Chapters

Definition of Rational Numbers
Rational numbers are of the form
 with the special case that
with the special case that 
because division by  is meaningless (undefined)
is meaningless (undefined)
where  is any integer and
is any integer and  is any integer other than
is any integer other than 
 with
with 
Recall that the Integers  are the positive and negative whole numbers along with
are the positive and negative whole numbers along with  .
.
Division of 2 Rational Numbers
One should be familiar with the process of multiplying 2 fractions
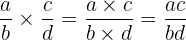
before moving forward with the lesson.
When we want to divide one Rational number  by another
by another 
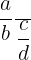
we need to simplify the expression by converting it into an equivalent one that involves only multiplication.
Multiplication by the Reciprocal of the Denominator
In the compound fraction
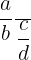
the Rational number  is the denominator, meaning the denominator is itself a fraction.
is the denominator, meaning the denominator is itself a fraction.
This complicated form of a compound fraction that occurs in a division problem can be simplified by 'flipping' the fraction in the denominator
 becomes
becomes 
When we 'flip' a fraction, we call it taking the reciprocal of that fraction
the reciprocal of  is
is 
We then multiply the new 'flipped' fraction  by the original numerator, the fraction
by the original numerator, the fraction 
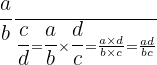
This rids us of the denominator in the complicated looking compound fraction and turns the problem into an equivalent one involving only multiplication.
Example
Divide  by
by 
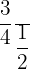
First we flip the bottom fraction 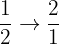
Then we multiply that by the top fraction 
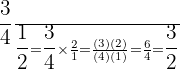
Example
Divide  by
by 
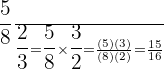
Example
Divide  by
by 
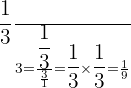
Notice that we could have just multiplied the 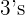 together and gotten the same answer
together and gotten the same answer
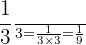
Example
Divide  by
by 
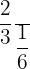
What is the problem asking for?
Basically it's asking how many 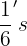 are in
are in  or how many of the bottom fraction are in the top fraction.
or how many of the bottom fraction are in the top fraction.
We know that
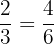
and now we can ask how many 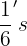 are in
are in  ?
?
It should be plain to see that there are four 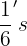 in the fraction
in the fraction  , just like there are three
, just like there are three 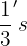 in
in 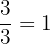 .
.
Rational Numbers and Division
The Rational Numbers 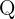 are the first set of numbers that allow us to introduce and use the operation of division. This essentially means that the Rationals are the first set of numbers that let us divide one integer by another integer and have that number always exist as another Rational.
are the first set of numbers that allow us to introduce and use the operation of division. This essentially means that the Rationals are the first set of numbers that let us divide one integer by another integer and have that number always exist as another Rational.
Just as the introduction of the Integers lets us extend our Algebraic operations to include subtraction (alongside addition and multiplication) by allowing the use of negative whole numbers, the introduction of the Rational Numbers does the same for division.
Find more Maths teacher here on Superprof.
Operations with Integers
If we add, subtract or multiply any integer by one or more other integers, that number will also always be an integer.
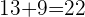
 and
and  are integers and their sum
are integers and their sum  is also an integer
is also an integer

 and
and  are integers and their difference
are integers and their difference  is also an integer
is also an integer
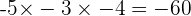
 ,
,  and
and  are all integers and their product
are all integers and their product  is also an integer
is also an integer
Division Counterexample with Integers
 and
and  are both integers, but whether we divide
are both integers, but whether we divide  by
by 
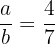
or divide 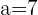 by
by 
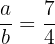
neither answer is also an integer.
Summarise with AI:













