Chapters
- Definition of a Fraction
- Division: Fractions as Quotients
- Rational Numbers: Ratio of Integers
- Negative Fractions
- Fractional Units
- Fractional Values
- Fractions of a Number
- Fractions: Ratios and Proportions
- Proper Fractions
- Improper Fractions
- Mixed Numbers
- Decimal Fractions
- Equivalent Fractions
- Simplifying Fractions
- Irreducible Fractions

Definition of a Fraction
Fractions are numbers that look like  where
where  because division by
because division by  is meaningless.
is meaningless.
 is the top of the fraction and is called the numerator.
is the top of the fraction and is called the numerator.
 is the bottom of the fraction and is called the denominator.
is the bottom of the fraction and is called the denominator.
Examples
All of these numbers are fractions



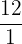
Division: Fractions as Quotients
A fraction  is also known as a quotient of
is also known as a quotient of  to
to  . A quotient of
. A quotient of  to
to  tells us to split the number
tells us to split the number  into
into  parts and it is equivalent to division.
parts and it is equivalent to division.
We may also say that  is broken into
is broken into  parts or that we divide the number
parts or that we divide the number  by
by  .
.
Example
Split  into
into  parts or perform the division of
parts or perform the division of 
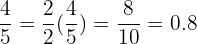
 split into
split into  parts is equivalent to saying
parts is equivalent to saying 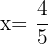 or
or 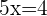 where
where 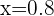
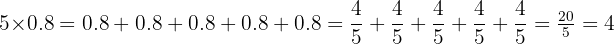
Rational Numbers: Ratio of Integers
Many fractions are also Rational numbers. The Rational Numbers 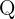 are a special case of fractions where
are a special case of fractions where  is any integer and
is any integer and  is any integer besides
is any integer besides  . The Integers
. The Integers 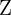 are the positive and negative whole numbers along with
are the positive and negative whole numbers along with  , like on a number line.
, like on a number line.

The Rational in Rational number means that there is a ratio between the two numbers  and
and  . The big
. The big 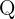 stands for quotient. The big
stands for quotient. The big 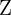 for the Integers is from the German word for numbers 'zahlen'.
for the Integers is from the German word for numbers 'zahlen'.
There are many fractions that are not rational, not the ratio of 2 integers. These numbers are called irrational numbers and have a decimal value that is never-ending (infinite) and non-repeating.
We will be sticking to fractions that are Rational numbers throughout these lessons.
Negative Fractions
If a fraction is negative, we put the negative sign in the numerator or out in front of the fraction itself
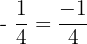
If the negative sign happens to be in the denominator, don't write 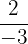 .
.
Move the negative sign up top or out front
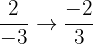
Fractional Units
A fractional unit is 'one part  numerator' of the 'whole'.
numerator' of the 'whole'.
The 'whole' is the number that we 'split the number  into', which is the denominator.
into', which is the denominator.
Example

The green shaded box represents 'one part' of the entire thing, which is 'split' into  parts.
parts.
The 'whole' thing would be  .
.
Example
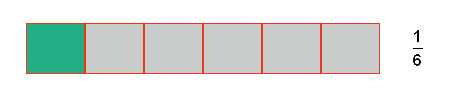
The green shaded box represents  unit out of
unit out of  total units that make up the 'whole' thing.
total units that make up the 'whole' thing.
There are  of these fractional units
of these fractional units  that make up the object.
that make up the object.
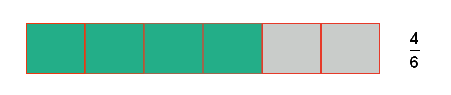
Fractional Values
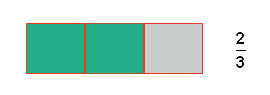
Example
The green boxes represent  of the whole amount or
of the whole amount or  parts out of
parts out of  .
.
Example
The green boxes represent  of the whole amount or
of the whole amount or  parts out of
parts out of  .
.
Fractions of a Number
We can take fractional amounts of numbers other than  . We can look at it as a multiplication exercise, a division exercise or a mixture of both.
. We can look at it as a multiplication exercise, a division exercise or a mixture of both.
Example
What is  of
of  ?
?
Multiplication
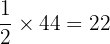
Division
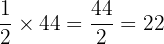
Example
What is  of
of  ?
?
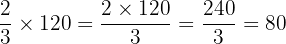
or
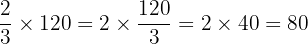
Fractions: Ratios and Proportions
When comparing different amounts or types of the same thing, you can form fractions from the ratios or proportions.
Example
Suppose we have  crayons:
crayons:  blue
blue  red
red  green
green  yellow.
yellow.
The  crayons can be placed in a
crayons can be placed in a 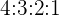 ratio of blue : red : green : yellow.
ratio of blue : red : green : yellow.
We can form 4 fractions: 1 for the amount that each color of crayon is of the whole amount of crayons 
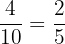 are blue
are blue
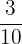 are red
are red
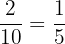 are green
are green
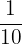 are yellow
are yellow
Proper Fractions
Proper fractions have the values of their numerators less than the value of their denominators.
They have a value greater than  and less than
and less than  if positive
if positive
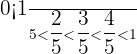
They have a value less than  and greater than
and greater than  if negative
if negative
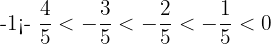
Improper Fractions
Improper fractions are fractions that have their numerators larger than their denominators, which means they have a value greater than 1.
Examples


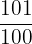
Mixed Numbers
A mixed number is the union of an integer and a fractional amount less than  .
.
They are equivalent to their improper fractional form.
Example
Express 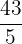 as a mixed number.
as a mixed number.
Divide the numerator  by the denominator
by the denominator  to obtain the highest whole number amount that will divide into it evenly.
to obtain the highest whole number amount that will divide into it evenly.
Here it is  because
because 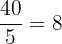 .
.
The remainder  is then the numerator of the fraction less than
is then the numerator of the fraction less than  that we attach next to the whole number,
that we attach next to the whole number,  .
.
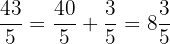
Decimal Fractions
Decimal fractions have a power of  in the denominator.
in the denominator.
Example
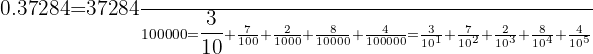
Equivalent Fractions
2 fractions  and
and  are equivalent if and only if the product of the extremes equals the product of the means
are equivalent if and only if the product of the extremes equals the product of the means
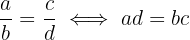
 and
and  are known as the extremes, while
are known as the extremes, while  and
and  are known as the means
are known as the means
Example
Determine whether 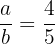 is equivalent to
is equivalent to 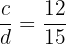
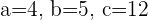 and
and 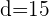
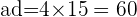 and
and 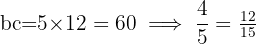
Simplifying Fractions
Most often we want fractions to be in simplest form. This means that the fraction is in lowest terms.
Lowest terms means that the numerator and denominator have no common factors or are relatively prime.
Example
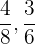 and
and  are not in lowest terms but are all equal to
are not in lowest terms but are all equal to  .
.
Both the numerators and denominators of each fraction have a common factor.
In  , both the
, both the  and the
and the  have
have  as a common factor.
as a common factor.
In  , both the
, both the  and the
and the  have
have  as a common factor.
as a common factor.
In  , both the
, both the  and the
and the  have
have  as a common factor.
as a common factor.
The simplified form of each of these fractions is  .
.
Example
Is 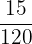 in lowest terms?
in lowest terms?
In 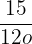 , both
, both  and
and  have the common factor of at least
have the common factor of at least  .
.
Actually, they both have the factor  in common
in common
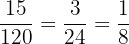
We first factored out a  to make
to make 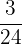 and then factored out another
and then factored out another  to make
to make  and
and 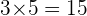 .
.
Example
Is 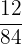 in lowest terms?
in lowest terms?
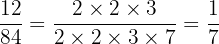
We took the Prime Factorization of both  and
and  and cancelled out the common factors of
and cancelled out the common factors of 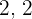 and
and  .
.
Irreducible Fractions
Irreducible fractions are those that cannot be simplified any further (the numerator and denominator are in lowest terms). The numerator and denominator do not have any common factors and are called co-prime.
Examples
All of these fractions are irreducible or in lowest terms


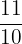
Summarise with AI:













