Chapters
In this article, we will discuss the external and internal structure of the mammalian heart. Besides this, we will also explain the differences in the thickness of the walls of the atria and ventricles, and the left ventricle and right ventricle. So, let us get started.

Structure of Heart
The mass of the human heart is approximately 300 grams and is almost the size of a closed fist. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ that is present in the chest cavity. In mammals and other animals, the heart is the organ that controls the circulatory system. The main function of the heart is to pump the blood around the body. Mammals have a double circulatory system which implies that the mammalian heart pumps the blood to the lungs and the remaining body simultaneously. In the chest cavity, it is protected by a tough and fibrous sac pericardium.
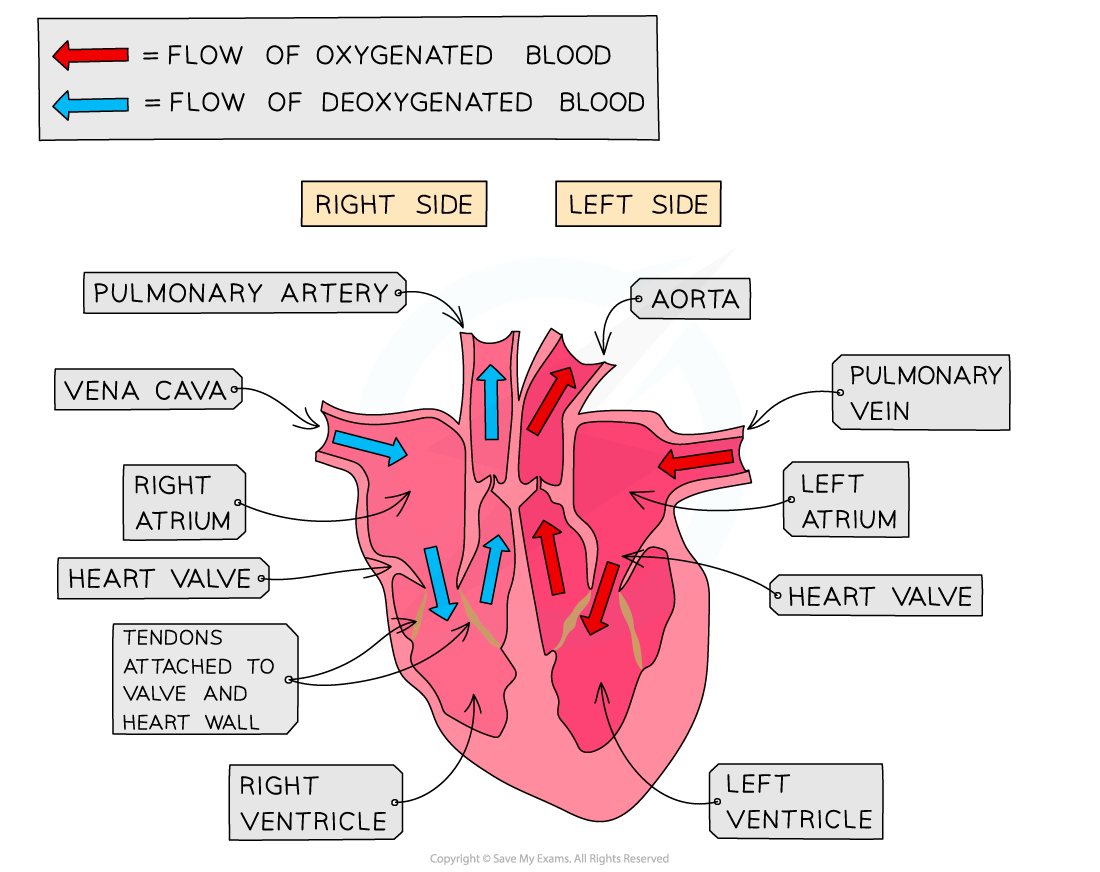
There are four chambers in the heart:
- The top two chambers are atria
- The bottom two chambers are known as ventricles
The right and left sides of the heart are segregated by a wall of muscular tissue known as the septum. The part of the septum that segregates the left and right atria is known as the interatrial septum. On the other hand, the part of the septum which segregates the left and right ventricles is known as the interventricular septum. The septum is critical for ensuring that the blood does not mix up between the left and right sides of the heart.
In the next section of the article, we will discuss the valves in the heart.
Valves in the Heart
The heart valves open and close in the following situations:
- Open when the blood pressure behind them is more than the pressure in front of them
- Close when the blood pressure in front of them is more than the pressure behind them
Valves are critical for keeping the flow of blood forward in the right direction and preventing it from flowing backwards. They are also vital for maintaining the right pressure in the heart chambers.
- The right atrium and the right ventricle are segregated by the atrioventricular valve which is also referred to as a tricuspid valve.
- The pulmonary valve segregates the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery.
- The mitral valve segregates the left atrium and the left ventricle, which is otherwise referred to as a bicuspid valve.
- The aortic valve segregates the left ventricle and aorta
- The two blood vessels that bring the blood to the heart are known as the vena cava and the pulmonary vein
- The two blood vessels that take the blood away from the heart are known as the pulmonary artery and the aorta.
The de-oxygenated blood from the body is supplied by the vena cava, which then flows into the right atrium followed by the right ventricle. The pulmonary artery pumps it to the lungs where this blood gets oxygenated before returning to the heart through the pulmonary vein. It flows through the left atrium into the left ventricle and then through the aorta, and it is pumped to the body. The blood eventually returns to the heart through the vena cava and the entire process repeats itself.
Coronary Arteries
The heart is a muscle and so it needs its blood supply for aerobic respiration. The heart receives blood through coronary arteries which are the arteries on its surface. These arteries must be clear of plaques to avoid angina or heart attack (myocardial infarction).
Differences in Thickness of Valves of the Atria and Ventricles
In this section, we will discuss the differences in the thickness of valves of the atria and the ventricles.
- The atrial walls are thin as they do not need to bear a lot of pressure. On the other hand, the ventricle walls are quite thicker. This is because when the ventricles contract, the blood pressure inside them becomes quite high. So, they have thicker walls as compared to atria to withstand high blood pressure.
- The walls of the left ventricle are also thicker as compared to the walls of the right ventricle. This is because the left side of the heart controls the systemic circuit, i.e., blood to the entire body, whereas the right side controls the pulmonary circuit, i.e., blood to the lungs.
- Blood in the systemic circuit should be at high pressure so that it can make its way around the entire body and back again.
- On the other hand, lungs are located close to the heart and have very delicate capillaries which can break if they are subjected to huge pressure. Therefore, the systemic circuit needs a greater blood pressure than the pulmonary circuit. Due to this reason, the walls of the left ventricle should be thicker than those of the right ventricle.
In the next section of the article, you will learn how to dissect a mammalian heart.
Mammalian Heart Dissection: Practical
- Dissections are important elements of scientific research.
- They help to examine the internal structures of the organs so that the scientists can come up with theories about how they function
- Although dissections help in the advancement of scientific research a lot, however, there are ethical concerns around these dissections:
- People show their concerns regarding the animals being dissected
- The dissections of animals are against the beliefs of certain people
The biological specimen that is employed for dissection should be from a reputable source and should be disposed of later correctly. If more than one specimen is being dissected, then they should be obtained from organisms of the same species or should almost be of the same age.
Materials
- Scalpel
- Gloves
- Tweezers / Forceps
- Dissection board
- Paper towels
- Scissors
- Biological specimen
- Goggles
- Pins
Procedure
- Wear a lab coat, gloves, and eye protection. This will help you to avoid any contamination with the biological material and prevent possible infection.
- Put the specimen on the dissecting board
- Use the tools to evaluate the desired structure
- While using the scalpel cut away from your body and keep your fingers away from the blade to minimize the risk of cutting yourself
- You can use scissors to cut large sections of tissues
- With scalpels, you can achieve finer and more precise cutting
- Use pins if you want to move the other parts of the specimens
Limitations
- It can be difficult to observe some of the smaller, finer structures present inside organs
- Remember that the specimens do not show how the tissues would look inside the living organism
- In case only one specimen is dissected, then anomalies present within that specimen should be ignored.
Summarise with AI:













Keep on teaching us,you are excellent teachers
This is great
Thanks a lot for this book,it really helped me a lot
It’s useful to me
Thanks a lot for your Better book!
It’s a perfect article, go ahead