Chapters

Definition of a Rational Number
Rational numbers are of the form
 with the special case that
with the special case that 
because division by  is meaningless (undefined)
is meaningless (undefined)
where  is any integer and
is any integer and  is any integer other than
is any integer other than 
 with
with 
Recall that the Integers  are the positive and negative whole numbers along with
are the positive and negative whole numbers along with  .
.
Definition of Multiplication of 2 Rational Numbers
The multiplication of 2 Rational numbers is performed the same way as other forms of multiplication.
With Rational numbers, we multiply the numerators together and the denominators together to form a new Rational number
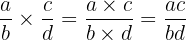
Example
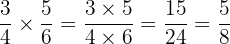
Commutative Property
The order that we multiply 2 Rational numbers does not matter.
This is a consequence of the operation of multiplication. It is the same for Natural Numbers and Integers.
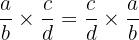
Example
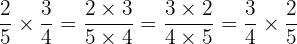
Also take note that we can form 2 fractions that are entirely different than the ones that we started with by using this property
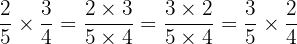
or
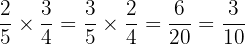
Multiplication of 3 or more Rational Numbers and the Associative Property
The property of commutativity extends to the multiplication of 3 or more Rational numbers. It also does not matter which 2 Rational numbers we multiply first, we will always get the same product.
This is called the Associative Property of Multiplication
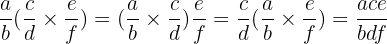
Example
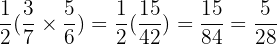
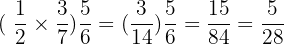
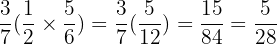
Distributive Property
We may encounter a problem where we need to multiply a sum of Rational numbers by another Rational number. We can just multiply each part of the sum by the number on the outside and then perform the sum.
This process is called distribution and the property is called the Distributive Property
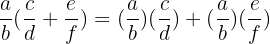
Example
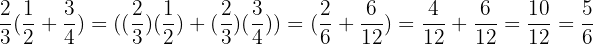
Multiplicative Inverse and Identity
The inverse of a Rational number  is
is 
the inverse of  is
is 
If we multiply a Rational number by its inverse, the product is 
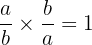
This is the Multiplicative Inverse of a Rational number.
Example
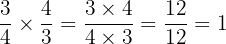
 is the Multiplicative Identity of any rational number. This means the product of a Rational number
is the Multiplicative Identity of any rational number. This means the product of a Rational number  and
and  is just
is just  .
.
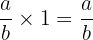
There are many different ways to form a Rational number that is equivalent to 
Examples
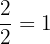
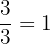
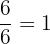
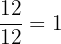
Common Factors
We can sometimes pull out a common factor of a multiplication problem to simplify it
Example
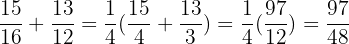
Summarise with AI:













