Chapters
In chemistry, all substances are either elements, compounds, or mixtures. Understanding the differences between them is a key part of GCSE science.
Key Definitions
An element is made of only one type of atom.
A compound is made when two or more elements are chemically joined together.
A mixture is made when two or more substances are put together without a chemical reaction.

The best Science tutors available
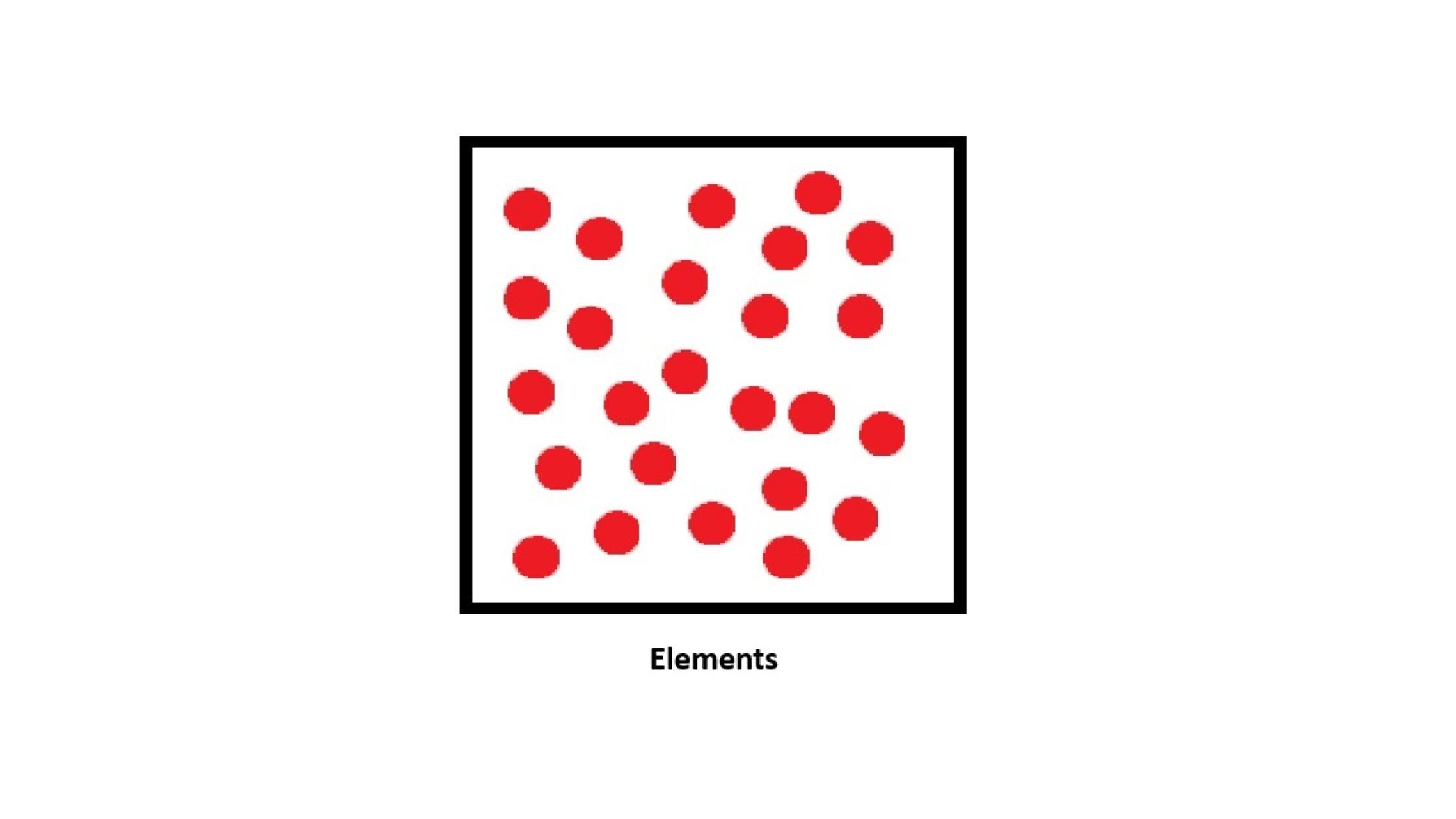
What is an Element?
- An element is a pure substance made of only one type of atom.
- It cannot be broken down into anything simpler by chemical means.
- Each element is identified by its atomic number (the number of protons in its atoms).
Examples:
- Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O), Nitrogen (N)
- Some elements use two-letter symbols, e.g. Calcium (Ca), Iron (Fe), Sodium (Na).
Elements can be:
- Metals, non-metals, or metalloids (depending on their properties).
- Found in different states at room temperature (most are solids, but some are liquids or gases).
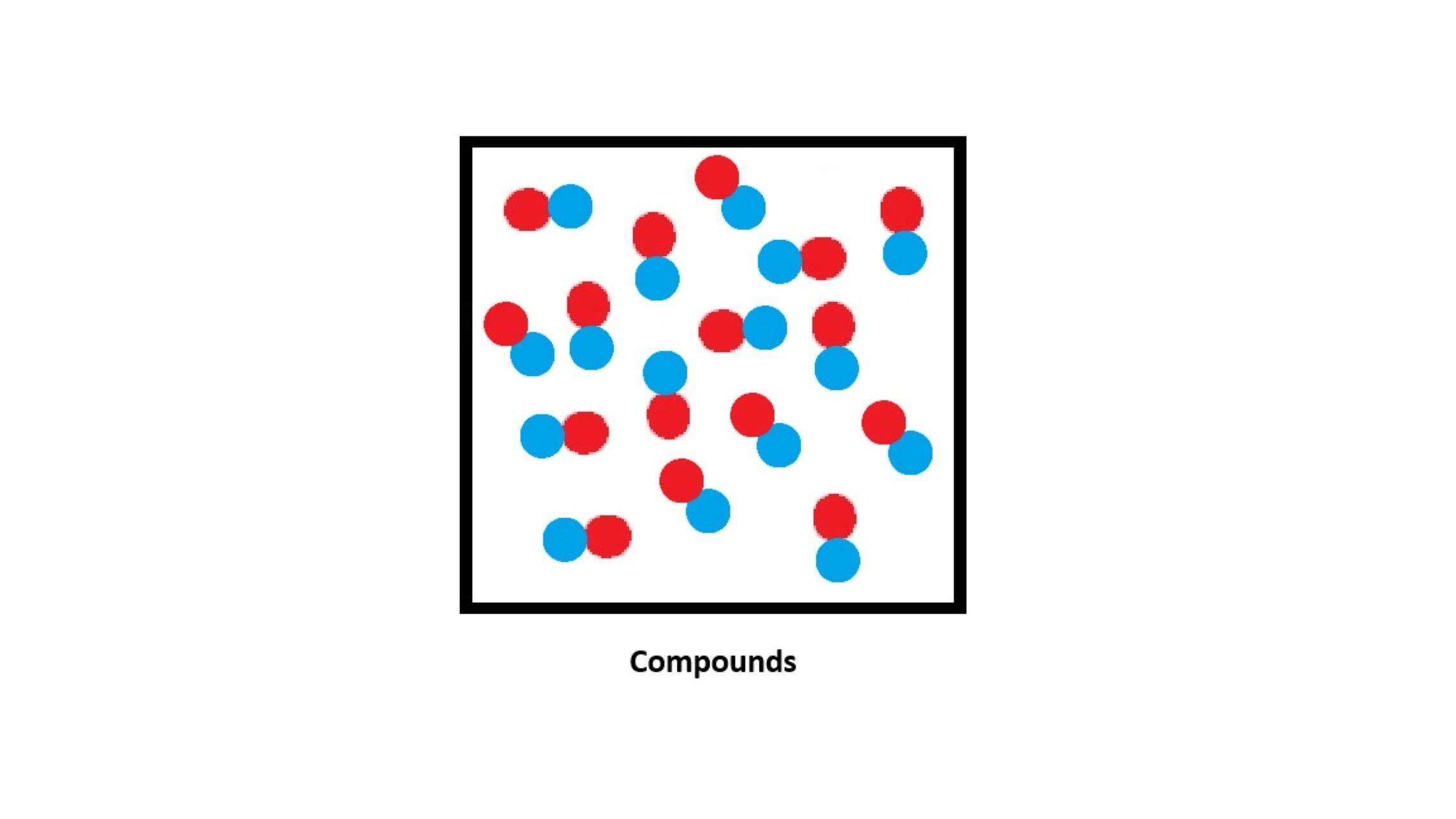
What is a Compound?
- A compound is a pure substance made when two or more elements are chemically joined together.
- Compounds always have a fixed ratio of elements.
- They have different properties from the elements they are made of.
Example:
- Water (H₂O) is made from hydrogen and oxygen.
- Hydrogen and oxygen are gases at room temperature.
- Water is a liquid with completely different properties.
Compounds are represented by chemical formulas, e.g.
- CO₂ = Carbon dioxide (1 carbon atom + 2 oxygen atoms).
- NaCl = Sodium chloride (1 sodium atom + 1 chlorine atom).
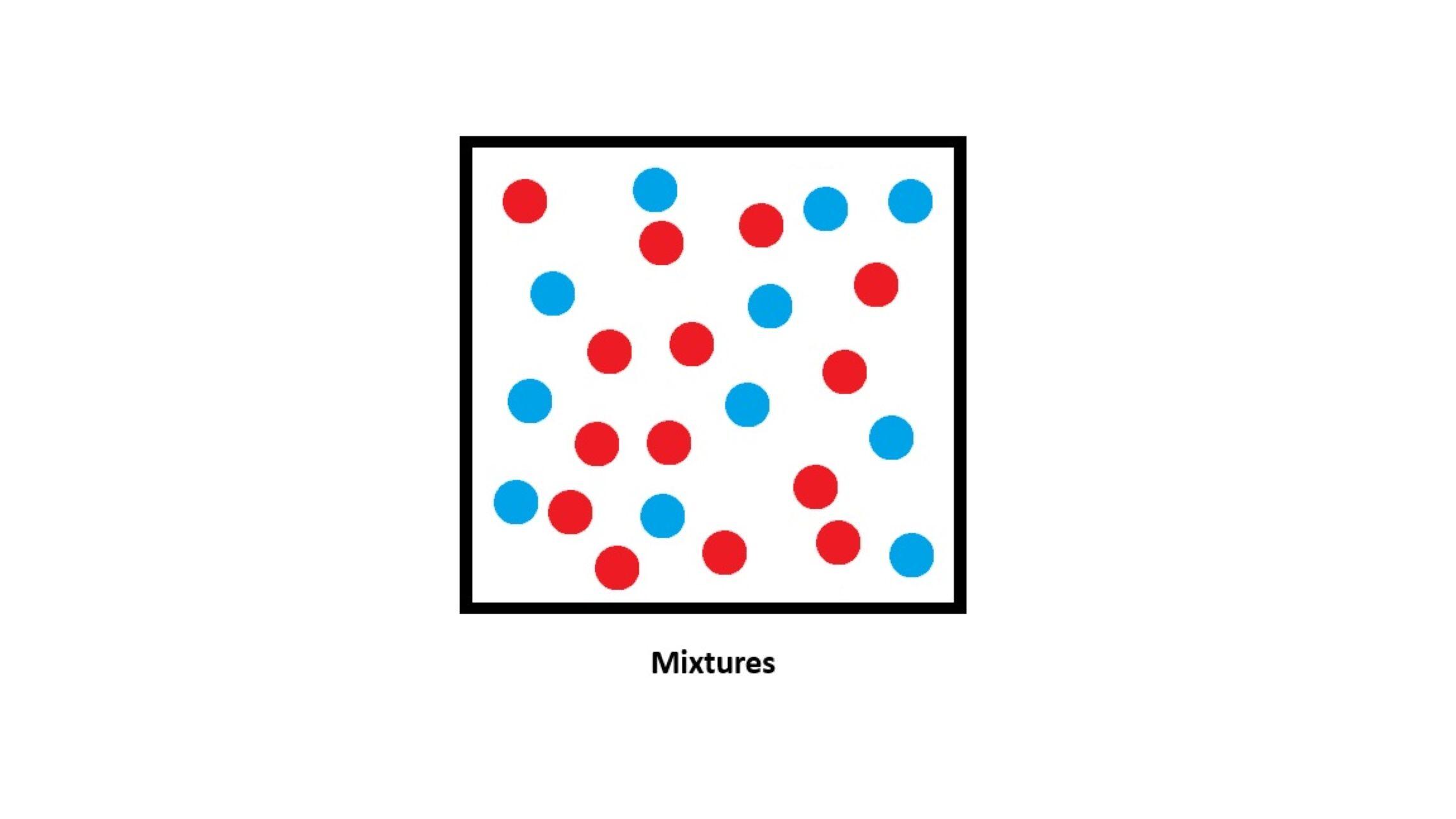
What is a Mixture?
- A mixture is made when two or more substances are put together without a chemical reaction.
- The substances keep their own properties.
- The composition can vary (you can have more or less of each substance).
Examples:
- Air (a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and other gases).
- Salt water (a mixture of salt and water).
Mixtures can be separated by physical methods, e.g. filtration, evaporation, distillation, or magnetic separation.
Key Differences Table
| Feature | Element | Compound | Mixture |
|---|---|---|---|
| Made of | One type of atom | Two or more elements chemically joined | Two or more substances not chemically joined |
| Can it be broken down? | No | Yes – by chemical reactions | Yes – by physical methods |
| Properties | Same as the element itself | Different from elements it’s made of | Keeps properties of components |
| Composition | Fixed (one atom type only) | Fixed ratio of elements | Variable (can change amounts) |
| Example | Oxygen (O₂) | Water (H₂O) | Air |
Conclusion
- Elements are the simplest substances, made of only one type of atom.
- Compounds are substances formed by chemical bonds between elements, with fixed compositions.
- Mixtures are physical combinations of substances, with no fixed ratios, and can be separated.
Understanding the differences between them is an essential foundation for GCSE Chemistry.
Summarise with AI:












Lithium is used in place of Fluorine
Hi Madan. You’re right to point that out – thanks very much for your comment!
amazing side
It’s very educative,I learnt alot thanks ❤️
Was very educative and help. Gave me a broader understanding of the topic