Chapters

Biological Molecules: Carbohydrates and Lipids
In this article, we will discuss the two forms of glucose which are α-glucose and β-glucose, define certain key terms related to biological molecules, and discuss the role of covalent bonds in joining smaller molecules together to form polymers. So, let us get started.
Two Forms of Glucose: α-glucose and β-glucose
In this section, we will discuss the two forms of glucose in detail.
Glucose ATP is the most popular carbohydrate monomer. The molecular formula of glucose is 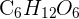 . Glucose is a well-known monosaccharide and is critical for the survival of many living beings. The molecules with different numbers of carbon atoms form various types of monosaccharides which include:
. Glucose is a well-known monosaccharide and is critical for the survival of many living beings. The molecules with different numbers of carbon atoms form various types of monosaccharides which include:
-
- Trioses (3C). The example includes glyceraldehyde
- Pentoses (5C). The example includes ribose
- Hexoses (6C). The example includes glucose
Since glucose has two structurally distinct forms: alpha (α) glucose and beta (β) glucose, therefore it is referred to as an isomer. Due to this variation in structure, carbohydrates have different functions.
The structure of alpha (α) glucose and beta (β) glucose is shown in the figure below:
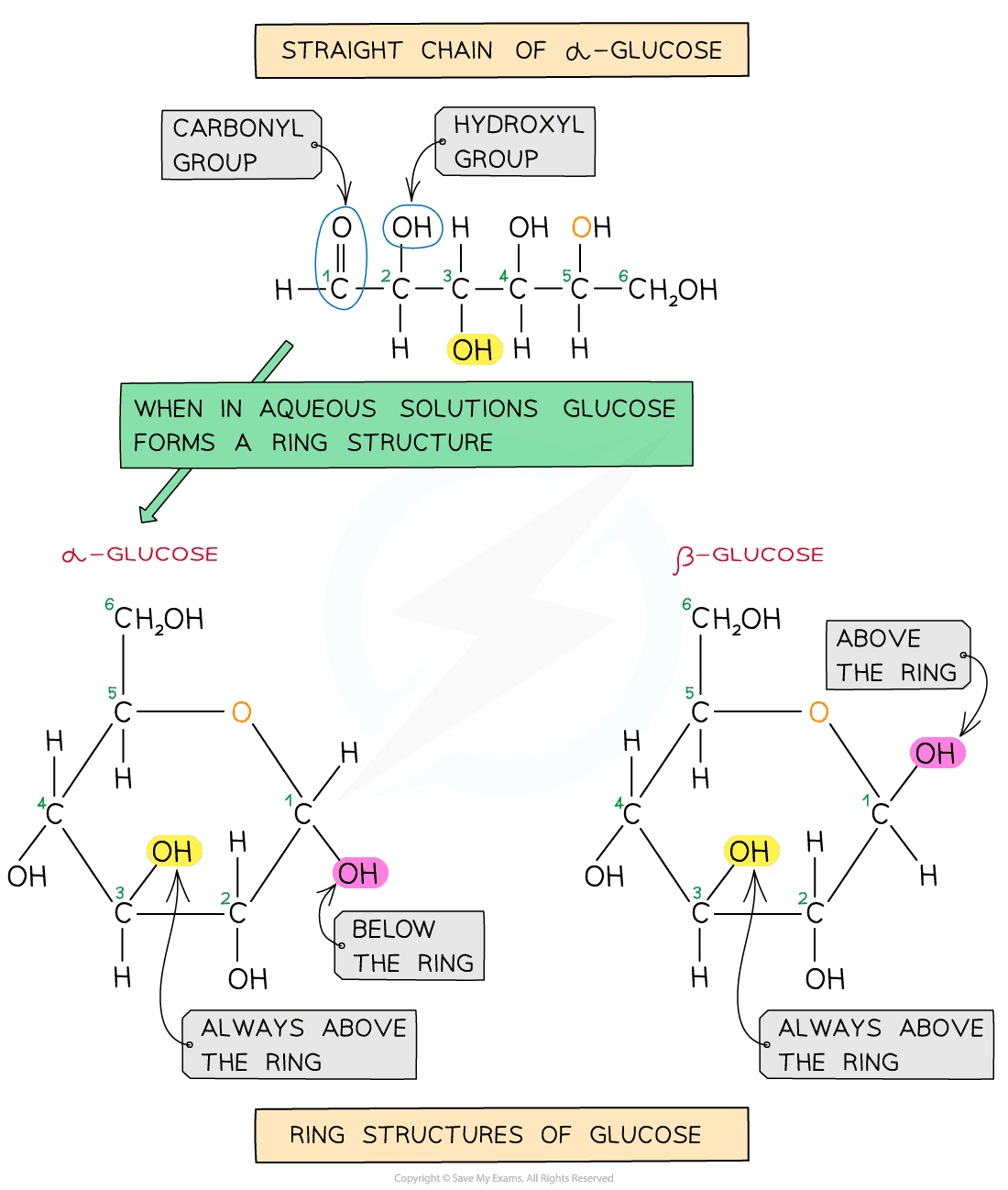
Two isomers of glucose create different polysaccharides.
-
Starch
Starch is created from several alpha glucose polymers. Its bonds create a helix and many hydrogen bonds are present in it. It acts as an energy store within plants because of the compact and insoluble nature of its molecules.
-
Glycogen
Glycogen refers to the primary long-term energy storage molecule in animals and humans. It is composed of long chains of alpha glucose with 1,4-glycosidic bonds. It is created in the liver, however, muscle tissue is the place where it is stored so that it is readily available for use in the process of respiration.
-
Cellulose
Cellulose is an example of a polysaccharide. Polysaccharides are macromolecules that are polymers created by several monosaccharides combined by glycosidic bonds in a condensation reaction to create chains. These chains can be either branched or unbranched, folded, or straight. Polysaccharides are not soluble in water. Cell walls of the plant cells are made up of cellulose. The cell wall is the outermost layer of the plant cell and is a freely permeable membrane.
Structure of Cellulose
Cellulose consists of long chains of β-glucose combined with 1, 4 glycosidic bonds. Because β-glucose is an isomer of alpha glucose, hence to create 1, 4 glycosidic bonds, consecutive β-glucose should be rotated at 180 degrees to each other.
In the next section of the article, we will define and discuss key terms related to biological molecules
Key Biological Molecules Terms
The life of every organism is different; however, all organisms have the same biochemical foundation of life. The main biological molecules that help the organisms to function include:
- Carbohydrates
- Lipids
- Proteins
- Water
- Nucleic Acid
Monomers and Polymers
- Monomers: Monomers refer to the smaller units from which larger molecules are created
- Polymers: Polymers refer to the molecules composed of a large number of monomers that are joined together in the form of a chain
Organic Compounds
- Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acid are termed organic compounds because they contain carbon and hydrogen elements
- The foundation of organic compounds is carbon atoms because:
- The compounds that contain carbon atoms are very stable as each carbon atom can create four covalent bonds (Covalent bonds are difficult to break owing to their strength. A huge amount of energy is needed to break these bonds).
- Carbon atoms can create covalent bonds with other atoms such as sulfur, nitrogen, and oxygen
- Carbon atoms can join to create rings and straight or branched chains
- Carbon atoms can form monomers which are small single subunits. Monomers can create a bond with several repeating subunits to create polymers which are large molecules. They do so by a process known as polymerization.
Macromolecules
- Macromolecules refer to very large molecules that have 1000 or more atoms. Due to this reason, macromolecules possess a high molecular mass.
- Polymers can be macromolecules, but all macromolecules are not polymers because the subunits of polymers must have the same repeating units.
Carbohydrates
- One of the key carbon-based compounds in living organisms is carbohydrates
- All molecules of carbohydrates contain carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen atoms
- Since oxygen and hydrogen atoms always exist in 2:1 (for instance,
 ), hence we can represent them using the formula
), hence we can represent them using the formula 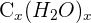
Types of Carbohydrates
There are three types of carbohydrates:
- Monosaccharide: Monosaccharide refers to the single sugar monomer that is a building block for polymers. Examples of monomers include glyceraldehyde (3C), ribose (5C), and glucose (6C).
- Disaccharide: When two monosaccharides are joined together by a glycosidic bond in a condensation reaction, a disaccharide is created. Examples of disaccharides include maltose, sucrose, and lactose.
- Polysaccharide: Polysaccharide refers to the polymers created by several monosaccharides joined by glycosidic bonds in a condensation reaction. Examples of polysaccharides include cellulose, starch, and glycogen.
In the next section, we will discuss covalent bonds in polymers.
Covalent Bonds in Polymers
- When two atoms share two or more electrons, a covalent bond is created between them.
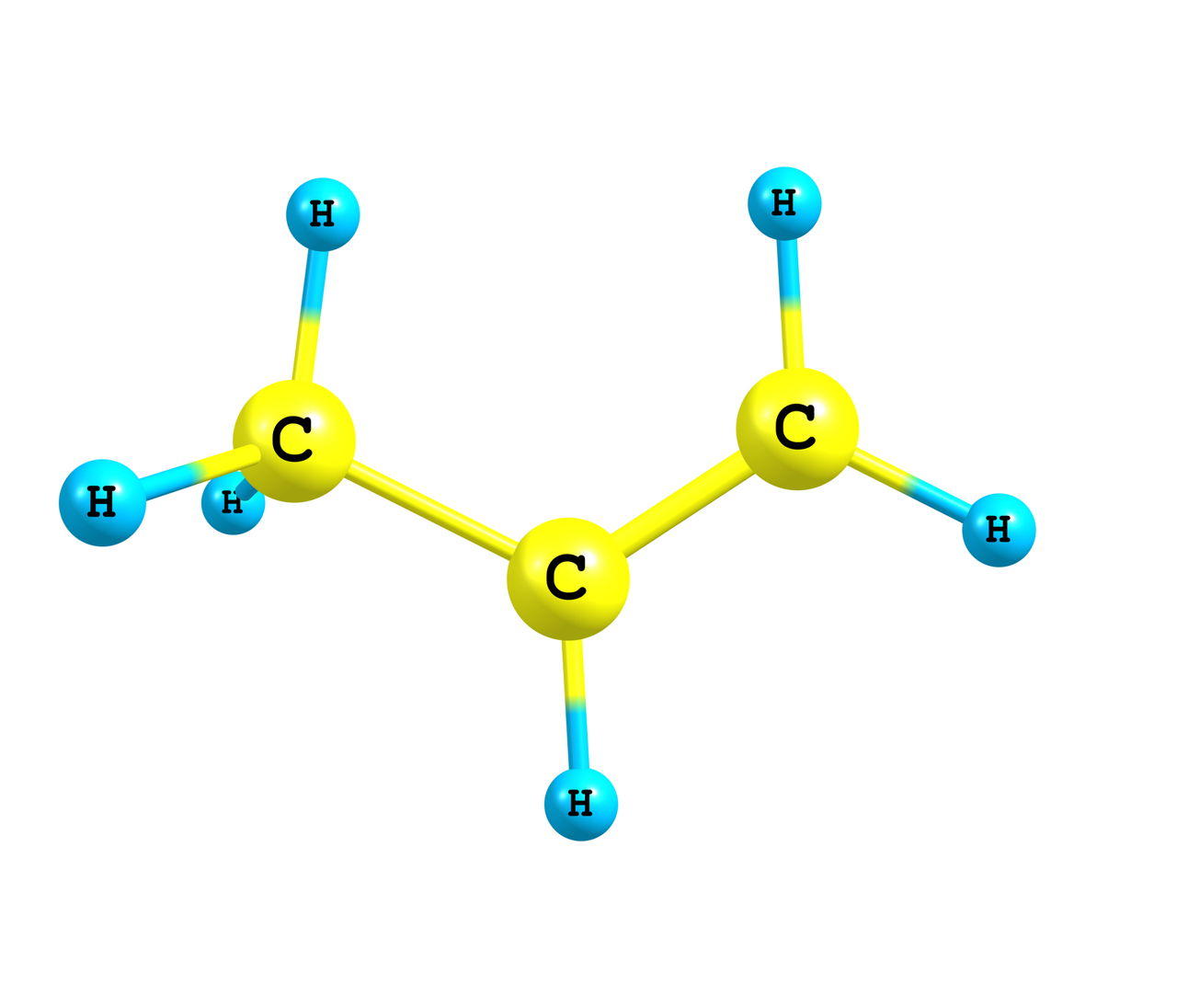
- There can be equal sharing of electrons to create a nonpolar covalent bond or unequal sharing to create a polar covalent bond.
- Usually, each atom creates a definite number of covalent bonds because of the number of free electrons in the outer orbital. For instance, H = 1 bond and C = 4 bonds.
- Covalent bonds are characterized by their higher degree of stability because high energies are needed to break them
- Several pairs of electrons can be shared to create double bonds. For instance, triple bonds or unsaturated fats C = C
- If the outer orbitals of two monomers overlap each other because they are very close to each other, then it culminates in the sharing of their electrons and the formation of covalent bonds. Polymerization occurs when more monomers are included.
What is Condensation?
- Condensation is also referred to as dehydration synthesis.
- A condensation reaction occurs when polymers and macromolecules are formed.
- Polymers and macromolecules are created when monomers are joined together by covalent bonds and water is removed.
Hydrolysis
- Hydrolysis is a combination of two terms: hydro and lyse
- Lyse means “to break” and hydro means “water”. Hence, the word hydrolysis means to break with water.
- To hydrolyze polymers, water is added which breaks the covalent bonds between them
Summarise with AI:













Keep on teaching us,you are excellent teachers
This is great
Thanks a lot for this book,it really helped me a lot
It’s useful to me
Thanks a lot for your Better book!
It’s a perfect article, go ahead