Chapters
Welcome to the world of ionic compounds! These remarkable structures are more than just a jumble of atoms - they're intricate arrangements of charged ions that come together to form substances with fascinating properties. From the salt on your dinner table to the advanced materials in your smartphone, ionic compounds are everywhere, influencing various aspects of our daily lives. So, buckle up as we dive deep into these incredible compounds' structure, properties, and real-world applications. Read on below to find out more.

Ionic Compounds: The Building Blocks of Matter
Essentially, ionic compounds are structures formed when cations and anions come together. From here, these ions are then held together by strong electrostatic forces in a crystal lattice structure. This lattice structure is a repeating pattern extending in three dimensions, giving the compound unique properties, such as high melting points and specific solubility behaviours. Moreover, these compounds are often formed when a metal reacts with a non-metal, leading to various compounds with differing properties. For example, sodium chloride (NaCl) is a typical ionic compound formed from sodium and chlorine ions. Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) is another example widely used in antacids and as a food additive.
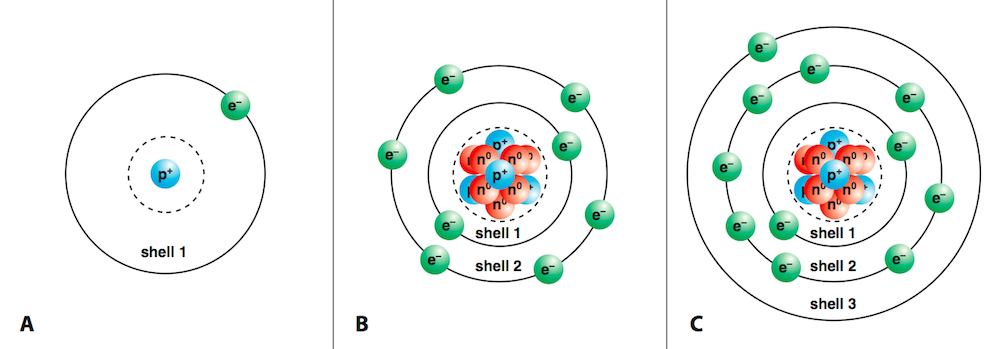
A Unique Crystal Lattice Type Structure
The lattice structure in ionic compounds is what makes them stand out. It's not just any random arrangement - it resembles a well-organized, three-dimensional pattern. This structure is crucial to the compound's unique characteristics and affects everything from its strength to its interaction with light. And breaking those electrostatic solid forces that hold the ions together requires massive energy. This is precisely why ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points - the energy needed to break these forces is substantial, making them stable at higher temperatures.
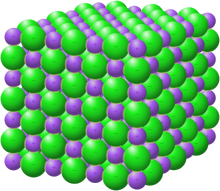
The Unique Electrical Properties of Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds have unique electrical properties and are not conductive in their solid state. This is because the ions are fixed in their positions within the crystal lattice and cannot move freely. However, when these compounds are melted or dissolved in a solution, they become excellent conductors of electricity. Why? This is because the ions are now free to move around, allowing them to carry an electrical charge. This characteristic plays a considerable role in crafting electrolytes for batteries and many other electrical products and equipment.
How Ionic Compounds Interact with Water
Ionic compounds are highly soluble in polar solvents like water. The partial charges present in water molecules can disrupt the ionic lattice, pulling the compound apart and allowing it to dissolve. This process, known as solvation, is essential in many chemical reactions and industrial processes. They dissolve so well in water due to the polar nature of water molecules. Essentially, the water molecule's positive and negative ends interact with the compound's respective ions, which speeds up the dissolution process. Due to this, ionic compounds are regularly used in water treatment processes and creating various solutions used in laboratories and industries.
A Splash of Color: Ionic Compounds and Light
Did you know ionic compounds are colourful due to their interaction with light? The crystal lattice's unique light-absorbing qualities make these compounds ideal for vibrant paints, dyes, and even eye-catching ceramics and glassware.
The Pros and Cons of Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds have several different advantages. For example, because of their high melting and boiling points, they are ideal candidates for high-temperature applications, as mentioned above. Additionally, their ability to conduct electricity when molten or dissolved makes them useful in various electrical applications. That being said, ionic compounds do have their limitations. First and foremost, they can't conduct electricity in their solid state, which can be a significant disadvantage in specific electrical applications. They are also generally brittle and lack the mechanical strength needed for some industrial uses. Last but not least, their high solubility can sometimes be a drawback, especially if they dissolve in environments where they shouldn't, which can lead to potential complications.
The Environmental Side of Ionic Compounds
While ionic compounds offer numerous benefits, it's crucial to consider their environmental effect on the world. Unfortunately, many ionic compounds, such as road salts, can harm aquatic life if they enter large bodies of water. Additionally, the production of certain ionic compounds can also create harmful waste or use a lot of energy, both of which are bad for the environment in general. Therefore, the implementation of sustainable practices is increasingly important in the production and application of these compounds.
Ionic Compounds in Healthcare
In medicine, ionic compounds are often used as antiseptics and in various pharmaceuticals. For example, silver nitrate is one such ionic compound used in carintoftakends. Additionally, some ionic compounds are used in medical imaging procedures, serving as contrast agents that help improve image quality. Barium sulfate is another typical example used as a contrast agent in gastrointestinal X-ray procedures in hospitals.
What are Complex Ionic Compounds?
Complex or polyatomic ionic compounds add another layer to the world of ionic compounds. These compounds often have unique properties and various uses, from industrial applications to household products. For example, ammonium carbonate ((NH4)2CO3) is used in various applications, including the food industry as a leavening agent. In addition, other complex ionic compounds are used in fertilizers to provide essential nutrients to plants.
Conclusion
In summary, ionic compounds are formed when cations and Anions come together and are held by strong electrostatic forces in a crystal lattice structure. What's more, they have unique properties like high melting and boiling points, solubility in water, and electrical conductivity when melted or dissolved. However, they also have plenty of limitations, such as their inability to conduct electricity in solid form and potential environmental concerns.
Summarise with AI:












Lithium is used in place of Fluorine
Hi Madan. You’re right to point that out – thanks very much for your comment!
amazing side
It’s very educative,I learnt alot thanks ❤️
Was very educative and help. Gave me a broader understanding of the topic