Chapters
In this article, we will explain what is meant by discontinuous and continuous variation. But before proceeding to discuss discontinuous and continuous variations.

What is Variation?
Variation explains the diversity in the genetic makeup of species in a population. Variation is the result of mutations. Usually, variations have a minute effect on the phenotype, however, there are examples where a variation has a huge effect on the phenotype and it results in the generation of different categories. Various factors such as rate of mutation, genetic drift, sexual reproduction, gene flow, and meiosis can influence the variation. Variation is crucial for adaptation and evolution.
For the evolution of a species, variation plays a central role because genetic diversity is a major factor that facilitates the occurrence of natural selection. It means that some variants are selected for and against, depending on the environment. Different versions of a gene or variants that are present within a population are referred to as alleles.
In the next section of the article, we will discuss the effect of variation
The Effect of Variation
Genotype and phenotype frequencies change with the changing alleles frequencies. Various genotypes can be attributed to the positive or negative effects on fitness in that environment. Hence, we can say that some of these genotypes or phenotypes are favourable, and these individuals are able to reproduce after reaching their reproductive age and transfer genetic information. As a result, the population is biased towards a particular phenotype which changes the frequencies in the gene pool.
In the next section of the article, we will discuss discontinuous and continuous variation in detail.
Types of Variation: Discontinuous and Continuous
We already know that the term variation means the differences existing between at least two things. It can be an amount, level, or quantity of characteristic of something. Concerning natural selection, variation means the differences that exist between individuals of the species. We can also call them intraspecific variations. A variation that is observed in phenotypes of organisms can be attributed to the quantitative and qualitative differences.
Now, let us see what discontinuous variation is.
Discontinuous Variation
The discontinuous variation within a population results from the qualitative differences in phenotypes of individuals within a population.
Qualitative differences can have two categories: discrete and distinguishable. There usually have no intermediates which refer to a feature that falls in between two categories. We can easily detect discontinuous variation when it is presented in the form of a graph or a table. This is due to the existence of different categories when data is plotted for specific features.
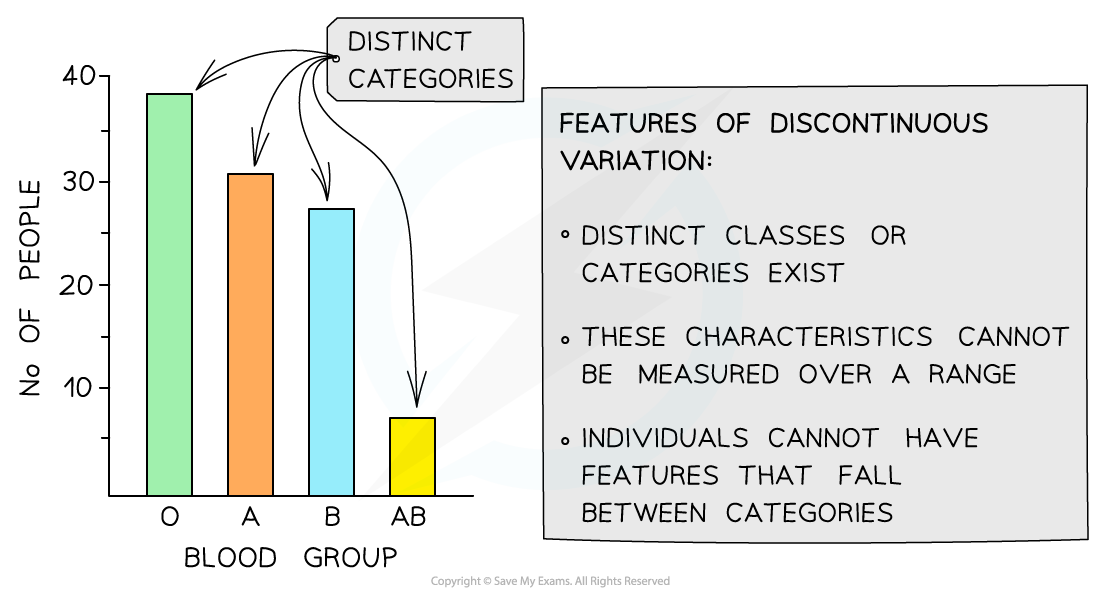
Now, let us see what is meant by continuous variation
Continuous Variation
When there are quantitative differences in the phenotypes of individuals with a population for specific features, then the variation taking place is known as continuous variation.
Unlike discontinuous variation, the quantitative differences are not divided into discrete categories. Rather for these characteristics, there is a range of values that occur between two extremes. The phenotype will fall within these extremes. For instance, a well-known example of continuous variation is the mass and height of human beings.
When continuous variation is presented in the form of a table or graph, we can identify it from the lack of categories and range of values.
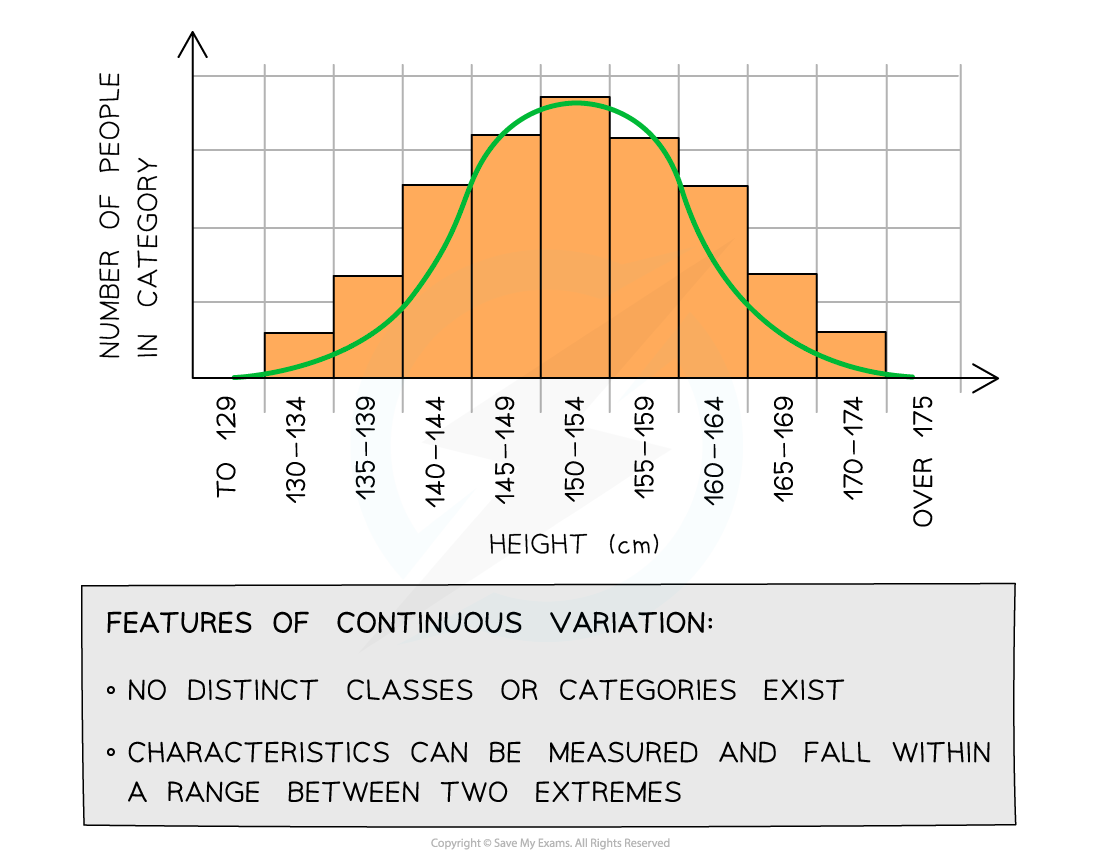
In the next section of the article, we will discuss the genetic basis of variation which will include discontinuous and continuous variations.
The Genetic Basis of Variation
- The differences between individuals of a species that are qualitative, i.e. categoric are referred to as discontinuous variation.
- The differences between individuals of a species where the differences are quantitative, i.e. measurable are referred to as continuous variation.
Genetic, environmental, or a combination of both factors can be used to explain both discontinuous and continuous variation.
Genetic basis of Discontinuous Variation
This type of variation takes place only due to genetic factors. It means that the environment has no direct effect on discontinuous variation. At the genetic level, various genes have varying effects on the phenotype. Various alleles at a single gene locus have a huge effect on the phenotype. Keep in mind that diploid organisms inherit two alleles of each gene and these alleles can be either the same or different.
Example
F8 gene is an example of discontinuous variation which codes for the blood clotting protein Factor VIII. The distinct alleles at the F8 gene locus determine whether a normal factor VIII will be produced or not. These different alleles also determine whether the individual has the condition known as haemophilia or not.
Genetic Basis of Continuous Variation
This type of variation takes place because of the interaction between genetics and the environment. We know that:
Genotype + Environment = Phenotype
At the genetic level, distinct alleles at a single locus have a minute effect on the phenotype. Various genes can have a similar effect on the phenotype, and they add together to have an additive effect. If several (large number of) genes have a combined effect on the phenotype, then they are referred to as polygenes.
In the next section of the article, we will discuss the additive effect of genes.
The Additive Effect of Genes
- Two unlinked genes control the height of the plant. These genes are H / h and T / t. The two genes combine to have an additive effect. The recessive genes are h and t which contribute x cm to the plant’s height. On the other hand, the dominant genes H and T contribute double, i.e. 2x cm to the plant’s height.
The genotypes below will have the following phenotypes:
- h h t t : x + x + x + x = 4x cm
- H h T t : 2x + x + 2x + x = 6x cm
- H h T T : 2x + x + 2x + 2x = 7x cm
- H H T t : 2x + 2x + 2x + x = 7x cm
- h h T t : x + x + 2x + x = 5x cm
- H H T T : 2x + 2x + 2x + 2x = 8x cm
- H h t t : 2x + x + x + x = 5x cm
Summarise with AI:













Keep on teaching us,you are excellent teachers
This is great
Thanks a lot for this book,it really helped me a lot
It’s useful to me
Thanks a lot for your Better book!
It’s a perfect article, go ahead