Chapters
0 ≤ p(A) ≤ 1
p(S) = 1
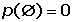

Probability Formula

Addition Rule
If A 
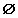
p(A ∪ B) = p(A) + p(B) − p(A 
p(A ∪ B ∪ C) = p(A) + p(B) + p(C) − p(A 
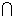

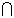
Multiplication Rule

The best Maths tutors available
Independent Events
p(A 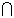
Dependent Events
p(A 
Conditional Probability

Independent Events
p(A|B) = p(A)
Dependent Events
p(A|B) ≠ p(A)
Law of Total Probability
p(B) = p(A1) · p(B|A1) + p(A2) · p(B|A2 ) + ... + p(An) · p(B|An )
Bayes' Theorem

Expected Value
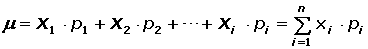
Variance of a Discrete Random Variable
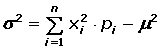
Standard Deviation of a Discrete Random Variable
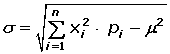
Binomial Distribution
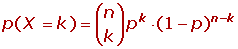
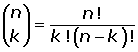
Normal Approximation to the Binomial

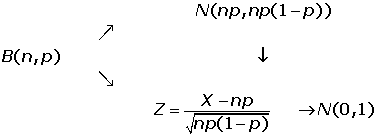
Summarise with AI:













