Chapters
Green plants use their leaves to absorb light and transform it into energy by a process known as photosynthesis. Certain limiting factors such as temperature, carbon dioxide concentration, and light intensity can affect the rate of photosynthesis. The leaves of the green plants are adapted to carry out photosynthesis effectively. In this article, we will discuss the structure of the leaf in detail.

Mechanisms Essential for Photosynthesis
The leaf has adaptations so that it can carry out photosynthesis. A leaf needs the following elements for photosynthesis:
- A mechanism to carry water to the leaf and glucose to the rest of the plant
- A mechanism for the exchange of gases like carbon dioxide and oxygen
- A capacity to absorb light energy from the sun efficiently
In the next sections of the article, we will discuss how the structure of the plant leaves enables all the above three mechanisms to facilitate the process of photosynthesis.
Gas Exchange
The spongy mesophyll tissue of the leaf is a place where gas exchange occurs. A thin layer of water covers the spongy mesophyll cells of the leaf and these cells are loosely packed.
During the day, when the plant is photosynthesizing, these attributes enable carbon dioxide to diffuse into the spongy mesophyll cells, and oxygen to diffuse out of it.
Stomata
Gases diffuse through tiny pores known as stomata to get to the spongy mesophyll cells inside the leaf. These pores also open and close to control the water loss from the leaf by a process known as transpiration.
Since stomata control gas exchange in the leaf, therefore each stoma opens or closes based on the turgidity of the guard cells. The main purpose of opening and closing of stomata is to allow gas exchange and regulate transpiration. The diffusion of water vapours, carbon dioxide, and oxygen into or out of the leaf is greatest during the day when the stomata are open.
Absorbing Light Energy
Light absorption occurs in the palisade mesophyll tissue of the leaf. The column-shaped palisade cells are packed with several chloroplasts. They are closely arranged together to allow maximum absorption of light energy.
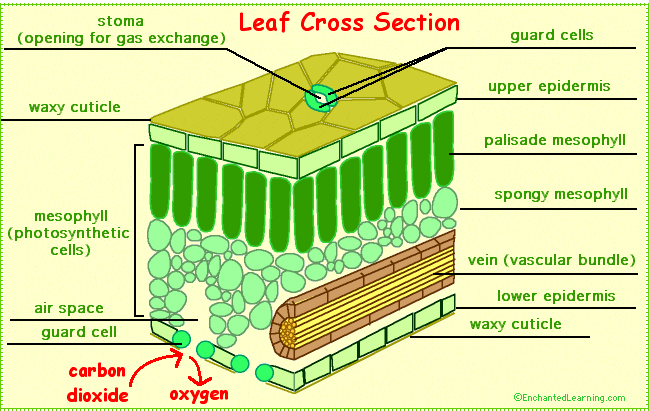
Structure of Leaf
The following structures are present in the leaves to help them photosynthesize effectively:
- Large surface area: We know that light energy is essential for photosynthesis. Plants must be able to absorb sufficient light to photosynthesize. The leaves of the plants naturally have a large surface area to allow maximum absorption of light energy from the sun.
- Thin: Plants need carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. It is one of the main reactants of the photosynthesis equation. The thin structure of plant leaves enables easy diffusion of carbon dioxide into the leaf cells by providing a short distance.
- Thin waxy cuticle: Plant leaves have a thin waxy cuticle that covers them. It acts as a protective covering for the leaf. This covering is thin and protects the leaf without blocking out the light. The main function of this protective covering in the leaf is to prevent water loss due to evaporation.
- Thin transparent epidermis: The thin transparent epidermis in the plant leaves allows light to reach palisade cells easily.
- Upper epidermis: The upper epidermis of the leaves is thin and transparent allowing light to enter the palisade mesophyll layer below it.
- Palisade mesophyll: These cells are column-shaped and are packed tightly with chloroplasts so that maximum light can be absorbed for photosynthesis.
- Spongy mesophyll: These cells have internal air spaces that enhance the surface area to volume ratio for the effective diffusion of gases, particularly carbon dioxide.
- Lower epidermis: The lower epidermis of the plant leaves contain guard cells and stomata.
- Guard cell: The guard cells in the plant leaves absorb and lose water to open and close the stomata so that carbon dioxide can diffuse in and oxygen can diffuse out.
- Stomata: They are the small pores where gas exchange occurs. They open during the day and close at night. Water evaporation also occurs here. In the majority of the plants, stomata are present in greater concentration in the upper part of the leaf than the lower part to prevent water loss due to evaporation.
- Vascular bundles: Vascular bundles in plant leaves contain xylem and phloem to carry substances to and from the leaf.
- Xylem: Xylem in plant leaves carries water into the plant leaves for mesophyll cells to use in photosynthesis and for transpiration from stomata.
- Phloem: Phloem carries sucrose and amino acids around the plant.
In the next section of the article, we will discuss the transportation system of plants in detail.
Transportation in Plants
Plants have specialized tissues to transport water, nutrients, and minerals. These tissues are known as xylem and phloem:
- Xylem: Xylem tissues in plants carry water and mineral salts from the roots up to other parts of the plant by a process known as transpiration stream.
- Phloem: Phloem carries amino acids and sucrose from the leaves to the other parts of the plants by a process known as translocation.
Xylem
The mature xylem is made up of elongated dead cells, that are arranged end to end to form continuous vessels (tubes).
Mature xylem vessels have the following attributes:
- They do not contain cytoplasm.
- They are impermeable to water
- They have tough walls that contain a woody material known as lignin.
Phloem
Phloem is made up of living cells arranged end to end. Unlike xylem vessels, phloem vessels have chloroplasts, and this extends through the holes in the sieve plates from one cell to another.
Sucrose and amino acids are crucial for plant growth and functions. Phloem transports these materials up and down the plant through a process referred to as translocation. Generally, this happens between where these substances are made, i.e. the sources, and where they are employed or stored, i.e. the sinks.
It means that the sucrose is transported:
- From sources in the root to the sinks present in the leaves during the springtime.
- From sources in the leaves to the sinks in the roots during the summertime.
The applied chemicals such as pesticides also move through the plant through the process of translocation.
Vascular Bundles
Xylem and phloem tissues are found in groups known as vascular bundles. The location of these vascular bundles differs in various parts of the plant. In the leaf, the phloem is usually located closer to the lower surface.
Roots
Since xylem vessels are tough and strong, therefore vascular bundles are present in the centre of the root to withstand forces that can pull the plant out of the ground.
Stems
The stem should withstand compression and bending forces caused by the wind and weight of the plant. The vascular bundles are arranged closer to the edge of the stem with the xylem on the inside and phloem on the outside.
Summarise with AI:













i like the article
Hi Sam! Thank you! Great to hear that you found this resource useful.
welcome
Hi Suunu! Thanks for reaching out. Hope you’ve found this resource useful 😊!
i have learnt a lot which i did not know
am senior three student but this is cool
Am impressed
Am impressed
learning is the best