Chapters
Welcome to our article on energy efficiency! In this article, we'll explore the fascinating concept of energy efficiency, how it is calculated, and the various factors that affect it. We'll also dive into real-life examples of energy efficiency and its significance in sustainable living.

What is Energy Efficiency?
The concept of energy is important in physics as it allows work to be accomplished. Power refers to the speed at which energy is transferred, while efficiency represents the amount of energy that is transferred effectively. Hence, we can define energy efficiency as:
The effectiveness of a device in converting energy input into useful energy output is referred to as efficiency
OR
Energy efficiency refers to the measurement of how much useful energy is produced or consumed in relation to the total amount of energy used.
Energy efficiency is commonly expressed as the percentage ratio of useful energy output to the total energy input. This concept plays a vital role in reducing energy wastage and promoting sustainability, which is crucial for minimizing the impact of human activities on the environment.

Role of Energy Efficiency in Designing Devices
In designing devices, energy efficiency is a critical factor that must be considered. The goal is to ensure that the device utilizes energy as efficiently as possible by minimizing any losses that may occur during energy conversion processes. This is because devices are generally designed to perform a specific function that requires the transfer of energy from one form to another.
For instance, in a light bulb, electrical energy is converted into light energy, and the efficiency of this conversion is crucial in determining the amount of light output for a given amount of electrical input. The higher the efficiency of the conversion process, the more effective the light bulb is in converting the input energy into useful light output, resulting in less wastage of energy.
From the above example, we can conclude that:
- The less the device wastes its input energy, the more efficient it will be
- The more the device wastes its input energy, the more inefficient it will be
Efficient use of energy is essential not only for reducing wastage but also for promoting sustainability and minimizing the environmental impact of human activities. By designing devices that waste as little energy as possible, we can help to conserve resources and promote a cleaner, healthier planet for future generations.
Calculating Energy Efficiency
The efficiency of a device refers to the percentage of supplied energy that is converted and utilized in useful ways. This can be determined by using either decimal or percentage calculations, as shown in the following equations:
Efficiency = 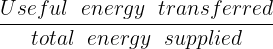
Percentage of Efficiency = Efficiency x 100
Percentage Efficiency = 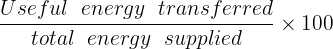
Example
Suppose you have a motor that runs on electricity and is used to power a machine. If the motor consumes 750 J of electrical energy and produces 600 J of mechanical energy to operate the machine, what is the efficiency of the motor?
Solution
To solve this problem, we first need to determine the useful energy output and the total energy input:
Useful energy output = 600 J
Total energy input = 750 J
Next, we can use the formula for efficiency:
Efficiency = 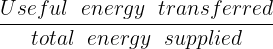
Efficiency = 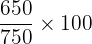
Efficiency = 80%
Therefore, the efficiency of the motor is 80%, indicating that 80% of the electrical energy supplied is converted into useful mechanical energy to operate the machine, while 20% of the energy is wasted as heat or other forms of energy.
Examples of Energy Efficiency From Everyday Life
Here are some examples of energy efficiency from everyday life:
- LED light bulbs: LED bulbs use up to 80% less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs, and they last much longer too.
- A programmable thermostat: A programmable thermostat can automatically adjust the temperature in your home to save energy when you're not home or sleeping.
- Refrigerators: Energy-efficient refrigerators use advanced insulation materials and technology, as well as compressors and motors that are designed to be more efficient, to reduce the amount of energy they use.
- Washing Machines: Energy-efficient washing machines often have features like load-sensing technology, which adjusts the amount of water used based on the size of the load, as well as high-speed spin cycles that reduce the amount of water that needs to be heated.
- Dishwashers: Energy-efficient dishwashers use less water and energy to clean dishes, often by using features like soil sensors that adjust the cycle time based on the level of dirtiness.
- Air Conditioners: Energy-efficient air conditioners use technology like variable-speed compressors and high-efficiency coils to cool air more efficiently, using less energy.
- Televisions: Energy-efficient televisions use LED technology and other advanced features to consume less energy than older, less efficient models.
Factors Affecting Energy Efficiency
There are many factors that affect energy efficiency, some of which are described below:
- Design: The design of a device can greatly impact its energy efficiency. Devices that are designed with energy efficiency in mind, such as appliances with better insulation or motors with higher efficiency, can use less energy while still providing the same level of performance.
- Size and capacity: The size and capacity of a device can also affect its energy efficiency. Oversized devices may use more energy than necessary, while undersized devices may not be able to meet the demand and can also waste energy.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance of devices can help ensure that they are operating at peak efficiency and using energy as efficiently as possible. Dirty air filters, for example, can cause appliances like air conditioners to work harder and use more energy.
- Insulation: The quality of insulation in a building can affect its energy efficiency. Good insulation can reduce heat loss in the winter and keep a building cooler in the summer, which can reduce the amount of energy needed for heating and cooling.
- Friction: Friction is the force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are in contact, and it can cause energy to be lost as heat. Friction can be a major source of energy loss in mechanical systems, such as engines and machines. Reducing friction can improve energy efficiency by minimizing the amount of energy that is lost due to friction. This can be accomplished through the use of lubricants, the design of parts with smoother surfaces, or the use of bearings or other components that can reduce friction.
- Renewable energy: The use of renewable energy sources, such as wind or solar power, can reduce the amount of energy needed from non-renewable sources, improving overall energy efficiency.
Improving Energy Efficiency
It is a fundamental law of physics that the efficiency of a device cannot be greater than 100% or greater than 1. Any efficiency greater than this would imply that more energy is being transferred than is being supplied, which would mean that energy is being created, violating the law of conservation of energy.
Devices waste energy due to various factors, including friction between their moving parts, electrical resistance, and unwanted sound energy. Therefore, it is always beneficial to improve the efficiency of a device or process. This can be achieved by minimizing the amount of wasted energy transfer, resulting in more useful energy transfer from the input energy.
Mechanical devices can be made more efficient by lubricating them to reduce friction between the moving parts of a machine, which increases the amount of useful energy transferred.
Similarly, for thermal energy transfer systems, efficiency can be enhanced by reducing the wasteful dissipation of thermal energy into the surroundings by using insulation, for example. This helps to prevent unwanted heat loss and to retain more thermal energy in the system.
Summarise with AI:












You are the best,, coz you have gotten content about the topics
Hello ! Glad to hear that you’ve found the content useful!