Chapters
In this article, we will discuss how test strips and biosensors operate. We will especially focus on using these tools for measuring the concentration of glucose in blood and urine, with reference to glucose oxidase and peroxidase enzymes. So, let us get started.

How to Measure Glucose Concentration in Urine?
- Diabetic people are unable to control glucose concentration in their blood. A healthy adult needs to maintain the glucose concentration within normal limits
- If the urine of a person contains glucose in it, then it may indicate that the person has diabetes
- If the glucose concentration in the blood increases beyond a value referred to as the renal threshold, then some of the glucose will be left in the urine. It implies that not all of the glucose gets reabsorbed from the filtrate in the proximal convoluted tubule.
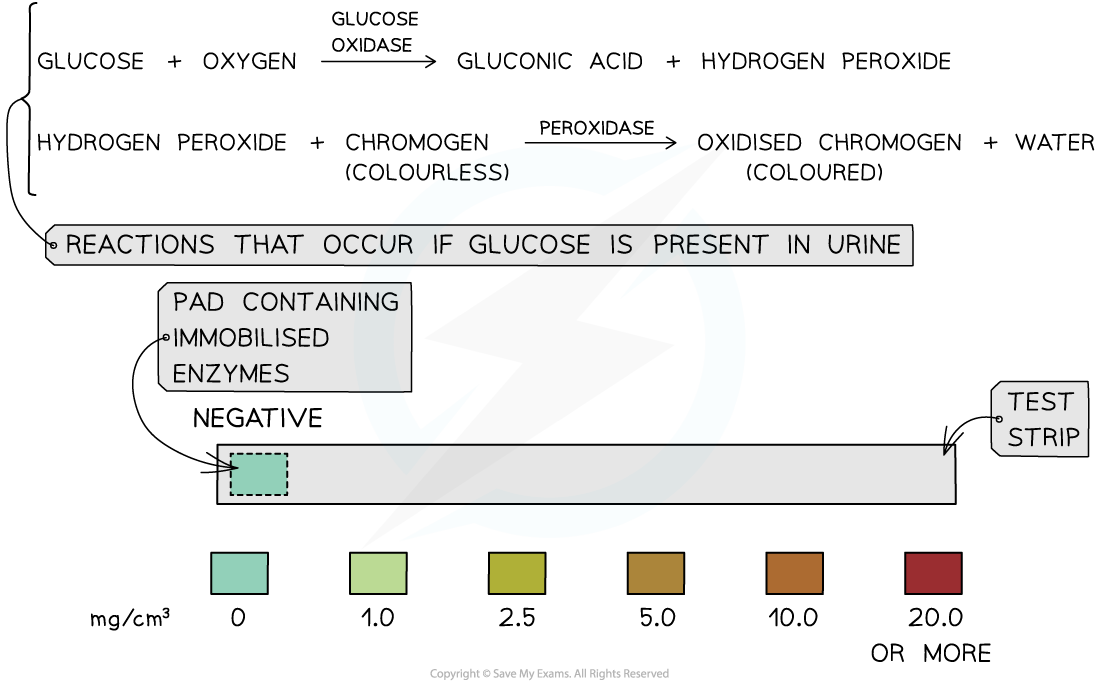
- Test strips are employed to test urine for the detection and concentration of glucose
- At one end of the test strip, two enzymes glucose oxidase and peroxidase are immobilized on a small pad
- This pad is then immersed in the urine sample of the person for some time
- The following events occur in the presence of glucose:
- The enzyme glucose oxidase catalyzes, i.e. speeds up the reaction in which glucose gets oxidized to produce hydrogen peroxide and gluconic acid
- After that, peroxide catalyzes the reaction between the hydrogen peroxide and a colourless chemical in the pad to create a brown compound and water
- The pad’s colour is compared to a colour chart. Various colours represent various concentrations of glucose. If the glucose concentration in the urine sample of the person is higher, then the colour is darker
- Remember that urine samples only indicate whether or not the glucose concentration in the blood was beyond the renal threshold while urine was accumulating in the bladder. It means that they do not show the current glucose concentration in the blood
Practical: Generating a Dilution Series and Calibration Curve
- We can employ an alternative version of Benedict’s solution to carrying out the quantitative test on an unknown sample to detect the concentration of reducing sugars, i.e. glucose in the sample
- The Benedict’s solution that is used has potassium thiocyanate which implies that it does not produce a red copper oxide when it reacts with glucose
- Whether glucose is present in the sample or not is measured by the loss of blue colour produced by copper sulfate along with the creation of a white precipitate
- Through filtration, we can remove the white precipitate and analyze the colour intensity of the remaining filtrate
- The intensity of variation in the colour relates to the concentration of reducing sugar present in the given sample
- A positive test is shown along a spectrum of colours from blue (it indicates low concentration) to colourless (it indicates a high concentration of glucose in the urine)
- You can carry out the quantitative test by setting up standard solutions with known concentrations of reducing sugars like glucose
- Use a serial dilution of an existing stock solution to set up these solutions
- After that, treat each solution, in the same way, i.e. add an equal volume of Benedict's solution to each sample and heat in a water bath that has been bought to boil (ideally the temperature should be the same each time) for a specific time, let say, 5 minutes, to enable colour variations to take place. After that, filter the solution to get the filtrate
- It is critical to ensure the use of excess Benedict’s solution
- Any variation in colour observed for each solution of a known concentration in that time can be linked with the concentration of reducing sugar in that solution
- Carry out the same process on a urine sample that contains an unknown concentration of reducing sugar. Then compare it with the stock solution colours to determine the concentration of reducing sugar present in the sample
- There can be a human error in the interpretation of colour. To avoid that use a colourimeter to measure the transmission or absorbance of light through the sugar solutions of known concentration. This is done to determine the range of values that an unspecified sample can be compared against a calibration curve.
What are Biosensors?
The bioanalytical systems that can sense biological samples are referred to as biosensors.
Biosensors are small, powerful tools that can analyze biological samples to comprehend their function, composition, and structure. They accomplish it by transforming a biological signal or response into a quantifiable response.
The word biosensor is made up of two words: bio and sensor. You might have observed someone using a glucometer for routine monitoring of glucose, or fingertip pulse oximeters to measure oxygen saturation levels and pulse rates. Similarly, some people use smartwatches to keep track of their daily physical activity. All these tools such as glucometers, pulse oximeters, and smartwatches are examples of biosensors.
There are many applications of biosensors. They play a crucial role in the discovery of drugs and the prevention of diseases. They can also be used to monitor the equality of food, soil, or environment.
So far we have discussed biosensors and their various applications in detail. Now, let us see how biosensors are employed to measure glucose concentration.
Using Biosensors to Measure Glucose Concentration
- People with diabetes can employ biosensors to determine the current concentration of glucose in their blood
- Just like the test strips, the biosensors use immobilized glucose oxidase on a recognition layer. However, unlike test strips, biosensors do not employ peroxidase.
- When the recognition layer is covered, it makes it a partially permeable membrane which means that the covering only allows small molecules from the blood to reach immobilized enzymes.
- If a small blood sample is tested, the enzyme glucose oxidase catalyzes the reaction in which any glucose in the blood sample gets oxidized to create hydrogen peroxide and gluconic acid
- The hydrogen peroxide generated is oxidized at an electrode that identifies transfers of electron
- The electron flow and glucose concentration of the blood are proportional to each other
- The current increases due to the biosensor, which is then interpreted by a processor to generate a digital reading for a concentration of glucose in the blood.
- The entire process takes only a few seconds to complete
Summarise with AI:












Keep on teaching us,you are excellent teachers
This is great
Thanks a lot for this book,it really helped me a lot
It’s useful to me
Thanks a lot for your Better book!
It’s a perfect article, go ahead