Chapters
In this article, we will describe the relationship between the structure of chloroplasts, as shown in diagrams and electron micrographs, and their function. Moreover, we will also explain that energy transferred as ATP and reduced NADP from the light-dependent stage is used during the light-independent stage (Calvin cycle) of photosynthesis to produce complex organic molecules. So, let us get started.

Structure of Chloroplasts
- Chloroplasts refer to the organelles in the plant cells where photosynthesis takes place.
- Photosynthesis is the process by which plants make their own food in the presence of sunlight. Several factors affect the rate of photosynthesis such as the intensity of light, water, carbon dioxide, and temperature.
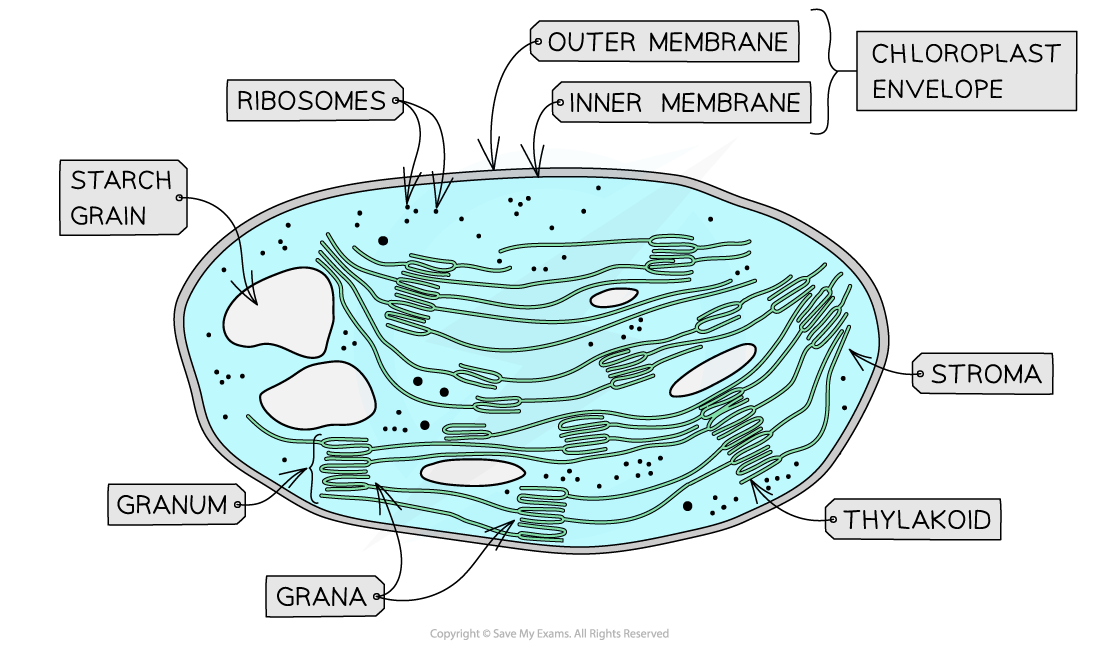
- A double membrane envelope surrounds each chloroplast. The membranes of each of the envelopes is a phospholipid bilayer
- The organelles chloroplasts are filled with a fluid which is referred to as the stroma
- In the stroma, a separate system of membranes is present
- This membrane system is the site where the light-dependent stage of photosynthesis takes place
- The membrane has enzymes, pigments, and electron carriers which are essential for the light-dependent reaction
- This system of the membrane contains a series of flattened sacs which are filled with fluid. These sacs are referred to as thylakoids
- These thylakoids stack up to create structures which are referred to as grana (singular: granum)
- The membranous channels known as stroma lamellae connect the grana which ensure that the stacks of sacs are attached but distanced from one another
- The membranes of the grana form a large surface area to enhance the number of light-dependent reactions that can take place
- This system of the membrane provides a large number of pigment molecules in such an arrangement that ensures the absorption of a sufficient amount of light
- Small (the 70S) ribosomes, a loop of DNA, and starch grains are also present in the stroma
- The DNA loop codes for a few chloroplast proteins (DNA codes other chloroplast proteins in the nucleus of the plant cell)
- At the 70S ribosomes, the proteins coded for this loop of chloroplasts are produced
- During photosynthesis, sugars are formed which are stored as starch inside the starch grains.
In the next section of the article, we will discuss the stages of photosynthesis.
Stages of Photosynthesis
We have already discussed above that chloroplasts are organelles found in the plant cells where photosynthesis occurs. These large organelles typically have a biconvex shape and are approximately 4-10μm long and 2-3μm wide. Inside the plants, the majority of the chloroplasts are present in the mesophyll cells of the leaves. The stages of photosynthesis occur inside the chloroplast. Stage 1 of the photosynthesis takes place within the granum and stage 2 occurs within the stroma.
There are two stages of photosynthesis:
- Stage 1 – It is a light-dependent stage
- Stage 2 – It is a light-independent stage
Stage 1 – Light Dependent stage of photosynthesis
As the name implies, the light-dependent stage of photosynthesis needs light to occur. On the other hand, the light-independent stage can take place either in the presence or in the absence of light. Now, let us see what happens in the light-dependent stage of photosynthesis.
- PSII – In PSII, the light energy is trapped and electrons are boosted to a higher energy level
- An electron receptor receives the electron
- The electrons are transferred from the electron receptor along with a series of electron carriers to PSI which is at a lower energy level
- The energy which is lost by the electrons is trapped by converting ADP to ATP. Hence, light energy is converted into chemical energy.
- PSI absorbs the light energy which in turn boosts electrons to a higher energy level
- Another electron receptor receives the electrons
- The electrons which were eliminated from the chlorophyll are replaced when other electrons are pulled in from a water molecule
- When the water molecule loses the electron, it dissociates into protons and oxygen gas
- The protons from the water molecule unite with the electrons from the second receptor to reduce NADP
- The cyclic reaction causes the recycling of electrons and is employed for the formation of more ATP
Let us see what happens in the light-independent stage of photosynthesis.
Stage 2 – Light independent stage of photosynthesis
- Through the stomata, the carbon dioxide diffuses into the leaf which then moves into the stroma of the chloroplasts
- After that, the carbon dioxide combines with five carbon ribulose biphosphate to create an unstable six-carbon intermediate
- The six-carbon intermediate divides into two, 3 carbon glycerate 3 phosphate molecules
- Some of the NADPH and ATP generated during the LDS are employed to transform glycerate 3 phosphates into triose phosphate
- The pairs of triose phosphate molecules are able to combine to generate an intermediate hexose sugar which can then be polymerized to create amino acids, sugars, lipids, and starch
- A part of the triose phosphate can regenerate the initial carbon dioxide
In the next section of the article, we will summarize the stages of photosynthesis.
Stages of Photosynthesis – Summary
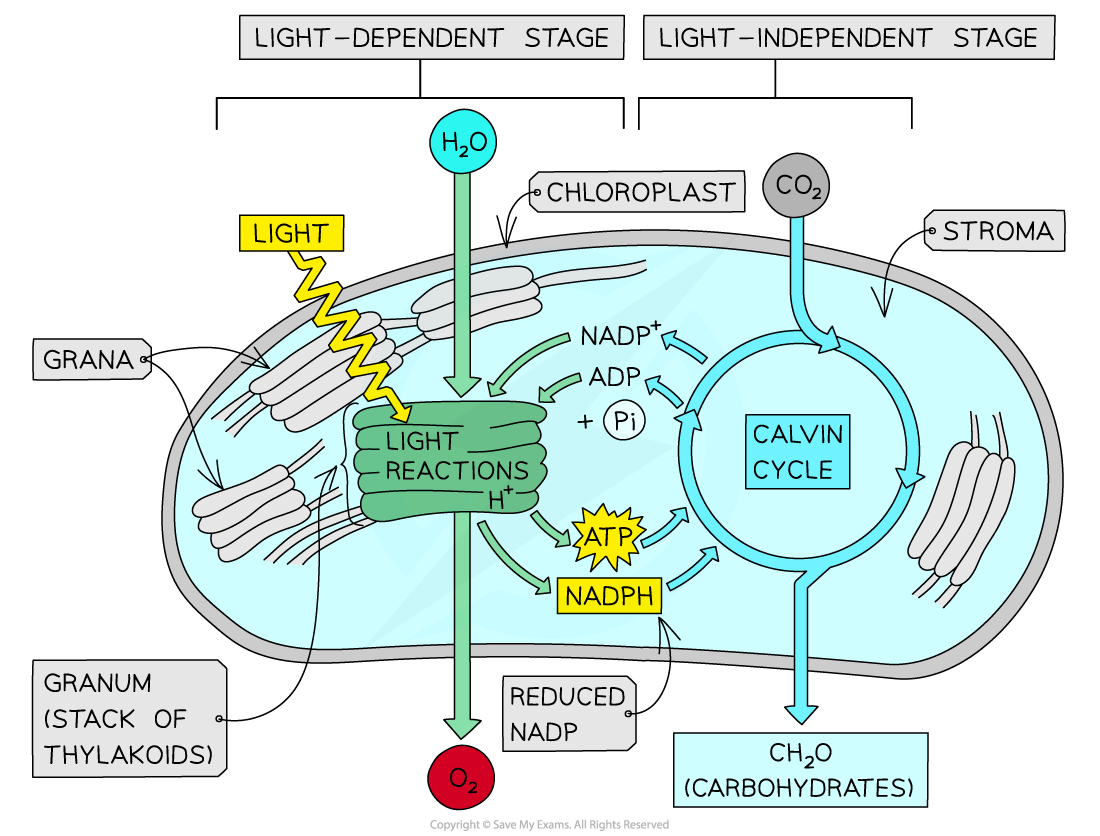
- The process of photosynthesis takes place in two stages: The light-dependent stage which occurs in the thylakoids and the light-independent stage which occurs in the stroma
Light-dependent stage
- During the light-dependent stage of the photosynthesis, the reduced NADP is generated using electrons from the photolysis of water
- In this stage, ATP is produced from ADP and Pi by ATP synthase in a process referred to as photophosphorylation (ADP + Pi → ATP)
- Phosphorylation employs the proton (H+) gradient produced by the photolysis of water
- Energy from ATP and hydrogen from reduced NADP are transferred from the light-dependent stage to the light-independent stage of the photosynthesis
Light-independent stage
The energy and hydrogen employed during the light-independent reaction are collectively referred to as the Calvin cycle. They are employed to generate complex organic molecules which include carbohydrates such as:
- Starch for storage
- Cellulose for creating cell walls
- Sucrose for translocation around the plant
Summarise with AI:













Keep on teaching us,you are excellent teachers
This is great
Thanks a lot for this book,it really helped me a lot
It’s useful to me
Thanks a lot for your Better book!
It’s a perfect article, go ahead