Chapters
Get ready to explore the fascinating world of gravitational potential energy! In this article, we'll dive into the depths of this concept, unraveling its definition, and discovering how it's calculated. Hold onto your seats as we take a thrilling journey through the various factors that affect this energy, and unravel the mysteries of one of the most fundamental forces in the universe. So, buckle up and get ready to embark on an exciting adventure into the fascinating world of gravitational potential energy!

Gravitational Potential Energy Defined
We can define gravitational potential energy as:
Energy possessed by an object by virtue of its height in a gravitational field is known as gravitational potential energy
Gravitational potential energy (GPE) is the energy that an object possesses due to its position in a gravitational field. It is the energy an object has because of its height above a reference point, usually the ground. The higher the object is, the more GPE it has. GPE is a form of potential energy because it has the potential to be converted into kinetic energy as the object falls or is lowered. Hence, we can conclude that:
- When an object is raised to a higher position, energy is transferred to its gravitational potential store.
- Conversely, when an object falls, energy is transferred away from its gravitational potential store.
Examples of GPE From Everyday Life
Some examples of gravitational potential energy from everyday life are given below:
An individual on the slide
A person at the top of a slide has GPE, which is converted to kinetic energy as they slide down.
A book on the shelf
A book on a high shelf has GPE, which is converted to kinetic energy if it falls off the shelf.
A rollercoaster on the top of the hill
A rollercoaster at the top of a hill has GPE, which is converted to kinetic energy as it goes down the hill.
A moving pendulum
A pendulum at its highest point has GPE, which is converted to kinetic energy as it swings back and forth.
A child on the swing
A child on a swing at its highest point has GPE, which is converted to kinetic energy as they swing back and forth.
Calculating Gravitational Potential Energy
Now, we will see how to calculate the gravitational potential energy.
The following equation is used to calculate the gravitational potential energy, 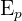 , on an object:
, on an object:
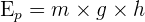
Here:
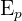 represents the gravitational potential energy. The unit of GPE is joules (J)
represents the gravitational potential energy. The unit of GPE is joules (J)- m represents mass of an object is kilograms (kg)
- g represents gravitational field strength in newtons per kilograms (N/kg)
- h represents height in meters (m)
Hence, to calculate GPE, you need to know the mass of the object, the height above the reference point, and the value of gravitational field strength.
Gravitational Field Strength
- Gravitational field strength is a measure of the strength of the gravitational force per unit mass at a given point in space.
- It is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude (size) and direction. Gravitational field strength is denoted by the symbol g and is measured in units of newtons per kilogram (N/kg).
- At any point in space, the gravitational field strength is determined by the mass of the object(s) that create the gravitational field and the distance from the object(s).
- The greater the mass of an object, the stronger the gravitational field it produces.
- The closer an object is to the source of the gravitational field, the stronger the gravitational field strength will be.
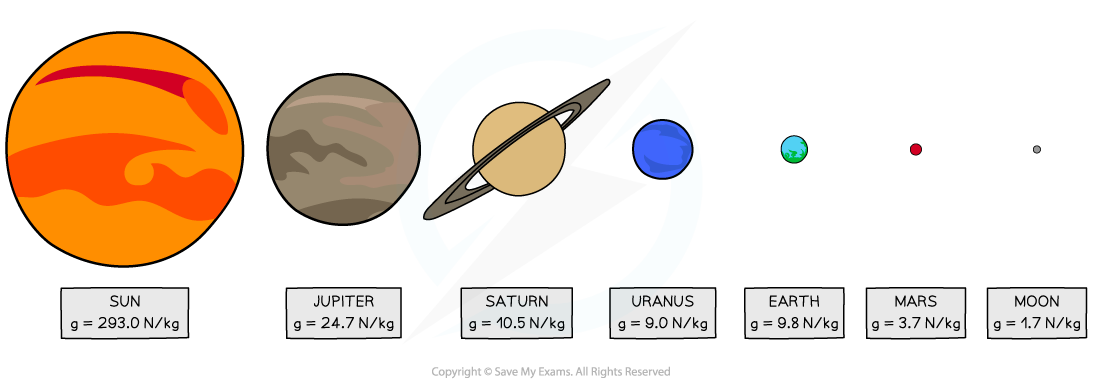
Gravitational Field Strength on Earth's Surface
- On the surface of the Earth, the gravitational field strength is approximately 9.8 N/kg, which means that an object with a mass of 1 kg experiences a force of approximately 9.8 N due to gravity.
- Gravitational field strength is an important concept in understanding the behavior of objects under the influence of gravity, such as the motion of planets, satellites, and other celestial bodies.
Gravitational Field Strength on Surface on Moon
- The surface of the Moon has a lower gravitational field strength than that of the Earth, which implies that lifting a mass on the Moon is easier compared to the Earth.
- On the other hand, the surface of gas giants like Jupiter and Saturn has a higher gravitational field strength than that of the Earth, which means that lifting a mass on the gas giants is harder compared to the Earth.
Now, we will solve some examples in which we will calculate gravitational potential energy using the above equation.
Example 1
Calculate the gravitational potential energy of a 10 kg object when it is lifted to a height of 5 meters above the ground.
Solution
Given, mass (m) = 10 kg
Height (h) = 5 m
Gravitational field strength on the surface of earth (g) = 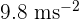
Using the formula for gravitational potential energy:
GPE = mgh
GPE = 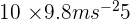
GPE = 490 J
Therefore, the gravitational potential energy of the object is 490 joules when it is lifted to a height of 5 meters above the ground.
Example 2
What is the gravitational potential energy of a 2 kg object when it falls from a height of 10 meters?
Solution
Given, mass (m) = 2 kg height
(h) = 10 m
Gravitational filed strength on the surface of Earth = 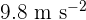
Using the formula for gravitational potential energy:
GPE = mgh
GPE = 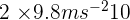
GPE = 196 J
Therefore, the gravitational potential energy of the object is 196 joules when it falls from a height of 10 meters.
Example 3
What is the mass of an object if it has a gravitational potential energy of 100 J and is at a height of 2 meters above the ground?
Solution
Given, gravitational potential energy (GPE) = 100 J
height (h) = 2 m
Gravitational field strength on the surface of Earth= 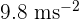
Using the formula for gravitational potential energy:
GPE = mgh
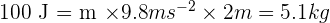
Therefore, the mass of the object is 5.1 kg when it has a gravitational potential energy of 100 J and is at a height of 2 meters above the ground.
Factors Affecting Gravitational Potential Energy
Gravitational potential energy depends on two main factors:
1. Mass of the object
The more massive an object is, the more gravitational potential energy it will possess when it is lifted to a certain height. This is because a heavier object requires more work to lift it against gravity, and hence more energy is stored in the object's gravitational potential energy.
2. Height of the object
The higher an object is lifted above the ground, the more gravitational potential energy it will have. This is because the object gains more potential energy as it is lifted against gravity to a greater height.
Additionally, the gravitational field strength also affects the gravitational potential energy of an object. The gravitational field strength varies depending on the location of the object in the universe. For example, the gravitational field strength is less on the Moon than on Earth, and this affects the gravitational potential energy of an object on the Moon.
Finally, it's important to note that gravitational potential energy is a relative measure, which means it is measured in relation to a reference point. The reference point is often chosen as the ground or a horizontal surface, but it can be any point in space.
Summarise with AI:












You are the best,, coz you have gotten content about the topics
Hello ! Glad to hear that you’ve found the content useful!