
Introduction
A trapezoid (or trapezium) is a quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides. These parallel sides are called the bases, while the non-parallel sides are called the legs.
Calculating the area of a trapezoid is a common geometry problem that appears in everything from land surveying to construction. The formula is straightforward: you average the two bases and multiply by the height.
Area Formula:
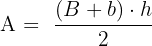
Where:
- B is the large base
- b is the small base
- h is the height (the perpendicular distance between the bases)
In this article, we will solve 5 practice problems ranging from calculating simple areas to finding missing side lengths using the Pythagorean theorem.
Practice Questions and Solutions
Find the area of a trapezoid with a large base of 14 cm, a small base of 10 cm, and a height of 7 cm.
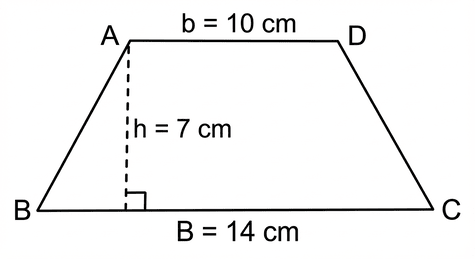
This is a direct application of the area formula.
Step 1: Identify the values B = 14, b = 10, h = 7
Step 2: Substitute into the formula:
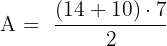
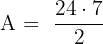
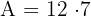
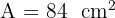
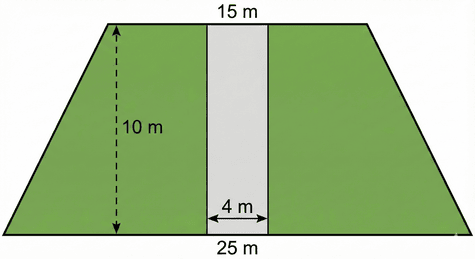
A wooded area is in the shape of a trapezoid whose bases measure 25 m and 15 m, and its height is 10 m. A 4m wide rectangular walkway is constructed which runs perpendicular from the two bases (cutting through the height). Calculate the area of the wooded area remaining after the addition of the walkway.
To find the remaining area, we must calculate the total area of the original trapezoid and subtract the area of the rectangular walkway.
Step 1: Calculate the total area of the trapezoid B = 25, b = 15, h = 10
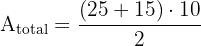
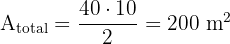
Step 2: Calculate the area of the walkway The walkway is a rectangle with a width of 4 m and a length equal to the height of the trapezoid (10 m).
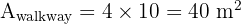
Step 3: Subtract to find the remaining area
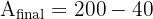
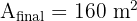
ABCD is a square with a side length of 6 cm. Point E is the midpoint of side BC. A line connects point D to point E. Calculate the area of the trapezoid formed by points ABED.
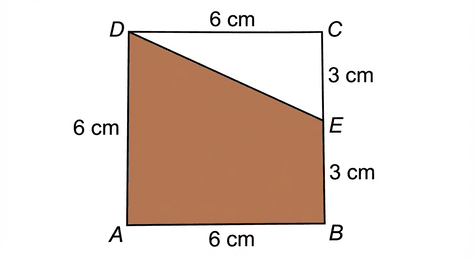
Since ABCD is a square, side AD is parallel to side BC. Therefore, the shape ABED is a trapezoid with parallel sides AD and BE. The height is the side AB (since the corner B is 90 degrees).
Step 1: Identify the dimensions
Large Base (AD): Since it is a square of side 6, AD = 6 cm.
Small Base (BE): E is the midpoint of BC (length 6), so BE = 3 cm.
Height (AB): The side of the square is 6 cm.
Step 2: Calculate the area
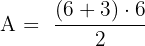
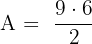
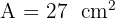
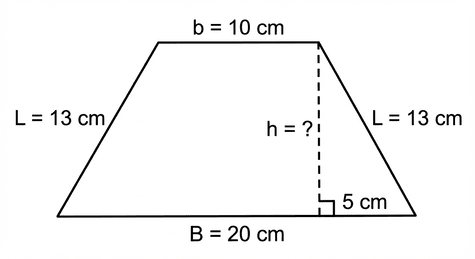
The perimeter of an isosceles trapezoid is 56 cm. The bases are 20 cm and 10 cm in length. Calculate the area of the trapezoid.
To calculate the area, we need the height. We must first find the length of the legs from the perimeter and then use the Pythagorean theorem.
Step 1: Find the length of the legs - an isosceles trapezoid has two equal legs. Perimeter = Base 1 + Base 2 + 2(Leg)
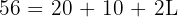
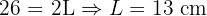
Step 2: Find the height using a triangle - as shown in the diagram, drawing the height creates a right-angled triangle with the leg (13) as the hypotenuse. The base of this triangle is half the difference between the bases: Base of triangle = (20 - 10) / 2 = 5 cm.
Using Pythagoras (a² + b² = c²):
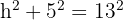

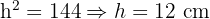
Step 3: Calculate the Area
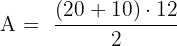
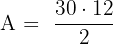

Calculate the length of the oblique (slanted) side of a right trapezoid given the following dimensions:
Large Base = 28 cm
Small Base = 20 cm
Height = 15 cm
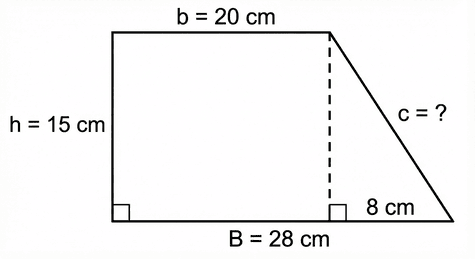
A right trapezoid has one vertical side (the height) and one oblique side. To find the length of the oblique side (c), we construct a right-angled triangle as shown in the diagram.
Step 1: Determine the base of the right-angled triangle - the base of the triangle is the difference between the large base and the small base.
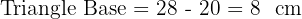
Step 2: Use Pythagoras to find the oblique side (hypotenuse) - the height of the triangle is the height of the trapezoid (15 cm).
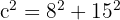
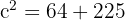
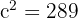
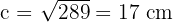
The oblique side is 17 cm.
Summarise with AI:












Hi Emma nice to meet u I love reading and solving mathematics problem