
Introduction
A circle is defined as the locus (set) of all points in a plane that are a fixed distance from a fixed point.
- The fixed point is called the centre (a,b).
- The fixed distance is called the radius (r).
We derive the equation of a circle using the distance formula (Pythagoras' Theorem). If a point P(x,y) is on the circle, the distance from the centre (a,b) to P must be equal to the radius r.
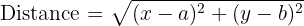
Since the distance is r, we square both sides to remove the square root. This gives us the Standard Equation of a Circle:
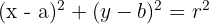
Sometimes, you will see the equation written in General Form:
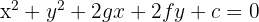
To work with the general form, we usually use "completing the square" to convert it back to the standard form.
How to Solve Circle Problems
When facing a circle geometry problem, your primary goal is almost always to find two things: the centre and the radius. Once you have these, you can write the equation.
Here is a simple checklist for common scenarios:
- If given the diameter: The centre is the midpoint of the diameter; the radius is half the length of the diameter.
- If given a tangent: The radius is the perpendicular distance from the centre to the tangent line.
- If given three points: You can set up simultaneous equations to solve for the centre (a, b) and radius r.
- If given the General Form: Use "completing the square" to rearrange it into the Standard Form so you can read off the centre and radius.
Practice Questions & Solutions
Calculate the equation of the circle that has its centre at (2, -3) and has the x-axis as a tangent.
If the x-axis is a tangent, the circle just touches the line y = 0.
The radius is the vertical distance from the centre to the x-axis.
Centre is (2, -3).
Vertical distance to y=0 is |-3| = 3.
So, radius r = 3.
Substitute into the standard equation:
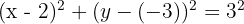
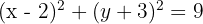
Calculate the equation of the circle that has its centre at (-1, 4) and has the y-axis as a tangent.
If the y-axis is a tangent, the circle just touches the line x = 0.
The radius is the horizontal distance from the centre to the y-axis.
Centre is (-1, 4).
Horizontal distance to x=0 is |-1| = 1.
So, radius r = 1.
Substitute into the standard equation:
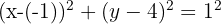
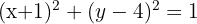
Calculate the equation of the circle which is centred at the point of intersection of the lines x + y = 4 and x - y = 2, and has a radius of 5.
First, find the centre by solving the simultaneous equations.
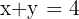
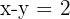
Add the two equations:
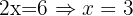
Substitute x=3 into equation 1:
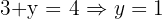
The centre is (3, 1). The radius is 5.
Equation:
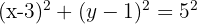
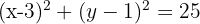
The ends of the diameter of a circle are the points A(-5, 3) and B(3, 1). What is the equation of this circle?
The centre is the midpoint of the diameter AB.
Midpoint formula:
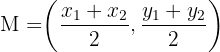
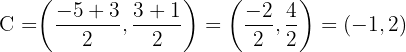
The radius is the distance from the centre (-1, 2) to point B(3, 1).
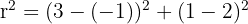
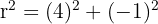
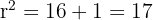
Equation:
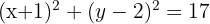
Find the equation of the circle that passes through points A(2, 1) and B(-2, 3) and has its centre on the line x + y = 4.
Let the centre be (a, b).
Since the centre lies on x + y = 4, we can write b = 4 - a. So the centre is (a, 4-a).
The distance from the centre to A equals the distance from the centre to B (both are radii).
Using distance squared:
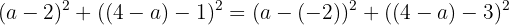
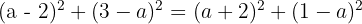
Expand:
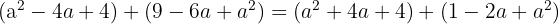
Simplify:
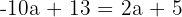

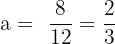
Find b:

Now find radius squared using point A:
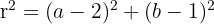
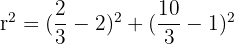

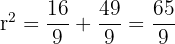
Equation:
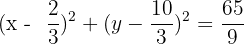
Summarise with AI:












Good.