In this article, we will discuss important terms in ecologies such as biotic and abiotic factors, interdependence, parasitism and mutualism, and biodiversity. So, let us get started with the definition of ecology.
Ecology is the branch of biology that deals with the relationship of living organisms with one another and to the physical environment.
'The geographical area in which the living organisms work together and with their surrounding physical environment is called Ecosystem. The factors that affect the ecosystem can be categorized into two types abiotic and biotic.

Abiotic Factors
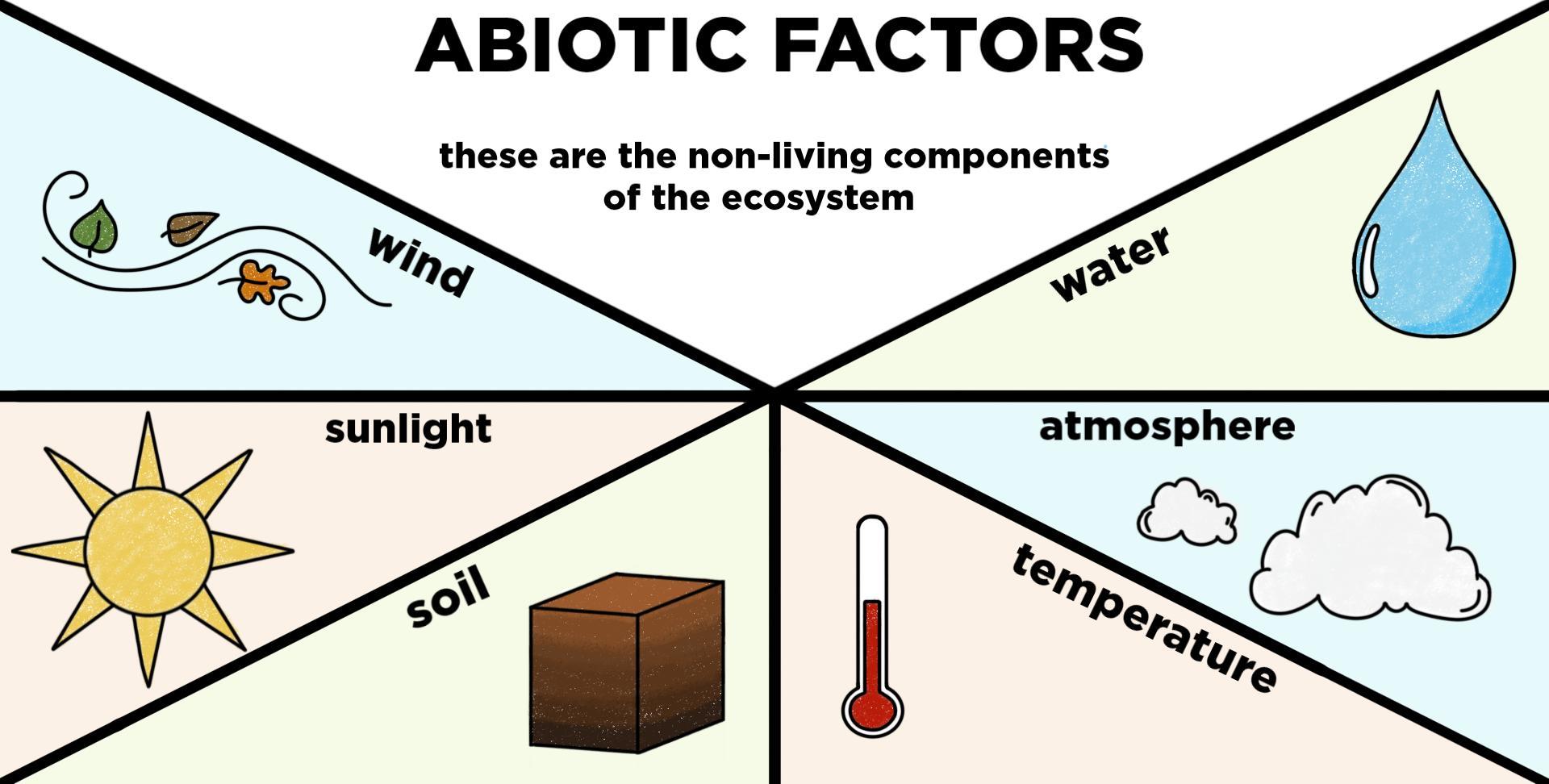
The abiotic factors are the non-living factors of the ecosystem which affect the living organisms in terms of growth, reproduction, and maintenance.
Abiotic factors include temperature, light, wind, water, soil composition, carbon dioxide concentration in water, air, and oxygen availability. Each living organism has its tolerance level of abiotic factors so there are no ideal levels of abiotic factors.
Temperature
Temperature affects the ecosystem in different ways. For example, if there is a low temperature, the rate of photosynthesis would decrease, and it would hinder the growth of plants. High temperatures can also decrease the rate of photosynthesis, so in the areas with extreme temperatures the diversity in species of plants and animals is low and only a few species can survive.
Light Intensity
Plants need light for photosynthesis so in the areas with low light, plants can’t survive. The animals which survive on plants are also very hard to find in low-light areas. On the other hand, too much light can also increase the risk of overheating.
Wind
The plants in windy areas usually grow much closer to the ground as strong winds are dangerous for them. Winds also affect the rate of transpiration in plants. The transpiration rate affects the rate of photosynthesis.
Soil Composition
Every plant species is adapted to different Ph levels and nutrients present in the soil. If the soil contains a Ph level ranging from 5.5 to 7 and has various minerals, it is considered fertile. Only a few plants can survive in rocky and salty soils.
Water
Plants need water for photosynthesis, while animals need water for different functions such as regulation of temperature, nutrient uptake, removing wastes, body weight, and health.
Carbon Dioxide and Oxygen
Plants use light and carbon dioxide for the process of photosynthesis. In this process, they release oxygen in the air which is necessary for the functioning of the lungs in animals and humans.
Biotic Factors
The living factors of the ecosystem are called biotic factors. Biotic factors consist of all living organisms ranging from animals and humans to plants, bacteria, and fungi. Several other factors influence biotic factors such as availability of food, presence of predators, presence of parasites, and the competition between species.
Food Availability
Animals can’t survive and reproduce without food. More food means they would survive and reproduce more and their population would increase.
Presence of Predators
Predators eat other organisms. Wolves are predators for cows and if there would be too many wolves in an ecosystem, then cow species may wipe out. So a balanced ecosystem is very necessary for the survival of the organisms. A new predator can disturb a balanced ecosystem. There are instances where a new predator was introduced in an ecosystem by authorities for recreational and other activities and it resulted in the decline of other native species.
Parasites and Pathogens
Parasites and pathogens are living organisms that live inside other organisms. The other organisms in which they live are referred to as “hosts”. Both parasites and pathogens harm the host, however, the pathogen causes disease, while parasites usually do not. They include viruses, bacteria, and macroparasites like worms.
If a new pathogen enters an ecosystem, the immune system of the population would take time to develop immunity against it and as a result, the host population may decline or wipe out. For instance, global pandemics such as Spanish flu and nowadays COVID. They are a threat to the existence of the human population.
Competition between Species
Organisms compete with each other for food, mates, territory, and other things. When several species eat the same food, they compete with each other. Animals within a species also compete with each other for mates which results in fighting and can cause serious injuries or deaths.
Interdependence
All organisms depend on each other to survive and reproduce. This phenomenon is called interdependence. This means that a change in the proportion of one species can have a significant impact on the other species in the ecosystem.
For example, a decrease in cow species would mean that there will be more grass, but the predators who eat cows will have less food and it will impact their population. If the population of earthworms would decrease it will impact the species of frogs and mice who eat them for their survival.
Parasitism and Mutualism
Parasitism is the relationship between the organisms in which one organism benefits while the other organism suffers. On the other hand, in mutualism, both organisms enjoy benefits. Head lice and worms inside the intestine wall of their hosts are some examples of parasitism.
On the other hand relationship between bees and the plant is the perfect example of mutualism. Bees obtain nectar from plants and spread the pollen from one flower to another which helps reproduction in plants. Different fish species also depict mutualism. Much small fish referred to as cleaner fish eat dead skin and the parasites of the larger fish. In return, they get protected from falling prey to other organisms.
Adaptations
Different species of organisms make behavioural, structural, or physical adaptations to survive in an ecosystem. These adaptations can result in altered genes and new species. Giraffes have a long neck that helps them in eating food and looking for predators.

Biodiversity
The variety of the organisms living in the ecosystem is called Biodiversity. Biodiversity is very important because different species depend on each other directly or indirectly. Biodiversity ensures a balanced ecosystem which is vital for the existence of humans and different species. Many human activities are negatively impacting biodiversity. Examples of these activities include deforestation, releasing of harmful chemicals by industries, high population growth, and other human actions that should be examined and controlled to maintain biodiversity.
Summarise with AI:













i like the article
Hi Sam! Thank you! Great to hear that you found this resource useful.
welcome
Hi Suunu! Thanks for reaching out. Hope you’ve found this resource useful 😊!
i have learnt a lot which i did not know
am senior three student but this is cool
Am impressed
Am impressed
learning is the best