Chapters
Step into the fascinating world of the electromagnetic spectrum, where a wide range of electromagnetic waves come together to shape our everyday lives. Each type of wave serves a unique purpose, from radio and TV broadcasting to communication technologies, medical imaging, and even nuclear radiation. Join us as we explore these waves' practical uses and applications, revealing the invisible forces that drive our interconnected world. Get ready to uncover the secrets of the electromagnetic spectrum and how it impacts our daily experiences.

Electromagnetic Spectrum
"The electromagnetic spectrum comprises of an uninterrupted (continuous) range of wavelengths"
It includes different types of radiation, each with its uses and risks, determined by their wavelength and frequency.
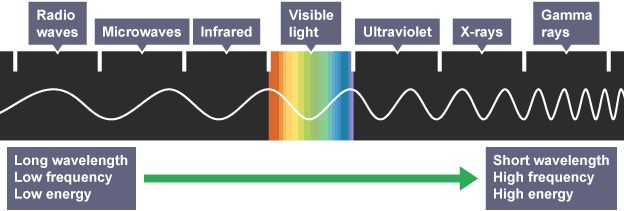
There are seven members in the electromagnetic family. Each member has unique characteristics. Radio waves have the lowest frequencies and longest wavelengths, while gamma waves have the highest and shortest wavelengths.
Interestingly, all these waves travel at the same speed in space. It's called the speed of light, about 300,000,000 meters per second.
Colours of the Visible Spectrum
When white light passes through a prism, something magical happens—it splits into a beautiful spectrum of colors
Imagine a unique prism, like a glass block with a triangle shape. As the light waves enter the prism, they change direction, or "refract," because they slow down.
This mesmerizing spectrum is formed because different colours of light travel at different speeds inside the prism. Interestingly, red light is affected the least and refracted only slightly. On the other hand, violet light is influenced the most and is refracted the most.
As a result, the colours spread out, creating a magnificent display of the whole spectrum of white light. This fascinating phenomenon is called dispersion.
To remember the key points:
- The spectrum of white light is produced because colours travel at different speeds in the prism.
- Red light is slowed down the least and refracted the least.
- Violet light is slowed down the most and refracted the most.
Applications of Electromagnetic Waves
The behaviour of electromagnetic (EM) waves varies depending on their frequency, and different groups within the electromagnetic spectrum have unique properties that make them suitable for various purposes. As the frequency of EM waves increases, they also become progressively more hazardous.
Radio Waves
Radio waves are commonly used for communication purposes, such as broadcasting television and radio signals and satellite transmissions.
Radio waves can readily travel through the air without significant obstacles. When absorbed by the human body, they do not cause harm or damage. Additionally, they can be reflected to change their direction, making them ideal for communication applications.
By creating oscillations in electrical circuits, radio waves can be generated. When a conductor absorbs these waves, they develop an alternating current with the same frequency as the radio waves. Before transmission, information is encoded into the lock, which can then be decoded upon reception. Television and radio systems utilize this principle to broadcast information effectively.
Microwaves
Microwaves find applications in cooking food, communication systems, and satellite communications. However, intense sources of microwaves can be dangerous due to their potential to heat body cells internally.
Infrared
Infrared (IR) light serves various purposes and finds applications in different areas. It is utilized by electrical heaters, cookers for cooking food, short-range communication devices like remote controls, optical fibres, security systems, and thermal imaging cameras that enable the detection of people in the dark.
It's important to note that the heating effect of infrared radiation can potentially cause burns to the skin if exposed for extended periods or at high intensities. Therefore, caution should be exercised when dealing with intense sources of infrared radiation.
Visible Light
Visible light refers to the visible light to the human eye and serves various purposes in different fields. It is commonly used in photography to capture images and in illumination to provide light for multiple settings. Additionally, visible light plays a crucial role in fibre optic communications. This communication system transmits coded light pulses through glass fibres, allowing information to travel from a source to a receiver efficiently and reliably.
Ultraviolet (UV) Light
Ultraviolet (UV) light falls outside the range of visible light to the human eye, yet it possesses specific characteristics that can be hazardous to the human body. Exposure to ultraviolet light in sunlight can lead to skin tanning or burning.
Fluorescent substances play a crucial role in energy-efficient lamps. These substances absorb the ultraviolet light generated within the lamp and then emit the energy as visible light. A similar principle is employed in creating security features on banknotes, where specific substances are used to detect counterfeit notes under ultraviolet light.
X-rays and Gamma Rays
Electromagnetic waves can be generated or absorbed when there are changes in atoms and their nuclei. Gamma rays, for instance, are produced by specific changes in the middle of a bit, making them a form of nuclear radiation.
High-energy waves like X-rays and gamma rays have the unique property of passing through body tissues with minimal absorption. This characteristic makes them exceptionally suitable for internal imaging purposes. X-rays, specifically, are absorbed by dense structures such as bones, which is why X-ray images are commonly used to identify fractures.
In addition to medical imaging, X-ray technology is utilized to scan objects' internal structures and for security purposes in airport scanners.
Gamma rays, on the other hand, find various applications. They are used for sterilizing food and medical instruments, as well as in the detection and treatment of cancer.
Dangers of Electromagnetic Radiation
Let's explore the potential dangers of different types of electromagnetic radiation. When we are exposed to certain kinds of radiation in excessive amounts, it can be harmful to our bodies.
The level of damage caused by radiation depends on its frequency. The higher the frequency, the more energy it carries and the more harm it can potentially inflict on our bodies. Let's take a closer look at each type:
- Radio waves: The main effect of radio waves on our bodies is a tiny increase in temperature, up to 0.2 degrees Celsius. Some people believe that low-frequency radio waves from power cables and mobile phone base stations near their homes have affected their health, but this hasn't been definitively proven.
- Microwaves: These waves can heat the tissues inside our bodies, causing internal heating.
- Infrared radiation: We feel infrared radiation as heat, which can cause our skin to burn.
- Visible light: Intense light from lasers can harm the retina at the back of our eyes, so we need to be cautious.
- Ultraviolet (UV) radiation: UV rays can damage our skin cells, leading to skin cancer and premature ageing of the skin. They can also harm our eyes. That's why protecting our skin and eyes from excessive UV exposure, such as wearing sunscreen, hats, and sunglasses, is crucial.
- X-rays: X-rays can damage cells inside our bodies. They cause ionization, which is dangerous for living cells. This ionization can harm the DNA within cells, potentially leading to cancer. To protect themselves, doctors and dentists stand behind protective screens when taking many X-rays.
- Gamma rays: Similar to X-rays, gamma rays can damage cells within our bodies by causing ionization. This ionization can lead to cell death and increase the risk of cancer.
Now let's focus on ultraviolet radiation specifically. UV radiation is naturally present in sunlight. Although we can't see or feel it, our skin responds to UV exposure by developing a darker colour, known as a suntan, over time. This natural process helps our bodies reduce the amount of UV radiation reaching more profound layers of skin tissue.
Darker skin absorbs more UV light, which means less UV radiation penetrates deeper tissues. This is important because prolonged exposure to UV radiation can cause skin cancer and damage our eyes.
To protect ourselves, it's advisable to use sunscreen with high UV protection on sunny days to minimize the risk of skin cancer. Additionally, wearing hats and sunglasses is recommended to shield our eyes from excessive UV radiation, which can potentially lead to blindness.
Summarise with AI:












You are the best,, coz you have gotten content about the topics
Hello ! Glad to hear that you’ve found the content useful!