Chapters
One of the most important nucleic acids present in our body is DNA. It stores all the information related to different processes performed by the cell. DNA also transfers genetic information to the next generation of cells. The latest advances in technology have enabled us to use DNA in different non-biological processes which are benefiting humanity. Some of the ways DNA is being used for the welfare of mankind include diagnosis of a genetic disorder, identification of a criminal, and settling disputes related to paternity. In the next section of the article, we will discuss the structure of DNA in detail.

Structure of DNA Summary
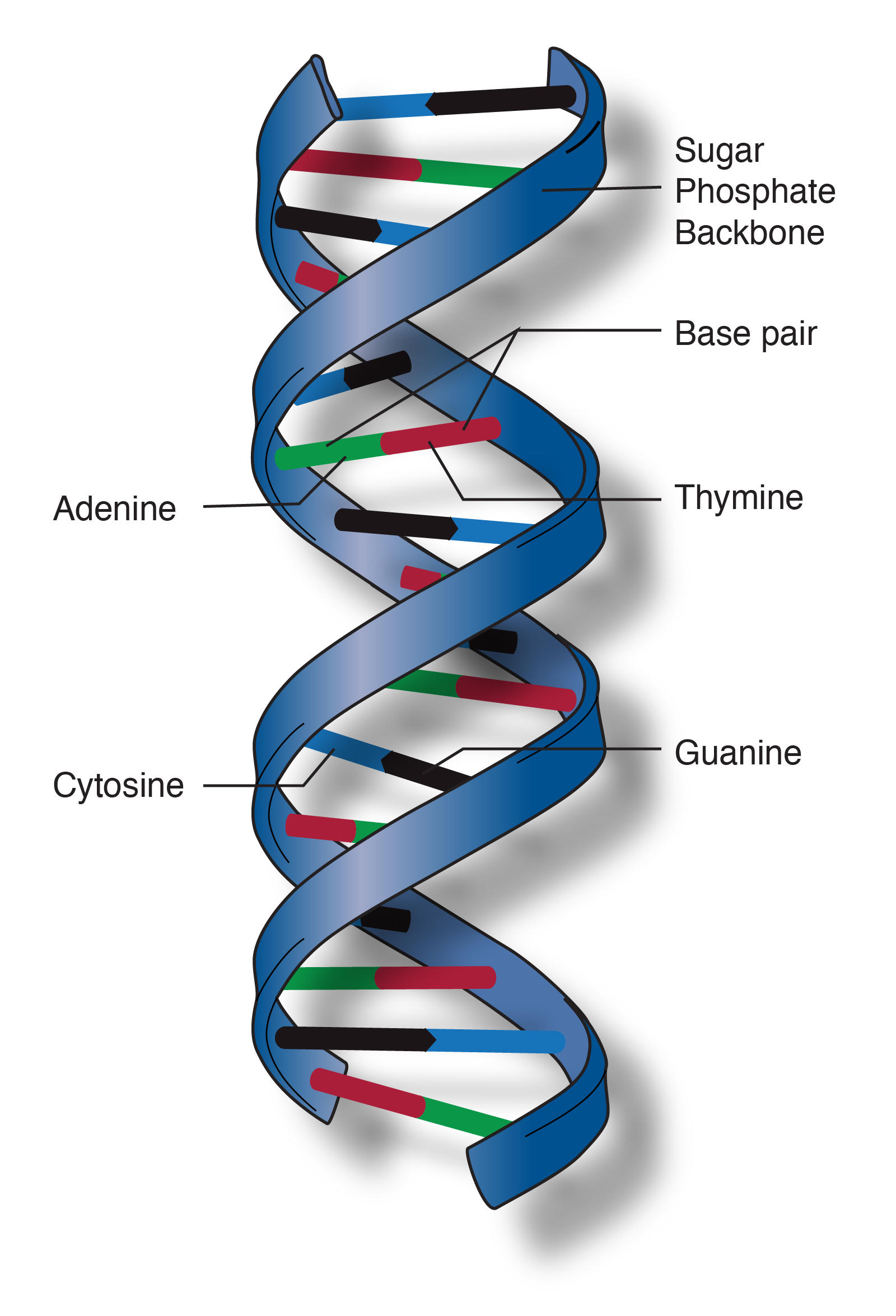
A DNA molecule has a double helix structure with two polynucleotide chains. Hydrogen bonds between particular complementary base pairs hold these chains together. The structure of DNA is explained below:
- The nucleic acid DNA is a polynucleotide that is composed of several nucleotides bonded together in a long chain
- DNA molecules are composed of two polynucleotide strands that lie side by side and run in opposite directions. It means that these strands are anti-parallel.
- Each DNA polynucleotide strand is composed of alternating deoxyribose sugars and phosphate groups which are bonded together by covalent bonds to create a sugar-phosphate backbone. These bonds are referred to as phosphodiester bonds.
- A link is created by phosphodiester bonds between the 5-carbon of a single deoxyribose sugar molecule and the phosphate group from the same nucleotide. The phosphate group from the nucleotide is itself linked by another phosphodiester bond to the 3-carbon of the deoxyribose sugar molecules of the subsequent nucleotide in the chain. These numbers are associated with the carbon on the pentose sugar that could be bonded with another nucleotide.
- It is considered that each DNA polynucleotide strand contains a 3’ end and a 5’ end.
- Because the strands run in opposite directions, i.e. they are anti-parallel, hence one is called 5’ to 3’ strand and the other is called 3’ to 5’ strand.
- There is an outward projection of the nitrogenous bases of each nucleotide from the backbone towards the interior of the double-stranded DNA molecule.
Hydrogen Bonding
- Hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous bases hold together the two anti-parallel DNA polynucleotide strands that create the DNA molecule
- These hydrogen bonds are always present between the same pairs of bases. It means that:
- The purine adenine pairs with pyrimidine thymine (there are two hydrogen bonds between these bases)
- The purine guanine pairs with the pyrimidine cytosine (there are three hydrogen bonds between these bases).
- These are referred to as complementary bases and the pairs are called DNA base pairs.
Double helix structure of DNA
The double-helical DNA structure was proposed by Watson and Crick and was detected by the use of X-ray diffraction methods to discover the three-dimensional DNA structure. The different postulates of the model proposed by Watson and Crick are discussed below:
- DNA is composed of two polynucleotide chains
It means that DNA is a polymer of nucleotides that are arranged in the form of two chains. The nucleotides that are found in DNA are deoxynucleotides that are composed of:
- Deoxyribose sugar
- One phosphate group
- A nitrogenous base
One of the following four bases is found in DNA nucleotides.
- Alanine
- Cytosine
- Guanine
- Thymine
Phosphodiester bonds link thousands of these nucleotides to create two polynucleotide chains. Each of the two chains contains a 3’ and a 5’ end. The polynucleotide chain end that has a free hydroxyl group at the third carbon of deoxyribose sugar is referred to as 3’end. The other end of the chain that has a free phosphate group attached to the fifth carbon of deoxyribose sugar is known as the 5’ end.
- The two polynucleotide chains have a coiled structure, i.e. they are coiled around each other.
A helix refers to a spiral-shaped structure. The polynucleotide chains in DNA are coiled around each other to create a double helix structure. It is referred to as a double helix because, in a three-dimensional model, the DNA molecule was observed to have a helical or spiral structure composed of two polynucleotide chains. The winding of two polynucleotide chains around each other creates a double-helical structure.
- The coiled polynucleotide chains are anti-parallel
It implies that in a DNA double helix, the two polynucleotide chains are arranged opposite to one another. The arrangement of one chain in a 3’ to 5’ direction with its sugar and phosphate molecules projected upwards causes the 5’ to 3’ direction of the other chain with the sugar and phosphate molecules facing downwards.
- The double helix DNA has a phosphate sugar backbone
The double helix DNA’s backbone is composed of sugar and phosphate molecules. The arrangement of polynucleotide chains in DNA is such that the sugar and phosphate molecules are arranged on the exterior side of the double helix with the nitrogenous bases facing inwards.
- Hydrogen bonds hold together the two chains of the DNA molecule
The hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases hold together the two polynucleotide chains in the DNA double helix. Through these hydrogen bonds, the purines of one chain pair with the pyrimidines of the other chain. It means that the alanine pairs with thymine and guanine with cytosine.
Two hydrogen bonds are present between alanine and thymine, whereas three hydrogen bonds are present between guanine and cytosine.
- DNA has an equal ratio of purines and pyrimidines
As discussed above, hydrogen bonds hold together the double-helical structure between purine and pyrimidine bases. Adenine always pairs with thymine and guanine pairs with cytosine. It implies that the amount of adenine in DNA is equal to the amount of thymine, and the amount of guanine is equal to the amount of cytosine. Hence, we can say that the purines and pyrimidines always occur in the same ratio within the DNA molecule.
- Each turn of the helix is composed of ten base pairs
According to the Watson and Crick model, there are ten base pairs in each turn of the DNA double helix. It was discovered through an X-ray diffraction technique that a single helix turn measures around 34 Angstrom units, where one angstrom is equal to 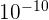 or 3.4 nm. Hence, we can conclude that each DNA double helix base pair is 3.4 Angstrom units or 0.34 nm apart.
or 3.4 nm. Hence, we can conclude that each DNA double helix base pair is 3.4 Angstrom units or 0.34 nm apart.
Groves in DNA Double helix
The two polynucleotide chains are unsymmetrical. The winding of two strands around each other, leave behind the spaces in the form of grooves. The two types of groves present in DNA double helix are:
- Major Groove: It is the widest groove that has a measurement of about 22 Angstrom units.
- Minor Groove: The width of this groove is 12 Angstrom units which is less than that of the major groove.
The major and minor grooves in DNA double-helical structure provide space for the attachment of enzymes and transcription factors, etc.
Summarise with AI:













Keep on teaching us,you are excellent teachers
This is great
Thanks a lot for this book,it really helped me a lot
It’s useful to me
Thanks a lot for your Better book!
It’s a perfect article, go ahead