Chapters
This article will explain that within a chloroplast, the thylakoids (thylakoid membranes and thylakoid spaces), which occur in stacks called grana, are the site of the light-dependent stage and the stroma is the site of the light-independent stage. We will also explain the role of chloroplast pigments (chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, carotene, and xanthophyll) in light absorption in thylakoids. Moreover, we will interpret absorption spectra of chloroplast pigments and action spectra for photosynthesis, and explain the use of chromatography to separate and identify chloroplast pigments. So, let us get started.

Thylakoids and the Stroma
- The organelles chloroplasts are found in the plant cells which are a site for photosynthesis.
- A fluid referred to as the stroma fills the chloroplasts
- The system of membranes present in the stroma of the chloroplasts consists of a series of thylakoids which are flattened sacs filled with the fluid.
- These thylakoids stack up to create structures referred to as grana (singular: granum) in places.
- There are two stages of photosynthesis: the light-dependent stage and the light-independent stage.
- The light-dependent stage occurs in the presence of light and the light-independent stage can take place in the presence or absence of light.
- The light-dependent stage of the photosynthesis takes place in the thylakoid membranes and the thylakoid spaces (thylakoid spaces are the spaces within the thylakoids)
- The pigments, enzymes, and electron carriers present within the thylakoid membranes are crucial for light-dependent reactions
- The grana membranes form a large surface area to enhance the number of light-dependent reactions that can take place
- This system of membranes offers a huge number of pigment molecules in a specific arrangement that allows as much light as necessary to get absorbed
- The pigment molecules are arranged in light-harvesting clusters referred to as photosystems
- In a photosystem, various pigment molecules are arranged in structures that resemble a funnel. These structures are called the thylakoid membrane. Each pigment molecule transfers energy down to the subsequent pigment molecule in the cluster until the primary reaction center is reached
- The stroma refers to the fluid that fills the chloroplasts and surrounds the thylakoids
- Sugars, enzymes, carbon dioxide, and other molecules are dissolved in the stroma
- The stroma is the site where the light-independent stage of the photosynthesis takes place
In the next section of the article, we will discuss the role of chloroplast pigments (chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, carotene, and xanthophyll) in light absorption in thylakoids.
Chloroplasts Pigments
- Many different photosynthetic pigments inside the thylakoids are present in the chloroplasts. The purpose of these pigments is to absorb different wavelengths of light. We have already discussed the points below which are necessary to understand the role of chloroplasts pigments:
- These thylakoids stack up to create structures called grana in places
- The thylakoid membrane system offers a huge number of pigment molecules in an arrangement that ensures the sufficient absorption of light
- The pigment molecules are arranged in light-harvesting clusters referred to as photosystems
- Various pigment molecules are arranged in funnel-like structures in a photosystem.
- In the thylakoid membranes and thylakoid spaces, the light-dependent stage of the photosynthesis takes place
- This is the reason, the thylakoid membranes have enzymes, pigments, and electron carriers needed for the light-dependent reactions.
Pigments have two groups:
- Chlorophylls (Chlorophyll a and b)
- Carotenoids (Carotene and xanthophyll)
- Chlorophylls (chlorophyll a and b) absorb wavelengths in the blue-violet and red areas of the light spectrum, and they reflect green light, making the plants appear green.
- On the other hand, carotenoids absorb wavelengths of light usually in the blue-violet area of the spectrum
In the next section of the article, we will interpret the absorption spectra of chloroplast pigments and action spectra for photosynthesis.
Absorption Spectra and Action Spectra of Photosynthesis
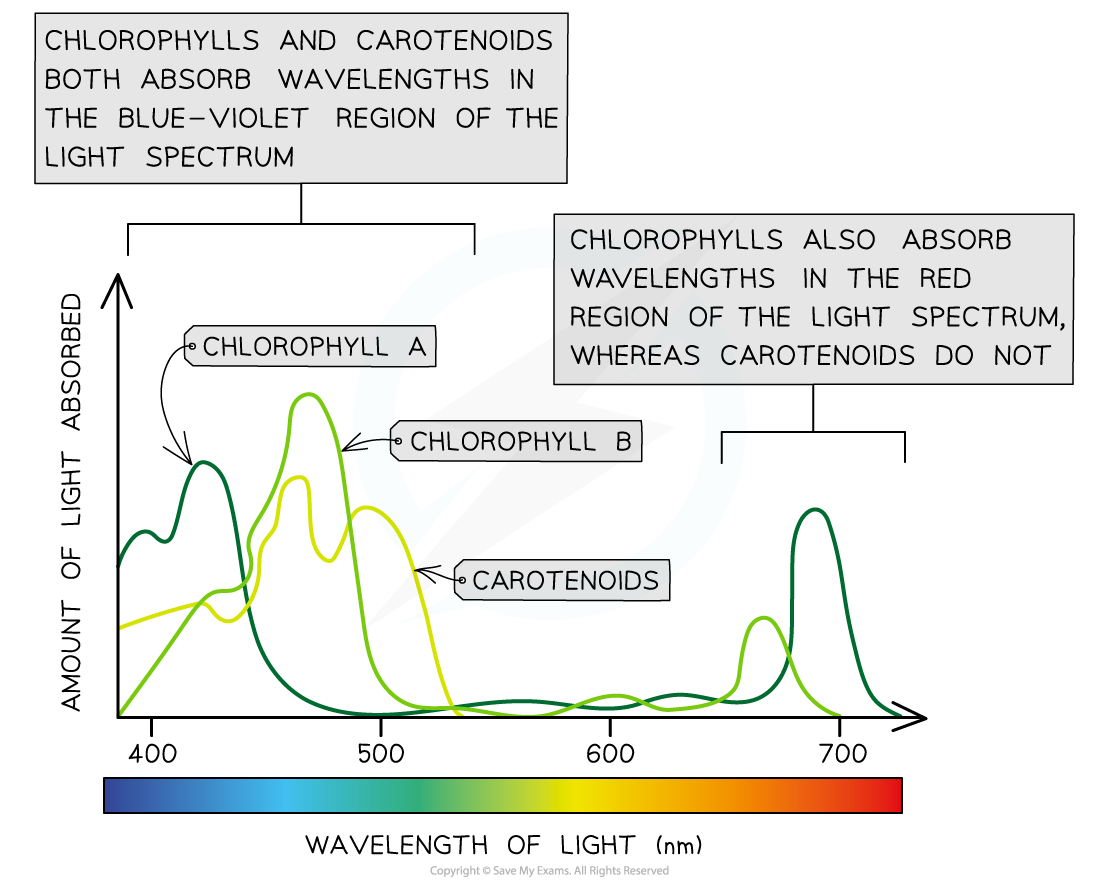
- An absorption spectrum refers to a graph that exhibits the absorbance of various wavelengths of light by a specific pigment
- Chlorophylls absorb wavelengths in the blue-violet and red areas of the light spectrum
- Carotenoids absorb wavelengths of light usually in the blue-violet area of the spectrum
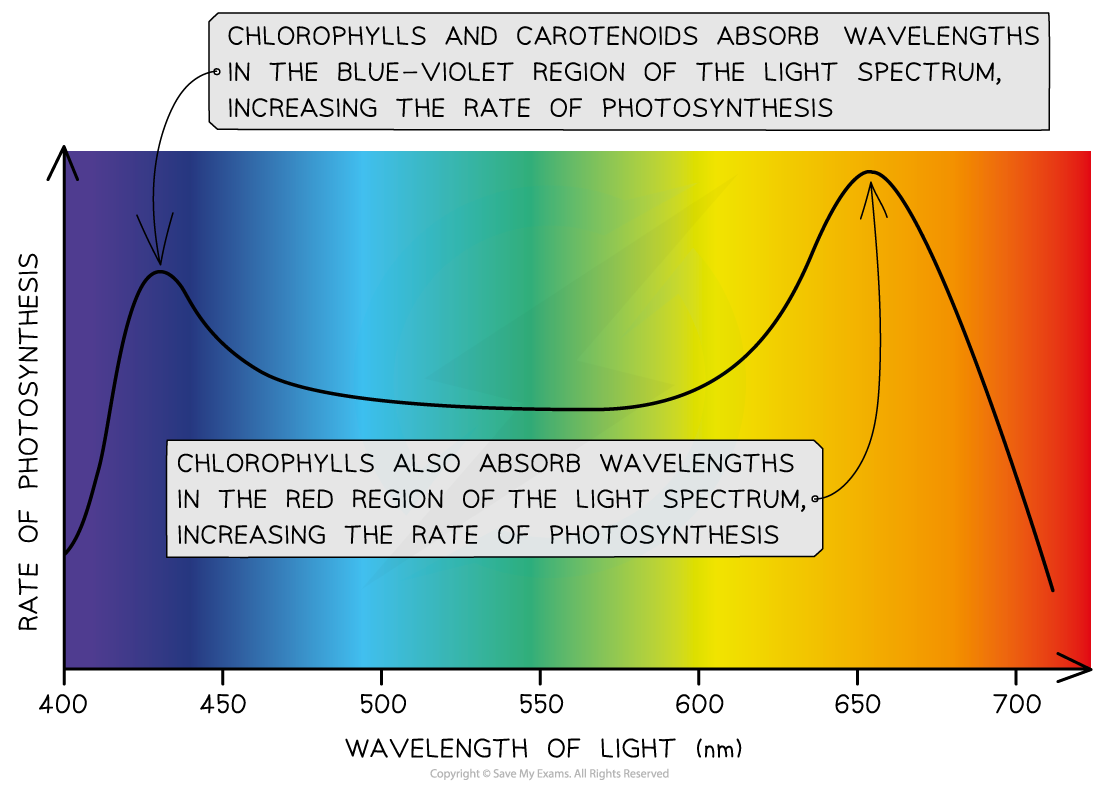
- An action spectrum refers to a graph that exhibits the photosynthesis rate at various wavelengths of light
- The photosynthesis rate is highest in the blue-violet and red areas of the light spectrum because at these wavelengths of light, the plants are able to absorb. It implies that these are the wavelengths that chlorophylls and carotenoids can absorb.
- A strong correlation is present between the cumulative absorption spectra of all pigments and the action spectrum
- There are two primary peaks in both the graphs (these peaks are at the blue-violet and red areas of the light spectrum
- Trough in the green-yellow region of the light spectrum is present in both the graphs
In the next section of the article, we will discuss the chromatography of the chloroplast pigments.
Chromatography of Chloroplast Pigments
- Chromatography refers to an experimental technique that is employed to separate mixtures.
- In this technique, the mixture is dissolved in the solvent or fluid known as the mobile phase. After that, the dissolved mixture is passed through a static material known as the stationary phase.
- Various components inside the mixture pass through the material at distinct speeds
- It causes various components to separate
- For each component of the mixture, a retardation factor Rf can be computed
The formula for the retardation factor is given below:
Rf value = distance covered by the component ÷ distance moved by solvent
- Two of the most common techniques that are employed to separate these photosynthetic pigments are:
- Paper chromatography: In this technique, the mixture of pigments is passed through the paper (cellulose)
- Thin-layer chromatography: In this technique, the mixture of pigments is moved through a thin layer of an adsorbent such as the silica gel. Through the adsorbent, the mixture moves faster and separates more noticeably
- Chromatography can be employed to separate and detect chloroplast pigments that are extracted from a leaf because each pigment has a distinct Rf value
- The Rf value shows how far a dissolved pigment moves through a stationary phase
- The smaller Rf value shows that the pigment is less soluble and larger in size
- Although particular Rf value is dependent on the solvent that is used, however, generally:
- Carotenoids contain the highest Rf values which are generally close to 1
- The Rf value of the chlorophyll is much lower
- The Rf value of the chlorophyll A is somewhere between those of carotenoids and chlorophyll B
- Smaller Rf values show that the pigment is less soluble and is larger in size
Summarise with AI:












Keep on teaching us,you are excellent teachers
This is great
Thanks a lot for this book,it really helped me a lot
It’s useful to me
Thanks a lot for your Better book!
It’s a perfect article, go ahead