Chapters
In this article, we will discuss viruses in detail. So, let us get started.

What are Viruses?
In this section, we will discuss what are viruses and whether they are considered living or non-living beings.
- Viruses are microorganisms that can only be viewed under an electron microscope.
- Viruses are acellular, i.e., they do not possess any cellular structure or metabolism.
- Viruses take over the DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) replication machinery in the host cells. DNA refers to the molecule that contains the genetic information of the organism.
- The process of respiration in the host cells provide energy to the viruses needed for replication
- Since viruses do not possess characteristics that are employed for classifying organisms into various groups, therefore they are not considered part of a three-domain classification system.
- The consensus has not been established yet on whether the viruses should be considered living or non-living beings because they are unable to carry out life activities when they are outside the host cell
So far, we have discussed what are viruses. In the next section, we will discuss some key features of viruses.
Important Characteristics of Viruses
- Viruses refer to the non-cellular infectious particles that lie on the boundary between living and non-living because they lack the defining features of life outside the host cells
- Their structure is comparatively simple and quite smaller than prokaryotic cells. The diameters of viruses range from 20 nm to 300 nm.
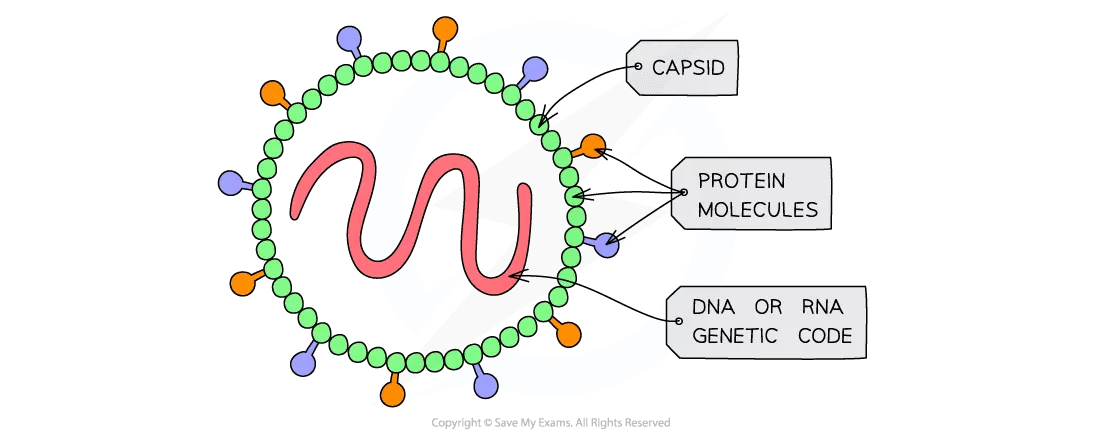
Structure of Viruses
In this section, we will discuss the structural features of viruses.
All viruses have:
- A nucleic acid core: The genome of the viruses can be either DNA or RNA, single-stranded or double-stranded
- A protein coat referred to as a “capsid”
- An outer layer known as an envelope is present in a few viruses. It is usually created from the membrane-phospholipids of a cell they were created in
Every virus is parasitic. It means that it reproduces only when it infects living cells and produces new viral particles by employing its protein-building machinery, i.e., ribosomes.
Classification of Viruses by Their Genetic Material
- We can classify viruses based on the kind of nucleic acid whether RNA or DNA their genome is composed of.
- They are also classified on whether they are single-stranded or double-stranded.
- Remember that RNA is always single-stranded, and DNA is always double-stranded in cellular organisms like plants and animals.
- However, RNA and DNA in the viruses can be either single-stranded or double-stranded. Therefore, based on this, we can say that there are four groups of viruses:
- Viruses that have a single-stranded DNA
- Viruses that have a double-stranded DNA
- Viruses that have a single-stranded RNA (The example of this genome is SARS-CoV-2. This kind of virus has caused COVID-19 pandemic)
- Viruses that have a double-stranded RNA
Why are Viruses Dangerous?
Each one of us has encountered viruses in our lives. They are considered the common cause of colds. Every year the world fights the influenza virus, especially in the colder regions. Influenza is one of the most common diseases caused by the virus which affects billions of people worldwide. Since the influenza virus changes and adapts its nature, hence there is no universal vaccine that is 100% effective for flu. In addition to influenza, viruses also cause several other diseases like HIV or viral hepatitis. Treating these diseases is quite challenging. We need to comprehend the functioning of viruses in detail to find out the cure for diseases they cause.
We can hardly call viruses organisms as they lie on the boundary between living and non-living. There is a debate among scientists on whether these infectious organisms should be considered alive or not. Like the cells of other organisms, viruses do not possess organelles or membranes. Instead, they are made up of two kinds of molecules:
- Nucleic acid (RNA or DNA)
- Proteins
Nucleic acid refers to the genetic material of the virus because it has information about viral proteins. The proteins create a protective capsid around the nucleic acid. The capsid is connected to the tail with hook-like fibres. These hook-like fibres assist the virus to attach to the plasma membranes of the cell. If the virus is not present inside the host cell, then it does not seem or act like a living thing. Few viruses are even unable to survive in an open-air environment. However, the situation changes completely once the virus finds the host cell.
How Viruses Cause Diseases?
Viruses invade when they encounter a host cell. They employ the fibres of their tails to connect to the membrane. After that, the genetic material of the viruses is injected into the host cell. The nucleic acid of the virus goes after the genome and takes over the “headquarters”.
The cell does not make the protein it requires anymore and starts creating viral proteins and nucleic acid instead. Besides this, it also creates proteins that assist in viral packaging. After some time, several virus particles pack the cell. When the cell is unable to make any more viruses, it bursts and releases the material inside it. The materials can then infect and kill the cells nearby.
How are Viruses Treated?
It is difficult to treat viruses because they are hidden inside the cells. Antibiotics that are used to kill the bacteria are ineffective on viruses. Viruses change very often and this process is referred to as a mutation. The best example of mutation is the flu virus as we encounter a new strain of flu virus every single year.
It is quite challenging to produce an effective vaccine against a novel strain of the virus timely. Luckily, our immune system can fight some common viral diseases like colds. However, the situation worsens in the case of dangerous diseases like hepatitis C. The viruses that cause these diseases damage the immune system itself which would otherwise act as a defence system for external invading organisms.
Why Vaccination is Essential?
One of the best ways to fight against common viral diseases is to get vaccinated in advance. Generally, the vaccines have components of viruses or a culture of cells that contain viruses. The main idea behind vaccination is to mimic a real viral invasion. Our immune system acquaints itself with all the information about the virus and if the real viral invasion occurs, then it can fight it. Some viral diseases like rubella, measles, and poliomyelitis are especially dangerous for young children. Therefore, vaccination is critical for them.
Summarise with AI:













Keep on teaching us,you are excellent teachers
This is great
Thanks a lot for this book,it really helped me a lot
It’s useful to me
Thanks a lot for your Better book!
It’s a perfect article, go ahead