Chapters
In this article, we will define the term recombinant DNA and discuss that genetic engineering refers to the deliberate manipulation of genetic material to alter specific characteristics of an organism and that this may include transferring a gene into an organism so that the gene is expressed. So, let us get started.

Recombinant DNA
The genetic code is universal which implies that almost every organism employs the same four nitrogenous bases, i.e. A, T, C, and G. However, some exceptions do exist. The same four nitrogenous bases mean that the same codons code for the same amino acids in all living beings. Now, what does it implicate? Well, it shows that genetic information can be transferred between species.
The ability of genetic information to get transferred between species allows scientists to artificially modify the DNA of an organism by combining lengths of nucleotides from various sources. Generally, the nucleotides are from different species.
This modified DNA, with the introduced nucleotides, is referred to as recombinant DNA (rDNA)
If nucleotide sequences from a different species are present in an organism, then it is referred to as a transgenic organism. The organism that is genetically engineered will contain recombinant DNA. Such an organism is known as a genetically modified organism (GMO).
Remember that the universal nature of genetic code enables the formation of recombinant DNA. All forms of life on Earth employ the same genetic code. It is strong evidence of evolution. The basis of storing instructions is the genetic code which along with the environmental influences governs the behavior of the cells.
In the next section of the article, we will discuss that genetic engineering is the intentional manipulation of genetic material to alter specific characteristics of an organism and that this may include transferring a gene into an organism so that the gene is expressed
Genetic Engineering
We can define genetic engineering like this:
A technique that is used to intentionally alter a specific characteristic of an organism is referred to as genetic engineering.
Genetically Modified Organism (GMO)
This technique includes the removal of a gene or genes with the desired attribute from one organism and the transfer of the gene using a vector into another organism where the desired gene is expressed. The organism that is genetically engineered using this technique will contain recombinant DNA and we will call it a genetically modified organism (GMO). The genome of the genetically modified organism (GMO) has been engineered in the laboratory to promote the expression of desired physiological characteristics or the production of desired biological products.
In traditional crop farming, livestock production, and pet breeding, selective breeding has been used for many years to produce offspring with desirable characteristics. However, in genetic modification, recombinant genetic technologies are used to produce organisms whose genomes have been particularly modified at a molecular level, generally by introducing genes from unrelated species of organisms that code for attributes that would not be easily achieved through traditional selective breeding.
Steps Involved in Genetic Engineering
To genetically engineer an organism, the following steps should be taken:
- Step 1 – Identify the desired gene
- Step 2 – Isolate the desired gene by cutting it from a chromosome. This is done by using enzymes (restriction endonucleases). Then, make a single strand of complementary DNA (cDNA) from mRNA by employing reverse transcriptase. Finally, create the artificial gene using nucleotides.
- Step 3 – This step involves multiplication of the gene using PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
- Step 4 – This step involves the transfer of the gene into an organism using a vector. For instance, viruses, plasmids, and liposomes
- Step 5 – This step involves the identification of the cells with the new gene by employing a marker which is cloned afterward
What is needed to modify an organism?
To modify an organism, genetic engineers need the elements listed below:
- Enzymes which include restriction endonucleases, ligase, and reverse transcriptase
- Vectors, for instance, plasmids, viruses, and liposomes that will transfer the genes into a cell
- Markers include genes that code for detectable substances that are traceable. For instance, GFP (Green Fluorescent Protein) shines under UV light or GUS β-glucuronidase enzyme which converts colorless or non-fluorescent substrates into products that are fluorescent or colored.
Uses of Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering is employed in the new field of science known as synthetic biology. This research area studies the design and creation of various biological pathways, devices, and organisms along with the redesigning of current natural biological systems.
Some of the important uses of genetic engineering are listed below:
Genetically Modified Crops
- Genetic engineering is used to genetically modify crops to increase crop yield via resistance to disease, drought, herbicides, and pesticides to offer enhanced nutritional value. The example includes the production of golden rice using this technique.
- Scientists have also used this technique to genetically alter the crops like maize which are more resistant to insect attacks and rice to generate β-carotene to provide vitamin A.
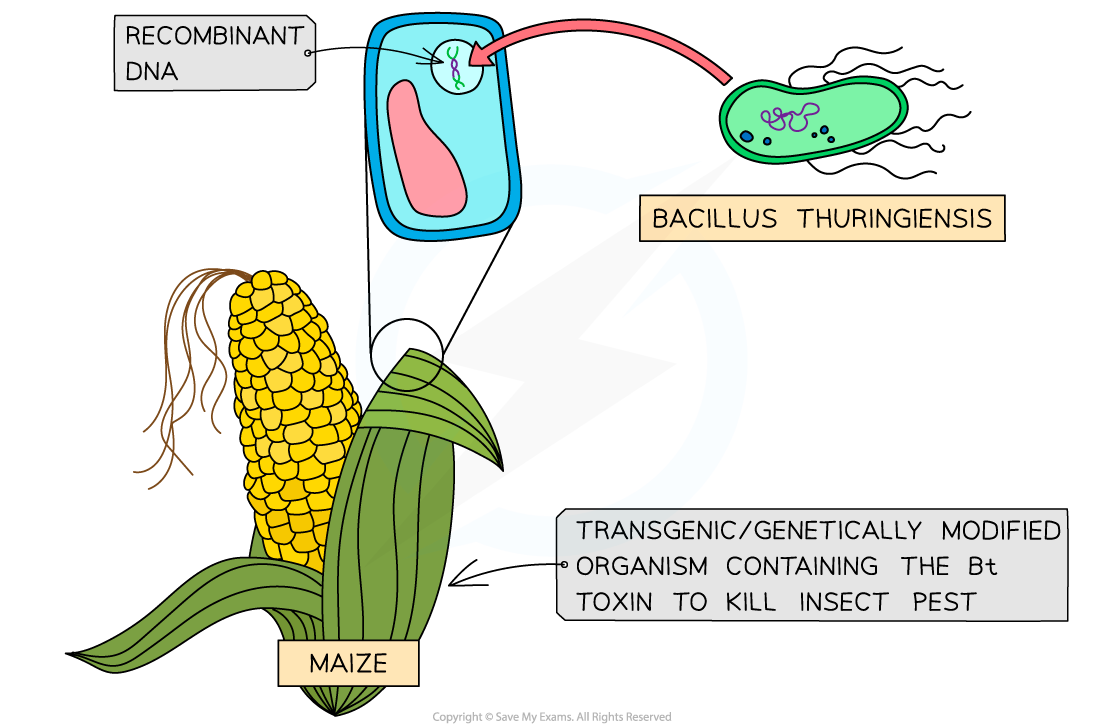
- Another example includes the soya plants that are prone to a huge number of insect pests that costs billions of dollars annually. Soya plants are altered with the Bt toxin gene to produce their insecticide. It implies that when an insect consumes the parts of the soya plants, the alkaline environment in their guts stimulates the toxin which is harmless to vertebrates. Consequently, the insect gets killed.
- Genetically modified crops can minimize the impacts of farming on the environment because there is less need to spray pesticides.
Genetically Modified Livestock
- It is also employed to genetically modify the livestock to make it resistant to diseases and pests which in turn increases productivity.
- Scientists are genetically modifying livestock to produce pharmaceutical drugs in a process called pharming. The biopharma goats and sheep are genetically modified for the production of a huge number of useful human proteins in their milk. For instance, a human blood protein called AAT in sheep milk and human protein antithrombin in goat milk.
Production of Medicines
- Scientists use genetic engineering to produce medicines by genetically modifying the bacteria. For example, in 1982, insulin was the first approved recombinant human protein used in the treatment of diabetes.
Production of Chemicals
- Bacterial modification is employed to decompose harmful pollutants or to produce chemicals on large scale.
Summarise with AI:












Keep on teaching us,you are excellent teachers
This is great
Thanks a lot for this book,it really helped me a lot
It’s useful to me
Thanks a lot for your Better book!
It’s a perfect article, go ahead