlorophyll is an important factor needed for photosynthesis. Now, the question arises from where the plants get chlorophyll? Well, the answer is quite simple as the leaves of the plants naturally contain a green pigment known as chlorophyll which plays a fundamental role in photosynthesis. This green pigment absorbs sunlight which is another important factor in photosynthesis. Chloroplasts in plant cells have chlorophyll, specifically the palisade and spongy mesophyll cells. Until now, it is very clear that the leaves of the plants are the major photosynthetic organ. However, keep in mind that any part of the plant that is exposed to sunlight will form chlorophyll for photosynthesis.
Besides chlorophyll, plants also need carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. The surrounding air of the plant is the major source of carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide enters the plants' leaves through stomata. Water is also needed for photosynthesis and soil is the major source of water for plants. Water enters the plants through their roots and is then transported to the leaves in the xylem.
Glucose and oxygen are produced by the plants as a result of photosynthesis. Some of the glucose is used by the plants for respiration and other important functions, whereas the remaining is stored as starch. Plants use some of the oxygen produced as a result of photosynthesis for respiration, whereas the surplus oxygen is released into the air where it becomes available to animals and other microorganisms.
In the next section, we will discuss the importance of light for the rate of photosynthesis in detail.
Light and Rate of Photosynthesis
Without sufficient light, plants are unable to photosynthesize quickly even if there is an ample amount of water and carbon dioxide. When the intensity of light increases, the rate of photosynthesis also increases until some other limiting factor plays its role to slow down the reaction.
Remember that at extremely high light intensities, the process of photosynthesis slows down and eventually stops completely. But these extremely high light intensities do not occur in nature.
The following graph shows the relationship between light intensity and the rate of photosynthesis.
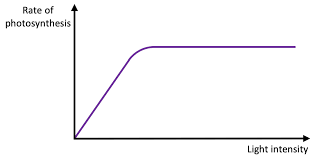
The impact of light intensity on photosynthesis can be investigated in many ways. Most of the experiments conducted to determine this impact involve a light source and a plant. The distance between the light source and plant is changed and the number of oxygen bubbles produced by the plant is recorded. We record the number of oxygen bubbles in these experiments because oxygen is a byproduct of photosynthesis.
Inverse Square Law
The inverse square law can be used to describe the intensity of light the plant receives at different distances from the light source. According to this law, the intensity of light is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source.
Practically, it means that when light is moved twice as far from the plant, then the plant will only receive a quarter of the light energy.
The following formula can be used to compute the intensity of light:
Light intensity 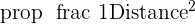
The symbol 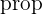 means “proportional to” and the distance is calculated in meters.
means “proportional to” and the distance is calculated in meters.
Hence, if the light is 20 cm apart from the plant, then the plant will receive:
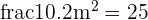 arbitrary units
arbitrary units
If the light is 10 cm far away from the plant, then the pant will receive:
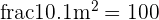 arbitrary units
arbitrary units
In the next section, we will discuss how to conduct a test to investigate the impact of light intensity on photosynthesis.
Investigating the Impact of Light Intensity on Photosynthesis
Let us experiment to investigate the impact of light intensity on photosynthesis.
Objective
The main objective of this experiment is to investigate the impact of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis using an aquatic organism like pondweed.
In this experiment you will:
- Measure the volume of oxygen generated by the pondweed as you change the light intensity by moving the light source.
- Measure and compute the rates of photosynthesis
- Extract and interpret graphs related to the rate of photosynthesis which includes one limiting factor.
The most widely used method to measure the rate of photosynthesis is to measure or observe the oxygen that is produced by the aquatic plants.
Method
Follow the procedure below to conduct this experiment:
- Place a piece of pondweed (the most frequently used are Elodeaor Cabomba) into a water beaker
- Use a light source and place it at a specific distance from the plant
- Record the number of bubbles produced by the plant for three minutes
- Repeat the above steps by changing the distance of the light source from the plant.
Important Considerations
- To collect the volume of gas generated, use a gas syringe
- For each distance, repeat the experiment twice and take the average of number of bubbles
- Remember to use a glass tank between the lamp and plant to avoid heating of the plant. Alternatively, you can also use an LED bulb because it produces very little heat.
Variables
- Besides light, this method is also very useful to investigate other variables such as temperature and carbon dioxide.
Results
Draw the graph of the light intensity against the number of bubbles produced in a single minute to see a pattern and trend. The conclusion of the experiment would be:
As the light is closer to the beaker, more bubbles are produced which depicts that increasing the intensity of light increases the rate of photosynthesis.
Evaluation
In this section, you will learn how to determine whether your measurements are accurate, precise, repeatable, or reproducible.
Accurate measurement: The measurements will be accurate if they are close to their actual value.
Precise measurement: The measurements will be precise if they are the same when repeated.
Repeatable measurement: The measurements will be repeatable if you obtain precise measurements when they are repeated.
Reproducible measurements: The measurements will be reproducible if others get precise measurements after they repeat them.
Summarise with AI:













i like the article
Hi Sam! Thank you! Great to hear that you found this resource useful.
welcome
Hi Suunu! Thanks for reaching out. Hope you’ve found this resource useful 😊!
i have learnt a lot which i did not know
am senior three student but this is cool
Am impressed
Am impressed
learning is the best