In statistics, it’s often useful to describe how data is spread out — not just where the average lies.
That’s where quartiles, deciles, and percentiles come in. These are ways of dividing an ordered data set into equal parts, helping us understand how values compare to the rest.
- Quartiles divide data into 4 equal parts.
- Deciles divide data into 10 equal parts.
- Percentiles divide data into 100 equal parts.
Each measure tells us the position of a value in a dataset — for example, a test score at the 80th percentile means that 80% of students scored lower.

Percentiles
A percentile indicates the value below which a given percentage of data falls.
If you are at the 70th percentile, that means 70% of the data values are below your score.
Formula to Find the Percentile Position
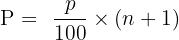
Where:
- P = position (or index) in the ordered dataset
- p = desired percentile (e.g. 25, 50, 90)
- n = number of data values
Example 1: Finding a Percentile
The following are the test scores (out of 100) of 10 students, arranged in ascending order:
| Observation Number | Score |
|---|---|
| 1 | 15 |
| 2 | 22 |
| 3 | 24 |
| 4 | 27 |
| 5 | 32 |
| 6 | 36 |
| 7 | 40 |
| 8 | 41 |
| 9 | 50 |
| 10 | 90 |
Find the 70th percentile.
Step 1: Use the formula for position.
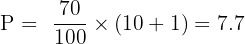
The 70th percentile lies between the 7th and 8th scores.
Step 2: Interpolate between the 7th and 8th values.
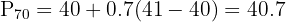
The 70th percentile is approximately 40.7.
That means 70% of students scored below about 41 marks.
Quartiles
Quartiles split data into four equal parts, each containing 25% of the observations.
| Quartile | Symbol | Percentile Equivalent | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Quartile | Q1 | 25th | 25% of data below |
| 2nd Quartile | Q2 | 50th | Median (50% below) |
| 3rd Quartile | Q3 | 75th | 75% of data below |
| 4th Quartile | Q4 | 100th | Maximum value |
Formula for Quartiles
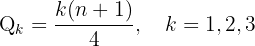
Example 2: Finding Quartiles
Using the same test score dataset:
| Score | 15 | 22 | 24 | 27 | 32 | 36 | 40 | 41 | 50 | 90 |
Find Q₁, Q₂, and Q₃.

Between the 2nd and 3rd values (22 and 24):
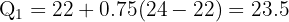
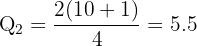
Between the 5th and 6th values (32 and 36):
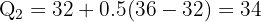

Between the 8th and 9th values (41 and 50):

Quartiles: Q₁ = 23.5, Q₂ = 34, Q₃ = 43.25
Deciles
Deciles divide a dataset into 10 equal parts, each representing 10% of the ordered data.
| Decile | Percentile Equivalent | Percent of Data |
|---|---|---|
| D1 | 10th | 10% |
| D2 | 20th | 20% |
| D3 | 30th | 30% |
| D4 | 40th | 40% |
| D5 | 50th | 50% |
| D6 | 60th | 60% |
| D7 | 70th | 70% |
| D8 | 80th | 80% |
| D9 | 90th | 90% |
Formula for Deciles
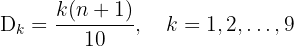
Example 3: Finding the 6th Decile
Using the same test score dataset:
| Score | 15 | 22 | 24 | 27 | 32 | 36 | 40 | 41 | 50 | 90 |
Find D₆.
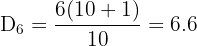
Between the 6th and 7th values (36 and 40):
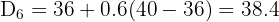
The 6th decile is 38.4, meaning 60% of students scored below approximately 38 marks.
Practice Questions and Solutions
Find the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd quartiles for:
12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 30, 33, 35, 40
n = 9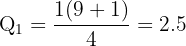
Between 2nd and 3rd values (15 and 18):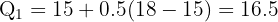
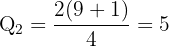
5th value = 24 → Q₂ = 24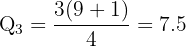
Between 7th and 8th values (33 and 35):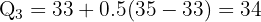
Q₁ = 16.5, Q₂ = 24, Q₃ = 34
For the data:
20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 60, 70, 80
Find the 7th decile and 85th percentile.
n = 10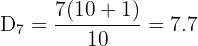
Between 7th and 8th values (50 and 60):
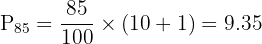
Between 9th and 10th values (70 and 80):
✅ D₇ = 57, P₈₅ = 73.5
Exam results:
25, 28, 30, 33, 37, 40, 41, 45, 49, 52, 55, 60
Find Q₂ (median) and Q₃.
n = 12
Between 6th and 7th values (40 and 41):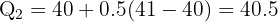
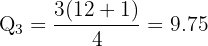
Between 9th and 10th values (49 and 52):
✅ Q₂ = 40.5, Q₃ = 51.25
Summarise with AI:












Can you help me answer my activities