Chapters
Get ready to unlock the secrets of energy and power! In this article, we'll explore the definitions of energy and power, how to calculate them, and the units used to measure them. Moreover, we'll delve into the intriguing relationship between these two fundamental concepts. Join us for a thrilling journey through the world of physics!

What is Energy?
Energy is defined as:
"The ability of a body to do work"
It is a scalar quantity and can exist in various forms such as mechanical, electrical, chemical, nuclear, and thermal. There are different types of energy, some of which are described below:
- Kinetic energy: This is the energy of motion.
- Gravitational potential energy: This is the energy an object has due to its position in a gravitational field.
- Elastic potential energy: This is the energy stored in an object when it is stretched or compressed.
- Thermal energy: This is the energy that is associated with the temperature of an object.
- Chemical energy: This is the energy stored in chemical bonds.
- Nuclear energy: This is the energy that is released when the nucleus of an atom is split or combined with another nucleus.
- Electrical energy: This is the energy that is associated with the movement of electrons. Electrical energy can be used to power electronic devices and appliances.
- Light energy: This is the energy that is associated with electromagnetic radiation in the visible spectrum.
Unit of Energy
Energy is measured in joules (J) and is conserved, meaning that it cannot be created or destroyed, but can only be transformed from one form to another. One joule is the amount of energy needed to perform work of one newton-meter (Nm). It can also be defined as the energy transferred when a force of one newton is applied over a distance of one meter in the direction of the force.
How to Calculate Energy?
the amount of energy can be calculated using the following formula:
E = P x t
Where:
- E is the energy in joules (J)
- P is the power in watts (W)
- t is the time in seconds (s)
Alternatively, if the force and distance are known, the energy can be calculated using:
E = F x d
Where:
- E is the energy in joules (J)
- F is the force in newtons (N)
- d is the distance in meters (m)
What is Power?
Energy is transferred when work is done on an object. The measure of how fast this energy is transferred is known as power.
A more powerful device transfers a greater amount of energy in a given time, compared to a less powerful one.
Unit of Power
Unit of power is watt (W). One watt is defined as the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred when one joule (J) of energy is transferred per second (s). Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
1 W = 1 J/s
Therefore, a device with a power rating of 1 watt can transfer 1 joule of energy in 1 second or 10 joules of energy in 10 seconds. Power is a measure of how quickly energy is transferred or work is done. The higher the power rating of a device, the more energy it can transfer per unit time.
How to Calculate Power?
The formula used to calculate power is:
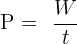
Where:
- Power (P) is measured in watts (W)
- Work done (W) is measured in joules (J)
- Time (t) is measured in seconds (s)
One watt is equivalent to one joule per second (J/s). This implies that the power increases by one watt for every additional joule transferred per second.
Example 1
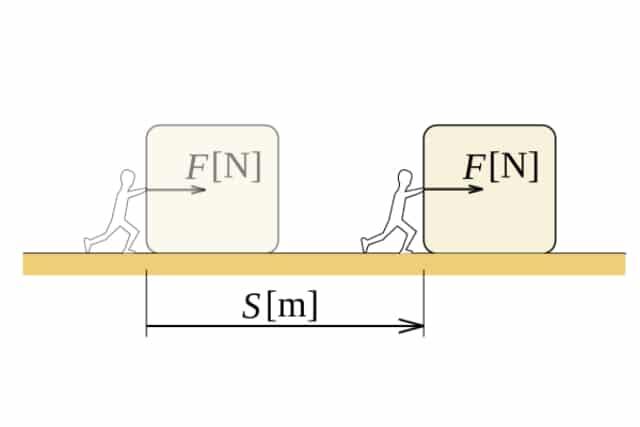
Suppose there are two electric motors that are used to lift a 3 N weight through a vertical height of 8 m. Motor one does this in 6 seconds and motor two does this in 12 seconds. Calculate powers of both the motors.
Solution
To calculate the power of each motor, we first need to calculate the amount of work done by each motor.
The amount of work done by each motor is:
Work = force x distance
Work = 3 N x 8 m = 24 J
Now, we can use the formula for power:
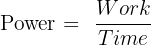
For Motor one: Power = 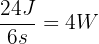
For Motor two: Power = 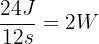
Therefore, Motor one is more powerful as it can lift the weight in a shorter amount of time and transfer more energy per second.
Example 2
A pump is used to move water from a well to a storage tank. The pump can lift 50 kg of water to a height of 10 meters in 15 seconds. Another pump can lift the same amount of water to the same height in 25 seconds. Calculate power of both the pumps.
Solution
The work done in lifting the weight is given by:
work = force x distance work = 50 N x 2 m work = 100 J
Using the given time taken by each pulley system, we can calculate the power of each system using the formula:
Power = 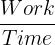
Power of pump one:
Power = 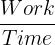
Power = 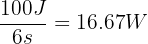
Power of pump two:
Power = 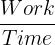
Power = 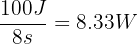
Therefore, pump one is more powerful as it has a power of 16.67 W compared to pump two which has a power of 8.33 W.
Example 3
A vacuum cleaner transfers 25,000 J of energy in 20 seconds. What is the power rating of the vacuum cleaner?
Solution
We can use the formula:
Power (P) = 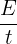
Where:
E = Energy transferred
t = time
Given that the energy transferred is 25,000 J and the time taken is 20 seconds, we can substitute these values into the formula:
P = 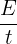
P = 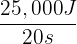
P = 1250 W
Therefore, the power rating of the vacuum cleaner is 1250 W.
Relationship Between Energy and Power
Energy and power are two important concepts in physics that are closely related. Energy is the ability to do work, while power is the rate at which work is done or the rate at which energy is transferred.
The relationship between energy and power can be expressed mathematically using the following equation:
Power = Energy ÷ Time
This means that the power of a system is directly proportional to the amount of energy it can transfer in a given time. For example, a more powerful engine can transfer more energy in a given time than a less powerful engine.
In addition, the amount of energy transferred by a system can be calculated by multiplying its power by the time during which it operates:
Energy = Power × Time
Therefore, the relationship between energy and power is crucial to understanding how energy is transferred and used in various systems.
Summarise with AI:












You are the best,, coz you have gotten content about the topics
Hello ! Glad to hear that you’ve found the content useful!