Chapters

Definition of a Rational Number
Rational numbers are of the form
$\frac{a}{b}$ with the special case that $b\neq0$
because division by $0$ is meaningless (undefined)
where $a$ is any integer and $b$ is any integer other than $0$
$a, b\in\mathbb{Z}$ with $b\neq0$
Recall that the Integers $\mathbb{Z}$ are the positive and negative whole numbers along with $0$.
Definition of Addition of 2 Rational Numbers
Here is a definition of the addition of Rational numbers. This is just a formula and it works.
$\frac{a}{b}+\frac{c}{d}=\frac{a\times d}{b\times d}+\frac{b\times c}{b\times d}=\frac{ac}{bd}$
Example
$\frac{3}{4}+\frac{2}{3}=\frac{3\times3}{4\times3}+\frac{2\times4}{4\times3}=\frac{9+8}{12}=\frac{17}{12}$
The best way to add 2 Rational numbers is to find the Least Common Denominator LCD between the 2 fractions. The formula does not always give the LCD, but it will reduce to the right answer. If the 2 denominators have a common factor, then their product will not be the LCD.
Commutative Property
The order in which we add 2 Rational numbers does not matter. It will always give the same sum no matter which Rational number we add to the other.
This is called the Commutative Property of Addition
$\frac{a}{b}+\frac{c}{d}=\frac{c}{d}+\frac{a}{b}$
Example
$\frac{3}{5}+\frac{2}{3}=\frac{2}{3}+\frac{3}{5}$
Addition of 3 or more Rational Numbers and the Associative Property
We add 3 or more Rational numbers in the same way, we just must account for each denominator while trying to find a common denominator.
The order in which we add the numbers together also does not matter.
This is called the Associative property of Addition
$\frac{a}{b}+(\frac{c}{d}+\frac{e}{f})=(\frac{a}{b}+\frac{c}{d})+\frac{e}{f}=\frac{c}{d}+(\frac{a}{b}+\frac{e}{f})$
Example
$\frac{3}{4}+(\frac{1}{3}+\frac{5}{6})=\frac{3}{4}+(\frac{2}{6}+\frac{5}{6})=\frac{3}{4}+\frac{7}{6}=\frac{9}{12}+\frac{14}{12}=\frac{23}{12}$
$(\frac{3}{4}+\frac{1}{3})+\frac{5}{6}=(\frac{9}{12}+\frac{4}{12})+\frac{5}{6}=\frac{13}{12}+\frac{7}{6}=\frac{13}{12}+\frac{10}{12}=\frac{23}{12}$
$\frac{1}{3}+(\frac{3}{4}+\frac{5}{6})=\frac{1}{3}+(\frac{9}{12}+\frac{10}{12})=\frac{1}{3}+\frac{19}{12}=\frac{4}{12}+\frac{19}{12}=\frac{23}{12}$$
Additive Inverse and Identity
$\frac{a}{b}+(-\frac{a}{b})=0$
$\frac{a}{b}+0=\frac{a}{b}$
a + b 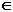

Associative:
The way in which the summands are grouped does not change the result.
(a + b) + c = a + (b + c)
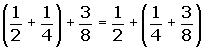
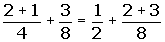
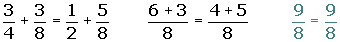
The opposite of the opposite of a number is equal to the same number.
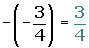
As a result of these properties, the subtraction of two rational numbers is defined as the addition of the minuend plus the opposite of the subtrahend.
a − b = a + (−b)
Find more Maths tutors near me here on Superprof.
Summarise with AI:













