Chapters
The Vietnam War was one of the 20th century's biggest conflicts and played a big role in the Cold War as a whole. What’s more, the events that occurred during this confrontation would lead to significant changes for the future of Vietnam in the long run. Unfortunately, the Vietnam War would also go down in history as one of the most brutal, intense and horrifying wars in modern history, with many battles taking place deep in the depths of the jungle.
And in today's world, the events of this conflict can still be felt in Vietnam - where it continues to impact everything from society, culture, and relations with countries around the world. So if you’re interested in learning more about this period of history, why not read on below?

How Did the Vietnam War Start?
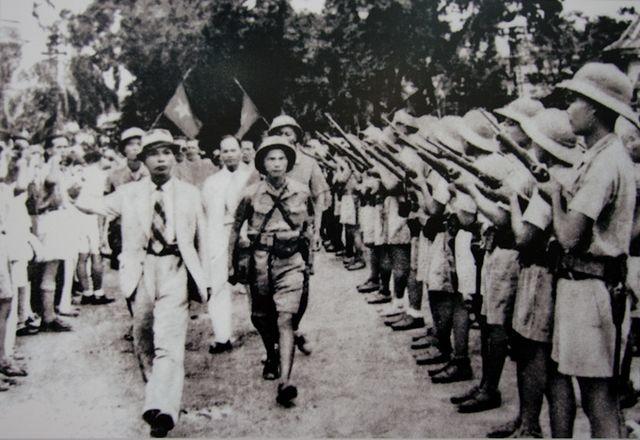
Vietnam's long-standing struggle against foreign domination eventually escalated into the First Indochina War. In this prolonged conflict, Vietnamese forces under French control clashed with the Viet Minh, a Communist-led group. The war culminated in a Viet Minh victory at Dien Bien Phu. Following this, the Geneva Accords were signed, and divided Vietnam into two sectors - the Communist-led North under Ho Chi Minh, and the anti-Communist South led by Ngo Dinh Diem.
This division was intended as a temporary measure, with plans for an election that would unify the two areas in 1956. However, the election never materialized, cementing the division and heightening tensions. The deep-seated political and ideological rifts between North and South Vietnam ultimately spiralled into the larger conflict known as the Vietnam War.

How Was the Vietnam War Related to the Cold War?
As mentioned in the intro, the Vietnam War was closely linked to the Cold War - an ongoing period of tension and hostilities between the Soviet Union and the United States, plus their allies.
Essentially, the U.S. feared that if South Vietnam fell to communism, there would be a high likelihood that communism would spread throughout the rest of Southeast Asia.
This belief was linked to the Domino theory, a theory which suggested that political events in one country (especially regarding the spread of communism) would cause similar events in neighbouring countries, like a falling row of dominoes. This fear led to the U.S. lending both financial and military support to South Vietnam.
On the other side of the conflict, the Soviet Union and China, wanting to extend their influence, chose to support North Vietnam. The result of this support resulted in Vietnam becoming yet another proxy battlefield for the ongoing clash between capitalism and communism.
Brutal Battles of the Vietnam War
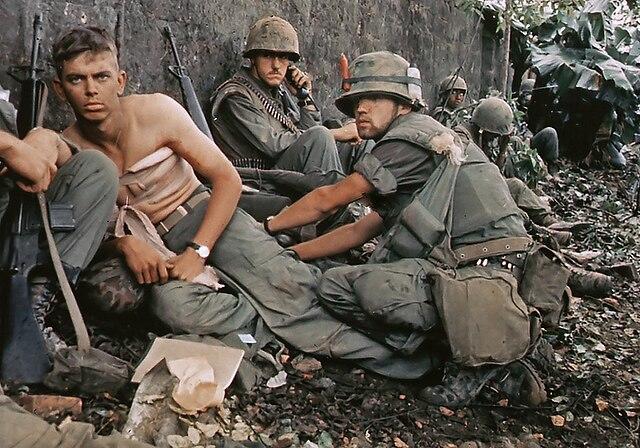
The Vietnam War featured several intense battles, combining traditional warfare and guerrilla tactics. Key among these was the Tet Offensive in 1968 - a large-scale surprise attack by North Vietnamese and Viet Cong forces. Other significant confrontations included the Battle of Hue and the Siege of Khe Sanh. The war's terrain, dominated by Vietnam's dense jungles, made combat extremely difficult for troops on both sides. Whilst the U.S. used air power heavily, the Viet Cong's local knowledge and tunnel networks gave them an edge when it came to guerrilla tactics.

How Did the American Public and the Rest of the World Respond to the War?
The American public's response to the Vietnam War evolved over time. At first, there was widespread support - partly because many people viewed it as a crucial part of the battle against communism. However, as the war led to more American deaths and the draft's effects became apparent, public opinion began to change a lot.
The media played a crucial role in this change, bringing the realities of war into American homes. Additionally, many countries, especially allies of the United States, were initially supportive or neutral. However, as the war got worse and reports of civilian casualties and military excesses increased - international opinion began to shift as well.
For example, in many parts of the world, particularly in Europe and among non-aligned nations, there was growing criticism of U.S. actions in Vietnam. This eventually led to widespread protests and demonstrations taking place in various countries worldwide.

Were Chemicals Used in the Vietnam War?
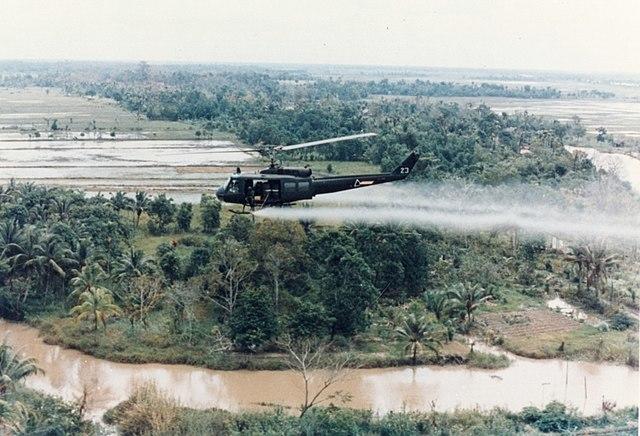
One of the most controversial aspects of the Vietnam War was the use of Agent Orange - a powerful herbicide. The U.S. military employed this chemical extensively throughout Vietnam's dense jungles, aiming to strip away vegetation and disrupt the Viet Cong's supply routes. But the broad use of Agent Orange had far-reaching and devastating consequences.
First and foremost, it wreaked havoc on the environment, decimating large swathes of forest and disrupting ecosystems all over Vietnam. Alongside the environmental damage, the health effects were also catastrophic too.
For example, both Vietnamese civilians in the sprayed areas and American soldiers exposed to the chemical suffered severe health problems. Over time, even more harmful effects of Agent Orange became evident, as many health problems and birth defects emerged, those of which were lasting reminders of the war's impact.

How did the Vietnam War End?
The Vietnam War drew to a close following a series of critical negotiations, with the 1973 Paris Peace Accords standing out as a key amongst them all. These accords marked the beginning of the withdrawal of U.S. troops from Vietnam, signalling a hopeful shift towards an enduring peace in the region.
However, despite these steps, Vietnam soon faced renewed upheaval again. In 1975, North Vietnam would go on to launch a decisive offensive, swiftly overtaking South Vietnam and capturing its capital, Saigon. This strategic move effectively ended the conflict and paved the way for the unification of Vietnam under a single communist regime.
Conclusion
To wrap it up, the Vietnam War played a crucial role in the 20th century and was closely linked to the clash of the Cold War era. It originated from the split of Vietnam into a Northern communist faction and a Southern anti-communist regime. On one side were the U.S. and its allies, concerned about the spread of communism, and on the other were the Soviet Union and China, who were backing the North.
The war, known for its intense combat and its global repercussions, significantly shifted public opinion in the US and sparked discussions around the world. Lastly, its end marked a significant moment in Cold War history, leaving a profound and enduring influence on both Vietnam and international diplomacy in the process.
Summarise with AI:








