Chapters
- What Sparked the Initial Conflicts on the Eastern Front?
- What Happened During the Battles of Tannenberg and the Masurian Lakes?
- Why Was Russian Success in Galicia so Important?
- How Did Warfare Differ on the Eastern Front?
- What Led to the Collapse of the Tsarist Government in Russia?
- How Did the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk Change the Eastern Front?
- Conclusion
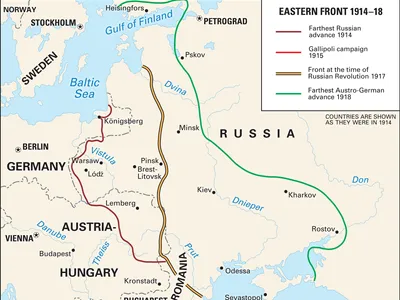
Although less talked about than the Western front, the Eastern front, which spanned from the Baltic to the Black Sea, was another pivotal conflict that took place during WW1. Unlike the close and claustrophobic battles that took place at the Western front, the conflicts of the Eastern Front happened over a much larger territory - with troops often moving across large areas, leading to more dynamic battles and significant shifts in control between sides. But what exactly happened during the Eastern Front, and how did it shape the course of the Great War? Keep reading below if you want to find out more.

What Sparked the Initial Conflicts on the Eastern Front?
The Eastern Front began when Russia decided to launch an offensive against Germany in August 1914. Unlike the Germans Schlieffen Plan, which had failed to realize how fast the Russians could spring into action - the Tsar’s army rapidly launched a two pronged attack against Prussia. Incredibly, around 1.3 million soldiers were involved in this offensive. Why did they do this? Well their main goal was to try and force Germany to redirect their troops from the Western front. This move caught Berlin off guard, as they had not anticipated the speed and scale of the Russian mobilization. Adding to the complexity, Austria-Hungary also faced Russian forces on its eastern borders, leading to a series of battles that further stretched the Central Powers resources. These early clashes set the tone for what was to come during the Eastern Front - large troop movements, strategic gambits, and a battle of endurance between both sides of the conflict.
What Happened During the Battles of Tannenberg and the Masurian Lakes?
The battles of Tannenberg and the Masurian Lakes in August 1914 were the first major conflicts to take place on the Eastern front. Although the Russians advance into Prussia looked promising at first, they would quickly encounter a setback when General Paul von Hindenberg of Germany ordered his troops to respond to the incursion. This was only made worse by the Russian Generals poor communication with one another and their own bitter rivalries, which led to critical mistakes. From here, the Germans would encircle and decimate the Russian Second Army at Tannenberg, capturing or killing most of its soldiers. But that wasn’t the end of the matter - days later, at the Masurian Lakes, another Russian force would also go on to suffer a similar fate.

Why Was Russian Success in Galicia so Important?
Despite their issues in Prussia, the Russian forces actually fared much better in Galicia. It was at this location that they clashed with the Austria-Hungarian forces. Taking advantage of their enemies' weaker military capabilities and their own larger number of troops, the Russian Army would push them back and capture a large number of prisoners in the process. This victory in Galicia, though overshadowed by the failures in East Prussia, was crucial as it provided a much needed morale boost to the Russian troops while also offsetting the impact of earlier defeats.
How Did Warfare Differ on the Eastern Front?
When we think about World War I, the image that often comes to mind is that of soldiers huddled in muddy trenches. Although this was the typical scene on the Western Front, the Eastern Front presented a very different kind of warfare, one that was more dynamic and constantly changing. For example, one key reason for this was the lower number of troops and less overall fortified positions on the battlefield. It was this setup that allowed armies to move across large areas of land, leading to a completely different style of combat. What’s more, battles were less about holding onto a fixed line of trenches or a single point, and more about moving quickly and figuring out how to outmaneuver the enemy. Although this might sound a lot less brutal compared to trench warfare, troops still suffered from the fierce battles, harsh living conditions, and low supplies of food and rations.
What Led to the Collapse of the Tsarist Government in Russia?
The war's impact on the Eastern Front didn’t only affect soldiers on the battlefield, it also had a major impact on the Russian people at home too. In Russia, the loss of countless lives and the devastating effect on the economy had begun to cause widespread frustration and anger amongst civilians. Eventually, these feelings would lead to the February Revolution of 1917, a turning point for not only Russia but the war as a whole. Due to this, Tsar Nicholas II, would make the decision to abdicate his throne and end centuries of imperial rule in Russia in the process. However, that wasn’t the end of the story. Without a tsar, there was a major power vacuum in Russia, and one group would eagerly step in to take advantage of it - the communist aligned Bolsheviks. Led by figures such as Lenin, their rise to power brought a new ideology to the country whilst also having a direct impact on their strategies for war. The Bolsheviks, driven by their communist beliefs, were determined to pull Russia out of the war, a move that would have significant repercussions not just within Russia but across the entire Eastern Front as a whole.

How Did the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk Change the Eastern Front?
During March 1918, the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk would officially be signed, forever altering the Eastern Front in the process. Essentially, this treaty was an agreement between the new government of Russia and the central powers that finalized Russia’s decision to pull out of the war for good, bringing an end to years of fighting. However, as part of the agreement, Russia had to agree to cede a large swath of its territory, including parts of present day Poland, Ukraine, and Belarus, over to the Central Powers. Despite the weakening of their territorial power, the Russian Government was all too happy to step back from the war and focus on rebuilding its resources and the trust of its people.

Conclusion
The Eastern Front in WWI, a vast battlefield stretching from the Baltic to the Black Sea, played a pivotal yet distinct role compared to the Western Front. It was marked by large scale troop movements and significant strategic shifts. This front saw key battles like Tannenberg and the Masurian Lakes, and successes in Galicia, which deeply influenced the course of the war. Its impact extended beyond the battlefield, contributing to the 1917 Russian Revolution, the fall of Tsar Nicholas II, and ultimately leading to the 1918 Treaty of Brest-Litovsk. This treaty, marking Russia's exit from the war, significantly altered the war's landscape.
Summarise with AI:








