Chapters
In this article, we will describe the structure and functions of the gas exchange system. We will especially describe the functions of ciliated epithelial cells, goblet cells, and mucous glands in maintaining the health of the gas exchange system. Moreover, we will also elucidate the functions in the gas exchange system of cartilage, smooth muscle, elastic fibres, and squamous epithelium. In the end, we will discuss how gas exchange occurs between the air in the alveoli and blood in the capillaries. So, let us get started.

The Human Gas Exchange System
The human thorax is the pace where gas exchange takes place in humans. The thorax is the set of organs and tissues present in the chest cavity. The structures present in the human thorax include:
- Trachea: It is the airway that is lined with mucus and leads from the mouth and nose to the bronchi.
- Lungs: Two lungs are present in the human body. Lungs are the main component of the respiratory system and they are the place where gas exchange occurs.
- Bronchi: The left and right bronchi are present at the bottom of the trachea.
- Bronchioles: Bronchioles are narrow tubes that are less than 1 mm. They move air from the bronchi to the alveoli.
- Capillary network: Capillary network surrounds the alveoli and acts as an exchange surface between the lungs and the blood
In the next section of the article, we will describe the functions of ciliated epithelial cells, goblet cells, and mucous glands in maintaining the health of the gas exchange system. In addition to this, we will also describe the functions in the gas exchange system of cartilage, smooth muscle, elastic fibres, and squamous epithelium
Structures and Functions in the Gas Exchange System
Goblet cells, ciliated epithelial cells, and mucous glands are critical for maintaining the health of the gas exchange system. On the other hand, cartilage, elastic fibres, smooth muscle, and squamous epithelial tissue play vital structural roles in the maintenance of the gas exchange system. Now, let us discuss all these structures and their related functions in detail.
1) Ciliated Epithelial Cells
Ciliated epithelial cells line the trachea to the bronchi and contain small projections known as cilia. The cilia are responsible for sweeping away the dust, bacteria, mucus, and other microorganisms up and away from the lungs to the mouth. In the mouth, they get swallowed and digested by the stomach acid.
2) Goblet cells
These cells are embedded throughout the ciliated epithelium and produce mucus. The mucus produced by the goblet cells traps bacteria, dust, and microorganisms.
3) Mucous Glands
As the name implies, the mucus glands produce mucus by working with the goblet cells in the trachea and bronchi
4) Cartilage
Rings of cartilage lining the trachea which is also known as the windpipe. The cartilage is a string and flexible tissue and plays an important role to keep the trachea open. Due to its flexibility, the cartilage can move and flex when we breathe.
5) Smooth Muscle
Smooth muscle is the muscle that is present in the walls of the bronchi and bronchioles. This muscle is not under conscious control, and it helps in the regulation of the airflow in and out of the lungs through dilation and widening when more air is required.
6) Elastic Fibers
Elastic fibres are present in the squamous epithelium of the alveolar walls. They are an essential component of the alveoli because they enable the small alveoli to stretch as they are filled with air. They also allow the alveoli to recoil to help force air out. Due to the elastic abilities of the alveoli, they have a large surface area. In cases of advanced emphysema, the alveoli lose their elasticity.
7) Squamous Epithelium
The squamous epithelium contains a flat, thin cell in the alveolar walls. Due to their thinness, oxygen and carbon dioxide have an extremely short diffusion pathway during the gas exchange.
So far we have described the structures and functions of ciliated epithelial cells, goblet cells, mucus glands, cartilage, smooth muscle, elastic fibres, and squamous epithelium. In the next section of the article, we will discuss how gas exchange occurs between the air in the alveoli and blood in the capillaries.
Gas Exchange Between Air in Alveoli and Capillaries in Lungs
- The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place between the alveoli and the capillaries in the lungs.
- Through a process of simple diffusion, oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged.
- Simple diffusion refers to a passive movement from a higher to lower concentration
- . A higher concentration of oxygen is present in the air in the alveoli. Before moving away to the rest of the body for aerobic respiration, this oxygen diffuses from the alveoli and into the blood capillaries.
- On the other hand, the blood in the capillaries contains a relatively lower concentration of oxygen and a higher concentration of carbon dioxide. The diffusion of carbon dioxide takes place from the blood and into the alveoli. After that, this carbon dioxide is exhaled.
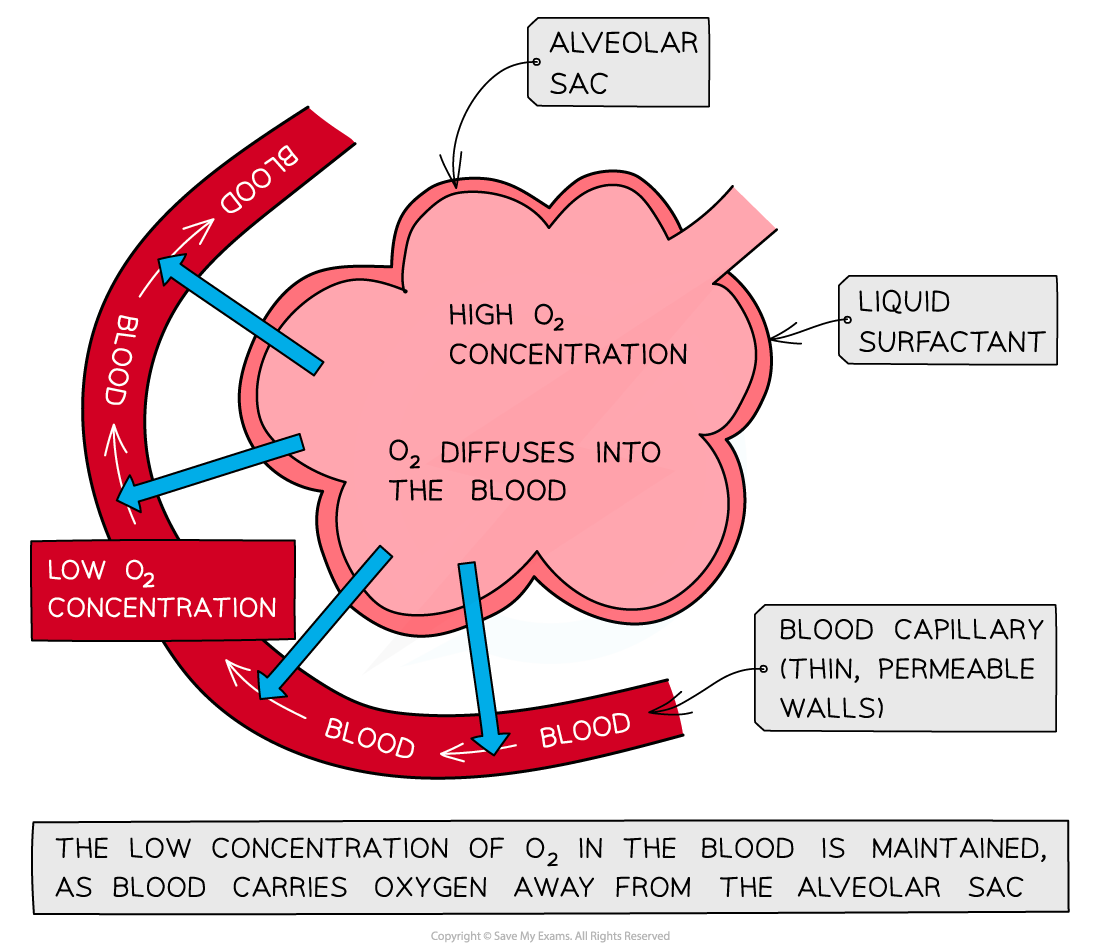
In the next section of the article, we will discuss the features of alveoli.
Features of Alveoli
Some features of alveoli are discussed below:
i) A large number of alveoli in the human body
- It is estimated that an average human adult body contains 480 – 500 million alveoli in their lungs which equals a surface area of 40 - 75 m2.
- The available surface area increases due to the presence of a large number of alveoli. This increased surface area helps the oxygen and carbon dioxide to diffuse across.
ii) Thin walls
- The alveolar walls are just one cell thick, and these cells are flattened.
- Because of their thinness, the gases have a very short diffusion distance, hence gas exchange becomes quick and efficient.
iii) An extensive network of capillaries
- The walls of capillaries are just one cell thick and these cells are flattened which keeps the diffusion distance short for gases.
- The constant blood flow through capillaries implies that oxygenated blood is brought away from the alveoli and deoxygenated blood is brought towards them.
- It helps to maintain a concentration gradient which is critical for gas exchange to take place.
Summarise with AI:













Keep on teaching us,you are excellent teachers
This is great
Thanks a lot for this book,it really helped me a lot
It’s useful to me
Thanks a lot for your Better book!
It’s a perfect article, go ahead