Chapters
In this article, we will discuss the importance of stem cells in detail. But before proceeding to explain the significance of stem cells, first, let us discuss what are stem cells.

Introduction
According to scientists, an adult human body contains almost 200 different types of cells. Each type of cell performs its specific function. Among these diverse groups of cells, stem cells are the most important ones. Generally, these cells are considered parent cells that produce all other types of cells.
In the next section of the article, we will discuss stem cells in detail.
What are Stem Cells?
The stem cells do not belong to a certain, dedicated or differentiated, and functionally active cell type. Instead, they can be differentiated into any certain cell type which is functionally active. They can also renew themselves. This is the most essential property of these cells. These cells also divide occasionally, moderately, or rapidly depending on their location and the organ system they belong. The stem cells occasionally divide in the muscles, moderately in the germinal epithelium, and rapidly in the epithelium of the gastrointestinal tract.
Before discussing stem cells, first, let us discuss cell differentiation.
Cell Differentiation
Cell differentiation is a process that is guided by signals. In this process, a cell is bound to be a part of a specific tissue. Nearly all the cells are composed of the same genetic material, however, most of the cells in our body are specialized to perform a certain function. Cell differentiation is a process by which the specific functionality of the cell is achieved. In this process, specific genes of the cell are inactivated, and specific genes are allowed for gene expression.
In the next section of the article, we will explain the classification of stem cells.
Classification of Stem Cells
As per potency, the stem cells are divided into the following five classes:
Totipotent
These stem cells are the real stem cells. They are entirely undifferentiated and can be differentiated into certain cell types. A totipotent stem cell can create complete viable offspring if provided with suitable conditions. The zygote is the best example of the totipotent stem cell which is mostly created after the first and sometimes created after the second cleavage. They are not found in an adult and are also referred to as embryonic stem cells.
Pluripotent stem cells
These stem cells are slightly differentiated and they give rise to almost all the cell types, but they cannot create an entire viable offspring if they are isolated and grown independently. The example includes cells of the morula stage of the embryo.
Multipotent stem cells
These stem cells are slightly more differentiated and result in cells of closely related families. The best example of this type of stem cell includes fibroblast found in adult connective tissue.
Oligopotent stem cells
These stem cells are more differentiated than the multipotent stem cells and they result in different cells of the cellular family. Examples of these stem cells include myeloid or lymphoid stem cells that can be differentiated into various kinds of white blood cells or leukocytes.
Unipotent stem cells
They are the most differentiated cells and result in only a specific type of cell to which they belong. They can renew themselves, unlike fully differentiated cells. Unipotent stem cells are abundantly present in the human body. The multipotent, oligopotent, and unipotent stem cells are also referred to as adult stem cells.
In the next section of the article, we will discuss the importance of stem cells in detail.
Importance of Stem Cells
A stem cell is a cell that undergoes division by mitosis an unlimited number of times. Every new cell that is produced as a result of stem cell division can remain a stem cell or develop into a specialized cell-like muscle or blood cell by a process called differentiation. The ability of stem cells to differentiate into more specialized types of cells is referred to as potency. The three types of potency include totipotency, pluripotency, and multipotency.
- Totipotency: Totipotent stem cells refer to the stem cells that can differentiate into any type of cell present in an embryo as well as extraembryonic cells (the cells that create the placenta). The zygote is totipotent and is created when a sperm cell fertilizes an egg cell.
- Pluripotency: Pluripotent stem cells refer to the embryonic stem cells that can differentiate into any type of cell present in an embryo. However, these cells are unable to differentiate into extra-embryonic cells (the cells that create the placenta).
- Multipotency: They refer to the adult stem cells that have lost some of the potency related to embryonic stem cells and are not pluripotent any longer.
Multipotent adult stem cells
- Cells become more and more specialized with the development of tissues, organs, and organ systems.
- Adult cells are differentiated and specialized to fulfill specific roles. They slowly lose the ability to divide until a time comes when they cannot divide any longer.
- However, a small number of stem cells referred to as adult stem cells remain to create new cells for important processes of cell replacement, growth, and tissue repair.
- Although the adult stem cells can divide by mitosis an unlimited number of times, however, they can produce only a few ranges of cell types which means that they are multipotent.
- For instance, the stem cells present in the bone marrow are multipotent adult stem cells. These cells can only differentiate into blood cells such as red blood cells, monocytes, neutrophils, and lymphocytes.
- Stem cells are present throughout the body of an adult. For example, in the skin, bone marrow, heart, gut, and brain.
- Scientists are researching stem cell therapy which will introduce the adult stem cells into damaged tissue to cure diseases like leukaemia and injuries like sunburns.
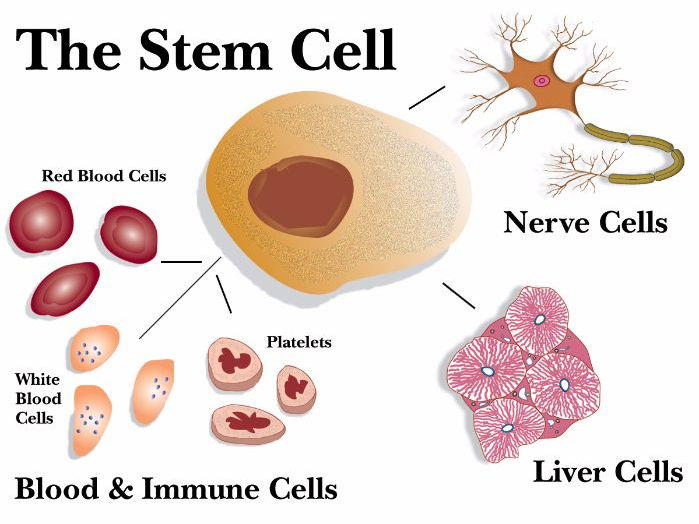
In the next section of the article, we have summarized the main functions of stem cells.
Functions of the Stem Cells
The main functions of the stem cells are:
- To maintain a reserve of self-renewing cell population
- To renew z certain type of cell after routine wear and tear or due to any physical or physiological trauma.
- To provide a non-stop supply line of fresh cells in epithelial regions where cells are continually slough
In the next section, we will discuss how uncontrolled cell division leads to cancers.
Formation of Tumors
The formation of cancers explains the importance of controlled cell division because they are the result of uncontrolled mitosis. Cancerous cells divide to form a tumour when they divide repeatedly and uncontrollably. They begin when changes take place in the genes that control cell division. A change in any gene is referred to as a mutation. If the mutated gene is responsible for causing cancer, then it is known as an oncogene. Remember that mutations are normal events that do not lead to cancer most of the time. The majority of the mutations either lead to early cell death or cells being destroyed by the immune system of the body.
The mutations that lead to the formation of cancerous cells do not result in early cell death or cells being destroyed by our immune system. This implies that the harmful mutation in the original cell can be transferred to the descendants of the cell. A normal tumour is composed of a thousand million cancerous cells by the time it is found.
What are carcinogens?
Carcinogens refer to the agents that are the possible cause of cancer. Examples include tar in tobacco, X-rays, and UV light. The agent causing the cancer is known as carcinogenic.
What are benign tumours?
Few tumours like warts do not spread from their original location. They are known as benign tumours and do not result in cancer.
What are malignant tumours?
Some tumours spread through the body, attacking, and destroying other tissues, and are referred to as malignant tumours. These tumours cause cancers and impede the organ or tissue from working properly. They can break off the tumour and move through the blood or lymphatic system to create secondary growths in other body parts. The cancers that spread in this manner are known as metastasis. Metastasis is quite dangerous because it is hard to detect, locate and eliminate secondary cancers.
Summarise with AI:













Keep on teaching us,you are excellent teachers
This is great
Thanks a lot for this book,it really helped me a lot
It’s useful to me
Thanks a lot for your Better book!
It’s a perfect article, go ahead